
The function $ f\left( x \right)=2\left| x \right|+\left| x+2 \right|-\left| \left| x+2 \right|-2\left| x \right| \right| $ has a local maximum or local minimum at x=
(a) –2
(b) $ \dfrac{-2}{3} $
(c) 2
(d) $ \dfrac{2}{3} $
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:
We start solving the problem by recalling the properties of modulus function $ \left| x-a \right| $ as $ \left| x-a \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x-a,\text{ for }x > a \\
0,\text{ for }x=a \\
-x+a,\text{ for }x < a \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ . We then take the intervals at which the modulus functions present in the given functions are positive, negative, and unchanged to proceed through the problem. We then make the necessary calculations by considering the properties of the modulus function to get the required function $ f\left( x \right) $ . We then plot the obtained function and check where we get the local maximum and local minimum for getting the required answer(s).
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are asked to find the values of x at which the function $ f\left( x \right)=2\left| x \right|+\left| x+2 \right|-\left| \left| x+2 \right|-2\left| x \right| \right| $ has local maximum or local minimum.
Let us recall the properties of modulus function $ \left| x-a \right| $ , which is as shown below:
$ \Rightarrow \left| x-a \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x-a,\text{ for }x > a \\
0,\text{ for }x=a \\
-x+a,\text{ for }x < a \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
So, let us check the values of the given function at the intervals $ x < -2 $ , $ -2 < x < 0 $ , $ x > 0 $ .
We have $ \left| x+2 \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x+2,\text{ for }x > -2 \\
0,\text{ for }x=-2 \\
-x-2,\text{ for }x < -2 \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ and $ \left| x \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x,\text{ for }x > 0 \\
0,\text{ for }x=0 \\
-x,\text{ for }x < 0 \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
Now, let us consider the interval $ x < -2 $ .
We get the given function as $ f\left( x \right)=2\left( -x \right)-x-2-\left| -x-2-2\left( -x \right) \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-2x-x-2-\left| -x-2+2x \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-3x-2-\left| x-2 \right| $ .
We can see that $ \left| x-2 \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x-2,\text{ for }x > 2 \\
0,\text{ for }x=2 \\
x+2,\text{ for }x < 2 \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-3x-2-\left( -x+2 \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-3x-2+x-2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-2x-4 $ , for $ x < -2 $ ---(1).
Now, let us consider the interval $ -2 < x < 0 $ .
We get the given function as $ f\left( x \right)=2\left( -x \right)+x+2-\left| x+2-2\left( -x \right) \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-2x+x+2-\left| x+2+2x \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-\left| 3x+2 \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-3\left| x+\dfrac{2}{3} \right| $ .
We can see that $ \left| x+\dfrac{2}{3} \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x+\dfrac{2}{3},\text{ for }x > \dfrac{-2}{3} \\
0,\text{ for }x=\dfrac{-2}{3} \\
-x-\dfrac{2}{3},\text{ for }x < \dfrac{-2}{3} \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
Now, let us consider the interval $ -2 < x < \dfrac{-2}{3} $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-3\left( -x-\dfrac{2}{3} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2+3x+2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2x+4 $ , for $ -2 < x < \dfrac{-2}{3} $ ---(2).
Now, let us consider the interval $ \dfrac{-2}{3} < x < 0 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-3\left( x+\dfrac{2}{3} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-3x-2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-4x $ , for $ \dfrac{-2}{3} < x < 0 $ ---(3).
Now, let us consider the interval $ x > 0 $ .
We get the given function as $ f\left( x \right)=2x+x+2-\left| x+2-2x \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2-\left| -x+2 \right| $ .
We can see that $ \left| -x+2 \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x-2,\text{ for }x > 2 \\
0,\text{ for }x=2 \\
-x+2,\text{ for }x < 2 \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
Now, let us consider the interval $ 0 < x < 2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2-\left( -x+2 \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2+x-2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=4x $ , for $ 0 < x < 2 $ ---(4).
Now, let us consider the interval $ x > 2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2-\left( x-2 \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2-x+2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2x+4 $ , for $ x > 0 $ ---(5).
From equations (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5), we get the given function as:
$ f\left( x \right)=\left\{ \begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
-2x-4,\text{ for }x < -2 \\
2x+4,\text{ for }-2 < x < \dfrac{-2}{3} \\
-4x,\text{ for }\dfrac{-2}{3} < x < 0 \\
4x,\text{ for }0 < x < 2 \\
2x+4,\text{ for }x > 2 \\
\end{array} \right. $ .
Let us draw the plot of the obtained function to find the points at which we get the local maximum or local minimum.
