
The Gaussian surface for calculating the electric field due to a charge distribution is
A) Any closed surface around the charge distribution.
B) Any surface near the charge distribution.
C) A spherical surface.
D) A closed surface at every point of which electric field has a normal component which is zero or a fixed value.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Define angular simple harmonic motion. Obtain the expression for the angular displacement of the particle. From the given quantities, find the time for the angular displacement. Obtain the expression for angular velocity by differentiating the angular displacement. By putting the given values, we can find the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
The Gaussian surface is a closed surface through which the flux is calculated for the electric or magnetic field. The Gaussian surface is associated with Gauss law. Here we have to define the Gaussian surface for the electric field due to a charge distribution. So we will discuss Gauss law and the properties of the Gaussian surface.
Complete solution step-by-step:
The Gauss law states that the flux generated by an electric field in a closed surface can be given as the surface integral of the electric field, its mathematical representation is
\[\phi =\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\limits_S
E\cdot dA \]
Where dA is the infinitesimal area.
As the law states that it calculates the electric field for closed surfaces, hence option B is incorrect.
For any closed surface around the charge distribution the charge distribution may be discrete and then the electric field will not be well defined. Hence option A will be incorrect.
To determine the electric field for the long wire of uniform charge we consider the cylindrical surface. Hence it is not necessary that the surface will be spherical. Therefore option C is also incorrect.
Now the D option says that the surface is closed hence it satisfies the law and it says that the electric field has a normal component which is either zero or fixed value that implies that the electric field is well defined. . Let us consider a charged rod whose flux has to be determined, so we draw a Gaussian surface or Gaussian cylinder of length l and radius r around the rod as shown below.
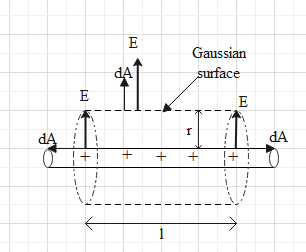
Here we can see that the surface is a closed surface with linear charge distribution where the electric field has a normal component. Inside the cylinder electric field will be zero as inside a charge conductor electric field is zero and all over the surface it will have fixed value as the electric is uniform. We can also see that at the ends of cylinder flux will be zero as E is perpendicular to dA and flux is given as dot product of both of them.
Hence option D is the correct option.
Note:
When the surface of which an electric field or flux has to be found is asymmetrical or the surface area is difficult to find, say a surface area for an infinite long wire or plane, then we draw an imaginary Gaussian surface around the given surface. The Gaussian surface is considered to make best use of symmetry.
Complete step by step answer:
The Gaussian surface is a closed surface through which the flux is calculated for the electric or magnetic field. The Gaussian surface is associated with Gauss law. Here we have to define the Gaussian surface for the electric field due to a charge distribution. So we will discuss Gauss law and the properties of the Gaussian surface.
Complete solution step-by-step:
The Gauss law states that the flux generated by an electric field in a closed surface can be given as the surface integral of the electric field, its mathematical representation is
\[\phi =\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\limits_S
E\cdot dA \]
Where dA is the infinitesimal area.
As the law states that it calculates the electric field for closed surfaces, hence option B is incorrect.
For any closed surface around the charge distribution the charge distribution may be discrete and then the electric field will not be well defined. Hence option A will be incorrect.
To determine the electric field for the long wire of uniform charge we consider the cylindrical surface. Hence it is not necessary that the surface will be spherical. Therefore option C is also incorrect.
Now the D option says that the surface is closed hence it satisfies the law and it says that the electric field has a normal component which is either zero or fixed value that implies that the electric field is well defined. . Let us consider a charged rod whose flux has to be determined, so we draw a Gaussian surface or Gaussian cylinder of length l and radius r around the rod as shown below.

Here we can see that the surface is a closed surface with linear charge distribution where the electric field has a normal component. Inside the cylinder electric field will be zero as inside a charge conductor electric field is zero and all over the surface it will have fixed value as the electric is uniform. We can also see that at the ends of cylinder flux will be zero as E is perpendicular to dA and flux is given as dot product of both of them.
Hence option D is the correct option.
Note:
When the surface of which an electric field or flux has to be found is asymmetrical or the surface area is difficult to find, say a surface area for an infinite long wire or plane, then we draw an imaginary Gaussian surface around the given surface. The Gaussian surface is considered to make best use of symmetry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




