
The general molecular formula, which represents the homologous series of alkanols is
(A)${C_n}{H_{2n}}{O_2}$
(B)${C_n}{H_{2n}}O$
(C)${C_n}{H_{2n + 1}}O$
(D)${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}O$
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Alkanols are basically those organic compounds which contain only carbon atoms , hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms . They belong to the group of alcohols ( which contain hydroxyl groups ).
Complete answer:
The molecular formula of alkanol is ${C_n}{H_n} + 1OH$ or ${C_2}{H_{2n}}O$
Alkanols contain a hydrocarbon chain in which the molecules are bonded by single bond only and they have hydroxy group as their functional group .
So correct answer is (B).
The preparation of alcohols is done by the hydrolysis of haloalkanes. When haloalkanes are boiled with aqueous solution of an alkali hydroxide or moist silver oxide alkanols are formed .
$RX + \;KOH\; \to \;ROH({\text{Alkanol}}) + KX$
Primary alkyl halides give good yields of alcohols. But in case of tertiary alkyl halides we do not get good yield as dehydrohalogenation takes place and alkenes are formed .
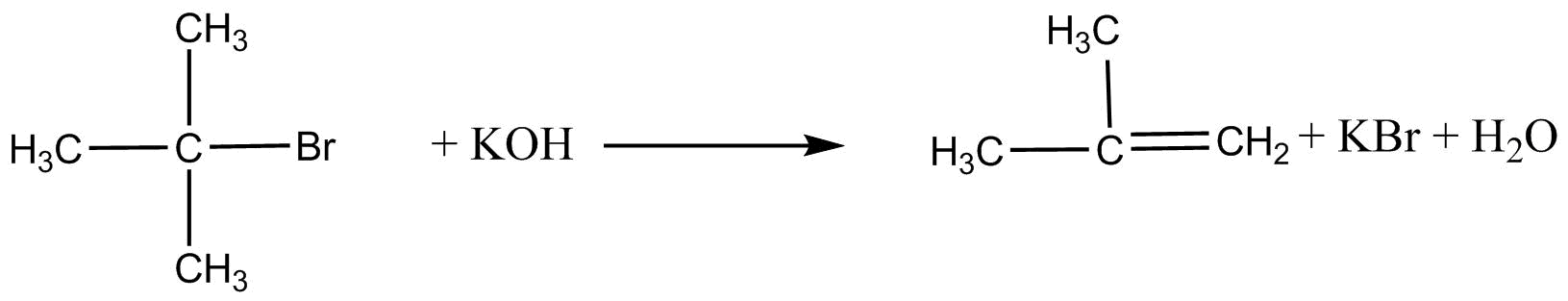 Secondary alkyl halides give a mixture of alkanol and alkene.
Secondary alkyl halides give a mixture of alkanol and alkene.
Alkenes react with carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of octal carbonyl dicobalt ${\left[ {CO{{\left( {CO} \right)}_4}} \right]_2}$ as catalyst and at high temperature and pressure to yield aldehydes. Catalytic hydrogenation of aldehyde gives primary alkanols.
And hence the correct option is B.
Additional information:-
Boiling point of primary alkanols depends upon the length of the carbon chain (or molecular mass). Boiling point of primary alkanol is more than that of the boiling point of the corresponding alkane because of greater molecular mass and also because of hydrogen bonding in alcohols .
Simple alkanols are soluble in polar solvents like water.
As we increase the number of polar $OH$ Hydroxy or hydroxyl functional groups on alkanol molecules the boiling point of alkanols increases .
Note:
-Alkanols react with alkanoic acids to produce Esters. The longer the carbon chain of the alkanol, the less vigorous the reaction between the alkanol and the active metal.
-Oxidation reactions occur in primary and secondary alkanols only.
Complete answer:
The molecular formula of alkanol is ${C_n}{H_n} + 1OH$ or ${C_2}{H_{2n}}O$
Alkanols contain a hydrocarbon chain in which the molecules are bonded by single bond only and they have hydroxy group as their functional group .
So correct answer is (B).
The preparation of alcohols is done by the hydrolysis of haloalkanes. When haloalkanes are boiled with aqueous solution of an alkali hydroxide or moist silver oxide alkanols are formed .
$RX + \;KOH\; \to \;ROH({\text{Alkanol}}) + KX$
Primary alkyl halides give good yields of alcohols. But in case of tertiary alkyl halides we do not get good yield as dehydrohalogenation takes place and alkenes are formed .

Alkenes react with carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of octal carbonyl dicobalt ${\left[ {CO{{\left( {CO} \right)}_4}} \right]_2}$ as catalyst and at high temperature and pressure to yield aldehydes. Catalytic hydrogenation of aldehyde gives primary alkanols.
And hence the correct option is B.
Additional information:-
Boiling point of primary alkanols depends upon the length of the carbon chain (or molecular mass). Boiling point of primary alkanol is more than that of the boiling point of the corresponding alkane because of greater molecular mass and also because of hydrogen bonding in alcohols .
Simple alkanols are soluble in polar solvents like water.
As we increase the number of polar $OH$ Hydroxy or hydroxyl functional groups on alkanol molecules the boiling point of alkanols increases .
Note:
-Alkanols react with alkanoic acids to produce Esters. The longer the carbon chain of the alkanol, the less vigorous the reaction between the alkanol and the active metal.
-Oxidation reactions occur in primary and secondary alkanols only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