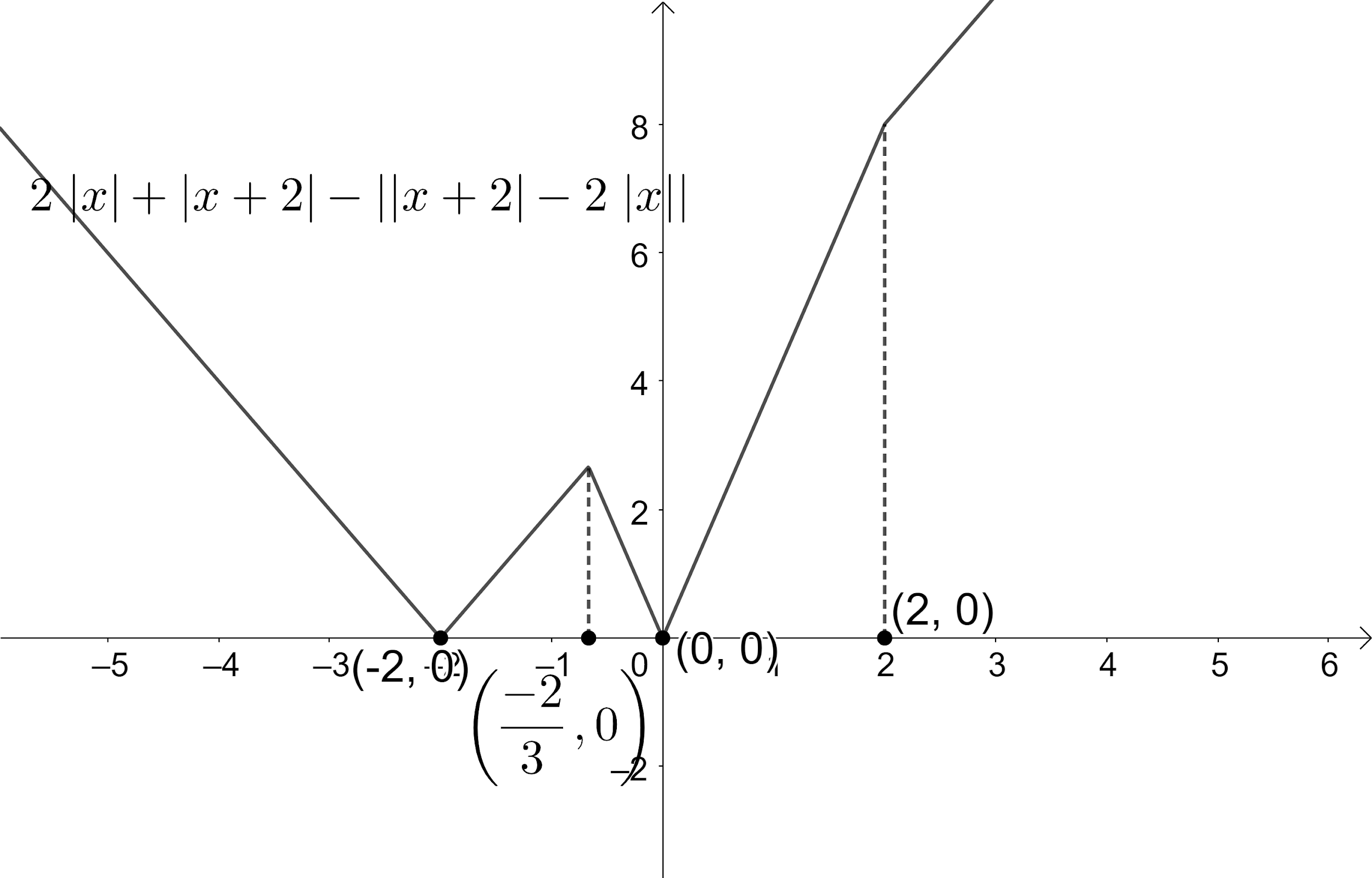
From the plot, we can see that the function has a local maximum at $ x=\dfrac{-2}{3} $ and local minimum at $ x=-2 $ and $ x=0 $ .
$ \therefore $ The correct options for the given problem are (a) and (b).
Note:
We can see that the given problem contains a huge amount of calculations, so we need to perform each step carefully in order to avoid confusion and calculation mistakes. Whenever we get problems involving modulus functions, greatest integer functions, etc, we always take the necessary intervals to solve the problem without any mistakes. We can also make use of differentiation after getting the function to find the local maximum and local minimum. We should keep in mind that the local maximum and the local minimum is different from the absolute maximum and absolute minimum.
We start solving the problem by recalling the properties of modulus function $ \left| x-a \right| $ as $ \left| x-a \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x-a,\text{ for }x > a \\
0,\text{ for }x=a \\
-x+a,\text{ for }x < a \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ . We then take the intervals at which the modulus functions present in the given functions are positive, negative, and unchanged to proceed through the problem. We then make the necessary calculations by considering the properties of the modulus function to get the required function $ f\left( x \right) $ . We then plot the obtained function and check where we get the local maximum and local minimum for getting the required answer(s).
