
The free radical which is most stable is:
(A)- $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-\dot{C}{{H}_{2}}$
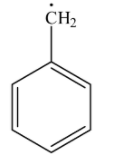
(B)-
(C)- ${{({{H}_{3}}C)}_{3}}C\cdot $
(D)- $\cdot {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$

Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: The species containing an unpaired or odd electron are called free radicals. Stability of free radicals depends on the extent of delocalization of the odd electron. Greater the delocalization of the unpaired electron more is the stability of the free radical.
Complete answer:
Free radicals are very reactive intermediates resulting due to homolytic cleavage of bonds. Depending on the type of carbon bearing the unpaired electron, free radicals can be primary (${{1}^{o}}$), secondary (${{2}^{o}}$) and tertiary (${{3}^{o}}$).
Alkyl free radicals are stabilized by hyperconjugation of methyl groups attached.
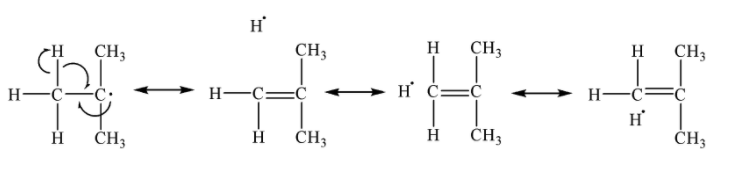
We can say that when a greater number of alkyl groups are attached to the carbon containing the free electron, more such hyperconjugation structures are possible, hence, more stable is the free radical.
Therefore, tertiary free radicals are more stable than secondary followed by primary, i.e. ${{3}^{o}} > {{2}^{o}} > {{1}^{o}}$
Based on the above argument we can now say that $\cdot {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ (${{1}^{o}}$ free radical) is less stable than ${{({{H}_{3}}C)}_{3}}C\cdot $(${{3}^{o}}$ free radical).
Allyl and benzyl free radicals are exceptionally stable as they are stabilized by resonance.
We know that more the number of resonating structures, greater is the stability. Since the number of resonating structures for benzyl free radical is more than that of allyl free radical as shown below, benzyl free radical is more stable than allyl free radical.
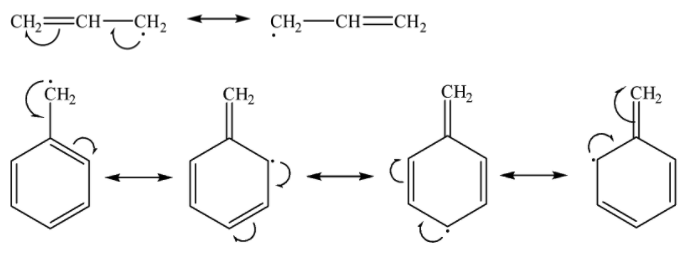
Now it is clear that the stability of $\cdot {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ is less than ${{({{H}_{3}}C)}_{3}}C\cdot $ and the stability of both these alkyl free radicals is less than allyl. Allyl radical is in turn less stable than benzyl free radical.
Therefore, the most stable free radical is benzyl free radical.
Hence the correct option is (B).
Note:
Resonance effect is stronger than hyperconjugation. Resonance is directly related to stability. That is why though benzyl is a primary free radical yet it is more stable than tertiary alkyl free radical because it is stabilized by resonance whereas tertiary alkyl free radical is stabilized by hyperconjugation.
Complete answer:
Free radicals are very reactive intermediates resulting due to homolytic cleavage of bonds. Depending on the type of carbon bearing the unpaired electron, free radicals can be primary (${{1}^{o}}$), secondary (${{2}^{o}}$) and tertiary (${{3}^{o}}$).
Alkyl free radicals are stabilized by hyperconjugation of methyl groups attached.

We can say that when a greater number of alkyl groups are attached to the carbon containing the free electron, more such hyperconjugation structures are possible, hence, more stable is the free radical.
Therefore, tertiary free radicals are more stable than secondary followed by primary, i.e. ${{3}^{o}} > {{2}^{o}} > {{1}^{o}}$
Based on the above argument we can now say that $\cdot {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ (${{1}^{o}}$ free radical) is less stable than ${{({{H}_{3}}C)}_{3}}C\cdot $(${{3}^{o}}$ free radical).
Allyl and benzyl free radicals are exceptionally stable as they are stabilized by resonance.
We know that more the number of resonating structures, greater is the stability. Since the number of resonating structures for benzyl free radical is more than that of allyl free radical as shown below, benzyl free radical is more stable than allyl free radical.

Now it is clear that the stability of $\cdot {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ is less than ${{({{H}_{3}}C)}_{3}}C\cdot $ and the stability of both these alkyl free radicals is less than allyl. Allyl radical is in turn less stable than benzyl free radical.
Therefore, the most stable free radical is benzyl free radical.
Hence the correct option is (B).
Note:
Resonance effect is stronger than hyperconjugation. Resonance is directly related to stability. That is why though benzyl is a primary free radical yet it is more stable than tertiary alkyl free radical because it is stabilized by resonance whereas tertiary alkyl free radical is stabilized by hyperconjugation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




