
The given image is a
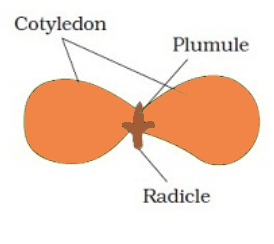
A. Dicot seed
B. Monocot seed
C. Winged seeds
D. Both A and B

Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Plants undergo sexual reproduction to form a zygote that develops into an embryo. The process of fertilization to form a zygote occurs in the ovule. The ovule, after fertilization, develops into a seed. The components of a seed are seed coat, endosperm and embryo. The seed coat protects the growing embryo. The endosperm provides nutrients to the growing embryo. The embryo, after the process of germination, develops into a seedling and then into a plant.
Complete answer:
The cotyledons or seed, leaves or embryonic leaves are all part of the embryo. They are functionally similar to a leaf. However, leaves develop from the shoot only after germination whereas cotyledons are formed once the embryo begins developing.
Seeds that only have one large cotyledon are known as monocot seeds. Species that belong to the grass family have monocot seeds. The shoot tip is called the plumule and the root tip is called the radicle. The plumule, in the case of monocots, is surrounded by coleoptile and the radicle is surrounded by a coleorhiza. Their function is to protect the shoot and root tip respectively.
Seeds with two cotyledons are known as dicot seeds. Flowering plants such as rose and magnolias, fall under this category. The cotyledons are quite large. Dicot seeds lack endosperm and the cotyledons are the source of nutrients. The shoot tip is called the plumule and the root tip is called the radicle. They lack coleoptile and coleorhiza.
Winged seeds are seeds that have a wing-like feature that helps in seed dispersal by the wind. For example, maple seeds.
The diagram shows two cotyledons therefore, the seed is a dicot seed.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Certain seeds such as legumes can be consumed directly. Seeds such as that of castor can be used to extract oil. Ferns and liverworts do not produce seeds. They produce haploid spores that can be easily dispersed by wind or water to various places. Seeds can be stored in seed banks at dry conditions and low temperatures. The germplasm is preserved and can also be used for genetic modification.
Complete answer:
The cotyledons or seed, leaves or embryonic leaves are all part of the embryo. They are functionally similar to a leaf. However, leaves develop from the shoot only after germination whereas cotyledons are formed once the embryo begins developing.
Seeds that only have one large cotyledon are known as monocot seeds. Species that belong to the grass family have monocot seeds. The shoot tip is called the plumule and the root tip is called the radicle. The plumule, in the case of monocots, is surrounded by coleoptile and the radicle is surrounded by a coleorhiza. Their function is to protect the shoot and root tip respectively.
Seeds with two cotyledons are known as dicot seeds. Flowering plants such as rose and magnolias, fall under this category. The cotyledons are quite large. Dicot seeds lack endosperm and the cotyledons are the source of nutrients. The shoot tip is called the plumule and the root tip is called the radicle. They lack coleoptile and coleorhiza.
Winged seeds are seeds that have a wing-like feature that helps in seed dispersal by the wind. For example, maple seeds.
The diagram shows two cotyledons therefore, the seed is a dicot seed.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Certain seeds such as legumes can be consumed directly. Seeds such as that of castor can be used to extract oil. Ferns and liverworts do not produce seeds. They produce haploid spores that can be easily dispersed by wind or water to various places. Seeds can be stored in seed banks at dry conditions and low temperatures. The germplasm is preserved and can also be used for genetic modification.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




