
The formula of PCC is:
A.
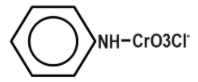
B.

C.
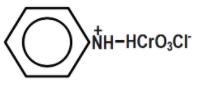
D.





Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: We know that PCC stands for pyridinium chlorochromate. Pyridinium chlorochromate is formed by the reaction of pyridine and chromium oxide, hydrochloric acid. You can now protonate the nitrogen atom present on the pyridine molecule and then perform the reaction. Based on this you can determine the possible structure of PCC i.e. pyridinium chlorochromate.
Complete step by step solution:
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) consists of a pyridinium cation, \[{{[{{C}_{5}}{{H}_{5}}NH]}^{+}}\] , and a tetrahedral chlorochromate anion \[{{[Cr{{O}_{3}}Cl]}^{-}}\] . It is a yellow-orange salt, used as an oxidant. It is commercially available. This reagent was discovered by accident which was originally prepared via addition of pyridine into a cold solution of chromium trioxide in concentrated hydrochloric acid. You can see the equation that represents the chemical reaction of Pyridinium chlorochromate formation below:
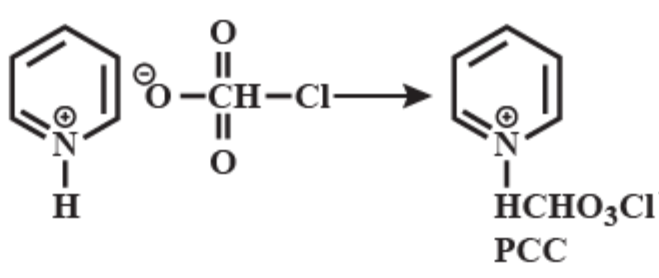
PCC is the most suitable reagent to oxidize primary alcohol to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones without affecting any other functional group. Thus it offers any other functional group. In fact, it is more selective than the related Jones reagent, so there is little chance of over-oxidation to form carboxylic acids as long as the water is not present in the reaction mixture. It also converts suitable unsaturated alcohols and aldehydes to cyclohexanes. One disadvantage to the use of PCC is its toxicity. Another more convenient or less toxic reagent for oxidizing alcohols is dimethyl sulfoxide. PCC is soluble in solvents like acetone, acetonitrile.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that Generally, confusion may arise to choose in between options a and b. Pyridinium chlorochromate is formed by combining the compounds, pyridinium cation \[{{[{{C}_{5}}{{H}_{5}}NH]}^{+}}\] and a chlorochromate anion \[{{[Cr{{O}_{3}}Cl]}^{-}}\]. We have to choose the option resembling these.
Complete step by step solution:
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) consists of a pyridinium cation, \[{{[{{C}_{5}}{{H}_{5}}NH]}^{+}}\] , and a tetrahedral chlorochromate anion \[{{[Cr{{O}_{3}}Cl]}^{-}}\] . It is a yellow-orange salt, used as an oxidant. It is commercially available. This reagent was discovered by accident which was originally prepared via addition of pyridine into a cold solution of chromium trioxide in concentrated hydrochloric acid. You can see the equation that represents the chemical reaction of Pyridinium chlorochromate formation below:

PCC is the most suitable reagent to oxidize primary alcohol to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones without affecting any other functional group. Thus it offers any other functional group. In fact, it is more selective than the related Jones reagent, so there is little chance of over-oxidation to form carboxylic acids as long as the water is not present in the reaction mixture. It also converts suitable unsaturated alcohols and aldehydes to cyclohexanes. One disadvantage to the use of PCC is its toxicity. Another more convenient or less toxic reagent for oxidizing alcohols is dimethyl sulfoxide. PCC is soluble in solvents like acetone, acetonitrile.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
Remember that Generally, confusion may arise to choose in between options a and b. Pyridinium chlorochromate is formed by combining the compounds, pyridinium cation \[{{[{{C}_{5}}{{H}_{5}}NH]}^{+}}\] and a chlorochromate anion \[{{[Cr{{O}_{3}}Cl]}^{-}}\]. We have to choose the option resembling these.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




