
The geometry of a methyl carbanion is likely to be:
A) Pyramidal
B) Tetrahedral
C) Planar
D) linear
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint:
To answer this question, you should recall the formula to calculate the hybridization of a molecule. Hybridization is defined as the concept of mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a degenerated new type of orbitals. This intermixing is based on quantum mechanics.
Complete step by step solution:
Carbanion refers to the group of species where carbon atoms exhibit trivalence and holds a formal negative charge whose magnitude is at least -1. Carbanions usually have a bent, linear, or a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry. An important point to remember is that all carbanions are conjugate bases of some carbon acids. In these molecules the electron density is highly concentrated at the negatively charged carbon atom. This means that this negative charge dense carbon becomes an ideal point of attack for many electrophiles and other electron-deficient species. The geometry of a methyl carbanion is likely to be pyramidal. The C atom is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. There are three bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons.
This results in a tetrahedral shape or geometry and pyramidal arrangement of electrons around the central atom. Hence, the correct option is option A.
The structure of this molecule can be represented as:
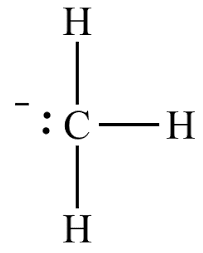
Note:
Hybridisation of a molecule can be found out using $(X)$ using the formula: \[\dfrac{1}{2}(V + H - C + A)\] where
$V$ = Number of valence electrons in the central atom
$H$ = Number of surrounding monovalent atoms
$C$ = Cationic charge
$A$ = Anionic charge. The value of X will determine the hybridisation of the molecule. If $X$ is 2 then $sp$ ; is 3 then $s{p^2}$ ; is 4 then $s{p^3}$ ; is 5 then $s{p^3}d$ ; is 6 then $s{p^3}{d^2}$ ; is 7 then $s{p^3}{d^3}$ hybridization.
To answer this question, you should recall the formula to calculate the hybridization of a molecule. Hybridization is defined as the concept of mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a degenerated new type of orbitals. This intermixing is based on quantum mechanics.
Complete step by step solution:
Carbanion refers to the group of species where carbon atoms exhibit trivalence and holds a formal negative charge whose magnitude is at least -1. Carbanions usually have a bent, linear, or a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry. An important point to remember is that all carbanions are conjugate bases of some carbon acids. In these molecules the electron density is highly concentrated at the negatively charged carbon atom. This means that this negative charge dense carbon becomes an ideal point of attack for many electrophiles and other electron-deficient species. The geometry of a methyl carbanion is likely to be pyramidal. The C atom is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. There are three bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons.
This results in a tetrahedral shape or geometry and pyramidal arrangement of electrons around the central atom. Hence, the correct option is option A.
The structure of this molecule can be represented as:

Note:
Hybridisation of a molecule can be found out using $(X)$ using the formula: \[\dfrac{1}{2}(V + H - C + A)\] where
$V$ = Number of valence electrons in the central atom
$H$ = Number of surrounding monovalent atoms
$C$ = Cationic charge
$A$ = Anionic charge. The value of X will determine the hybridisation of the molecule. If $X$ is 2 then $sp$ ; is 3 then $s{p^2}$ ; is 4 then $s{p^3}$ ; is 5 then $s{p^3}d$ ; is 6 then $s{p^3}{d^2}$ ; is 7 then $s{p^3}{d^3}$ hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