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are asked to find the values of x at which the function $ f\left( x \right)=2\left| x \right|+\left| x+2 \right|-\left| \left| x+2 \right|-2\left| x \right| \right| $ has local maximum or local minimum.
Let us recall the properties of modulus function $ \left| x-a \right| $ , which is as shown below:
$ \Rightarrow \left| x-a \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x-a,\text{ for }x > a \\
0,\text{ for }x=a \\
-x+a,\text{ for }x < a \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
So, let us check the values of the given function at the intervals $ x < -2 $ , $ -2 < x < 0 $ , $ x > 0 $ .
We have $ \left| x+2 \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x+2,\text{ for }x > -2 \\
0,\text{ for }x=-2 \\
-x-2,\text{ for }x < -2 \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ and $ \left| x \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x,\text{ for }x > 0 \\
0,\text{ for }x=0 \\
-x,\text{ for }x < 0 \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
Now, let us consider the interval $ x < -2 $ .
We get the given function as $ f\left( x \right)=2\left( -x \right)-x-2-\left| -x-2-2\left( -x \right) \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-2x-x-2-\left| -x-2+2x \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-3x-2-\left| x-2 \right| $ .
We can see that $ \left| x-2 \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x-2,\text{ for }x > 2 \\
0,\text{ for }x=2 \\
x+2,\text{ for }x < 2 \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-3x-2-\left( -x+2 \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-3x-2+x-2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-2x-4 $ , for $ x < -2 $ ---(1).
Now, let us consider the interval $ -2 < x < 0 $ .
We get the given function as $ f\left( x \right)=2\left( -x \right)+x+2-\left| x+2-2\left( -x \right) \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-2x+x+2-\left| x+2+2x \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-\left| 3x+2 \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-3\left| x+\dfrac{2}{3} \right| $ .
We can see that $ \left| x+\dfrac{2}{3} \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x+\dfrac{2}{3},\text{ for }x > \dfrac{-2}{3} \\
0,\text{ for }x=\dfrac{-2}{3} \\
-x-\dfrac{2}{3},\text{ for }x < \dfrac{-2}{3} \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
Now, let us consider the interval $ -2 < x < \dfrac{-2}{3} $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-3\left( -x-\dfrac{2}{3} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2+3x+2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2x+4 $ , for $ -2 < x < \dfrac{-2}{3} $ ---(2).
Now, let us consider the interval $ \dfrac{-2}{3} < x < 0 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-3\left( x+\dfrac{2}{3} \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x+2-3x-2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-4x $ , for $ \dfrac{-2}{3} < x < 0 $ ---(3).
Now, let us consider the interval $ x > 0 $ .
We get the given function as $ f\left( x \right)=2x+x+2-\left| x+2-2x \right| $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2-\left| -x+2 \right| $ .
We can see that $ \left| -x+2 \right|=\left\{ \begin{matrix}
x-2,\text{ for }x > 2 \\
0,\text{ for }x=2 \\
-x+2,\text{ for }x < 2 \\
\end{matrix} \right. $ .
Now, let us consider the interval $ 0 < x < 2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2-\left( -x+2 \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2+x-2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=4x $ , for $ 0 < x < 2 $ ---(4).
Now, let us consider the interval $ x > 2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2-\left( x-2 \right) $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=3x+2-x+2 $ .
$ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2x+4 $ , for $ x > 0 $ ---(5).
From equations (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5), we get the given function as:
$ f\left( x \right)=\left\{ \begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
-2x-4,\text{ for }x < -2 \\
2x+4,\text{ for }-2 < x < \dfrac{-2}{3} \\
-4x,\text{ for }\dfrac{-2}{3} < x < 0 \\
4x,\text{ for }0 < x < 2 \\
2x+4,\text{ for }x > 2 \\
\end{array} \right. $ .
Let us draw the plot of the obtained function to find the points at which we get the local maximum or local minimum.

From the plot, we can see that the function has a local maximum at $ x=\dfrac{-2}{3} $ and local minimum at $ x=-2 $ and $ x=0 $ .
$ \therefore $ The correct options for the given problem are (a) and (b).
Note:
We can see that the given problem contains a huge amount of calculations, so we need to perform each step carefully in order to avoid confusion and calculation mistakes. Whenever we get problems involving modulus functions, greatest integer functions, etc, we always take the necessary intervals to solve the problem without any mistakes. We can also make use of differentiation after getting the function to find the local maximum and local minimum. We should keep in mind that the local maximum and the local minimum is different from the absolute maximum and absolute minimum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




