
The free electron gas theory explains conduction in:
(a) Metals only
(b) Semiconductors only
(c) Insulators only
(d) All of these
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: As the question asks about the free movement of electrons inside the metals so, we will take the help of Drude theory which is totally dependent on the electrons, movement inside metals, semiconductors and insulators.
Complete step by step answer:
Free electron gas theory: We define this theory as a behavior of a charge which performs their tasks like carriers in the solid with the physical property of metal. It focuses on the bond created between positive and negative ions. This was proposed by the scientist named as Drude, who had performed the model for the movement of electrons inside metals. He named that model under his name. The following diagram shows the Drude model for materials.
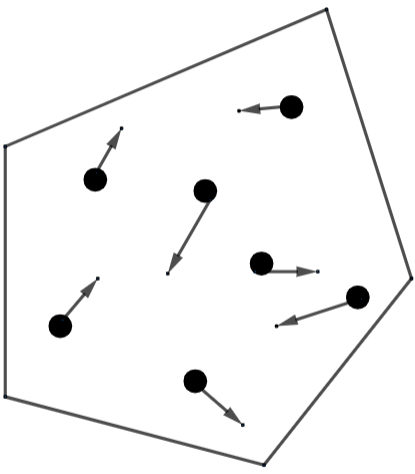
Considering the above enclosure as any material and the inside dots as electrons with arrows showing the free movement of electrons.
Metals: In metals, most of the electrons move freely due to the separation of valence electrons from its atom. This separation can take place under room temperature.
Semiconductors: As compared to the metals we will get to know that there are very few electrons present in the semiconductors which are available for the electrons to get free movements. This is due to the fact that less electrons get separated from its atom inside semiconductors.
Insulators: There is a strong between electrons and the atom which does not let the electrons to move freely at any level.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: (1) Kinetic theory of gas: This theory explains about the distance of the molecules in which the molecules are very small than the distance of separation between them.
(2) The popular British scientist and physicist gave this theory of gas. Their names were James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann.
Note: We will use the theory for the free movement of electrons. In this theory we basically see the movement present in the material which is similar to the movement present in particles of gases, but as the material is divided into three states like metal, semiconductor and insulators that is why the movements of electrons in the material will also be distinct from each other. This theory also helps us to understand the level of conduction by the material. Metal conducts electricity but insulators do not because of the bonding which is discussed here on the other hand, the semiconductors come as an intermediate.
Complete step by step answer:
Free electron gas theory: We define this theory as a behavior of a charge which performs their tasks like carriers in the solid with the physical property of metal. It focuses on the bond created between positive and negative ions. This was proposed by the scientist named as Drude, who had performed the model for the movement of electrons inside metals. He named that model under his name. The following diagram shows the Drude model for materials.

Considering the above enclosure as any material and the inside dots as electrons with arrows showing the free movement of electrons.
Metals: In metals, most of the electrons move freely due to the separation of valence electrons from its atom. This separation can take place under room temperature.
Semiconductors: As compared to the metals we will get to know that there are very few electrons present in the semiconductors which are available for the electrons to get free movements. This is due to the fact that less electrons get separated from its atom inside semiconductors.
Insulators: There is a strong between electrons and the atom which does not let the electrons to move freely at any level.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: (1) Kinetic theory of gas: This theory explains about the distance of the molecules in which the molecules are very small than the distance of separation between them.
(2) The popular British scientist and physicist gave this theory of gas. Their names were James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann.
Note: We will use the theory for the free movement of electrons. In this theory we basically see the movement present in the material which is similar to the movement present in particles of gases, but as the material is divided into three states like metal, semiconductor and insulators that is why the movements of electrons in the material will also be distinct from each other. This theory also helps us to understand the level of conduction by the material. Metal conducts electricity but insulators do not because of the bonding which is discussed here on the other hand, the semiconductors come as an intermediate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




