
The given figure shows three steps (A, B, C) of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Select the option of giving correct identification together with what it represents?
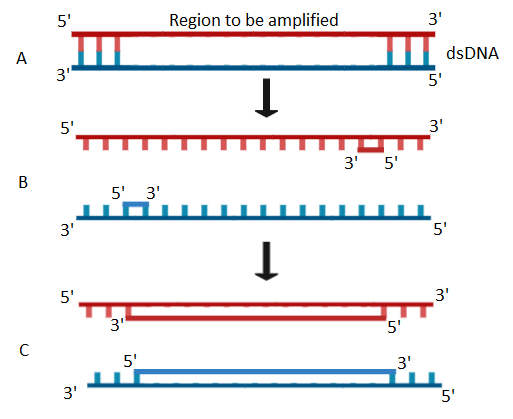
I. A- Denaturation at a temperature of about \[50{}^\circ C\]
II. C- Extension in the presence of heat-stable DNA polymerase
III. A- Annealing with two sets of primers
IV. B- Denaturation at a temperature of about \[98{}^\circ C\] separating the two DNA strands

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: PCR or Polymerase Chain Reaction is a technique that is used to create copies of desired segments of the DNA. It involves generally three steps including denaturation, annealing, and extension respectively. The process involves repeated cycles of the given three steps.
Complete answer: The polymerase chain reaction is an important technique that is used in various biotechnological, molecular biology, and forensic experiments. It enables the creation of thousands of copies of a given DNA strand. This can be used to study the DNA sequences and in the identification of diseases. The PCR reaction involves 3 basic steps that are Denaturation, Annealing, and Extension. It involves the addition of some materials that are DNA strands that need to be amplified, Primers, Taq Polymerase enzyme, and nucleotides. Some cofactors are also added along with the polymerase enzyme for its proper working. All these contents are added in a tube and are subjected to a PCR reaction.
Now, let us discuss each step involved in PCR to understand steps A, B, and C.
-Step A is Denaturation. In this step, the double-stranded DNA strand of interest is unwind using a high melting temperature around \[94{}^\circ C~\]. This temperature breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases of the DNA.
-Step B is Annealing. This step involves the attachment of primer sequences. Primers are short stretches of nucleotides around $18-20$ base pairs. This acts as a stimulator to initiate the working of the Taq DNA polymerase enzyme. The primers bind to complementary bases on single strands of the DNA at a cool temperature of \[55-65{}^\circ C\].
-Step C is called extension. In this step, the Taq DNA polymerase that is a heat resistant enzyme is used to add nucleotides that will extend the new complementary strand. It is synthesized from Thermus aquaticus that is thermophile, which means heat resistant. The temperature is \[72{}^\circ C\]. At this temperature, the extension of new strands takes place along with the separation of newly synthesized strands so that they can further be used in future cycles.
Thus, from the above discussion, we can conclude that options A, C, and D are wrong and the right answer is option II.
Note: The PCR is a fundamental technique used in various biotechnological experiments. The PCR has vast applications in forensics too as it can identify the DNA sample found at crime scenes. Also, in cases of viral or bacterial diseases, PCR can be used for viral or bacterial genome detection in the patient’s blood samples.
Complete answer: The polymerase chain reaction is an important technique that is used in various biotechnological, molecular biology, and forensic experiments. It enables the creation of thousands of copies of a given DNA strand. This can be used to study the DNA sequences and in the identification of diseases. The PCR reaction involves 3 basic steps that are Denaturation, Annealing, and Extension. It involves the addition of some materials that are DNA strands that need to be amplified, Primers, Taq Polymerase enzyme, and nucleotides. Some cofactors are also added along with the polymerase enzyme for its proper working. All these contents are added in a tube and are subjected to a PCR reaction.
Now, let us discuss each step involved in PCR to understand steps A, B, and C.
-Step A is Denaturation. In this step, the double-stranded DNA strand of interest is unwind using a high melting temperature around \[94{}^\circ C~\]. This temperature breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases of the DNA.
-Step B is Annealing. This step involves the attachment of primer sequences. Primers are short stretches of nucleotides around $18-20$ base pairs. This acts as a stimulator to initiate the working of the Taq DNA polymerase enzyme. The primers bind to complementary bases on single strands of the DNA at a cool temperature of \[55-65{}^\circ C\].
-Step C is called extension. In this step, the Taq DNA polymerase that is a heat resistant enzyme is used to add nucleotides that will extend the new complementary strand. It is synthesized from Thermus aquaticus that is thermophile, which means heat resistant. The temperature is \[72{}^\circ C\]. At this temperature, the extension of new strands takes place along with the separation of newly synthesized strands so that they can further be used in future cycles.
Thus, from the above discussion, we can conclude that options A, C, and D are wrong and the right answer is option II.
Note: The PCR is a fundamental technique used in various biotechnological experiments. The PCR has vast applications in forensics too as it can identify the DNA sample found at crime scenes. Also, in cases of viral or bacterial diseases, PCR can be used for viral or bacterial genome detection in the patient’s blood samples.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




