
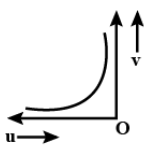
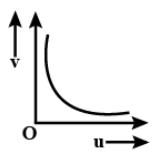
The graph between image distance \[(v)\] and object distance \[(u)\] from the convex lens, is:
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: The image formation by a convex lens could be found by drawing ray diagrams for several cases. The relation between object distance\[(u)\], image distance \[(v)\]and focal length\[f\] of a convex lens is given by \[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]. But object distance \[(u)\] will always be negative because of sign convention.
Complete answer:
We will keep the objects at particular points on the principle axis and conclude the trend of how the image is formed.
A convex lens can produce both real and virtual images. Real images can be captured by a screen and we cannot capture a virtual image on a screen but only to imagine the position of it by extending the ray diagram. The images formed could be either inverted (opposite direction of object) or erect (same direction as object).
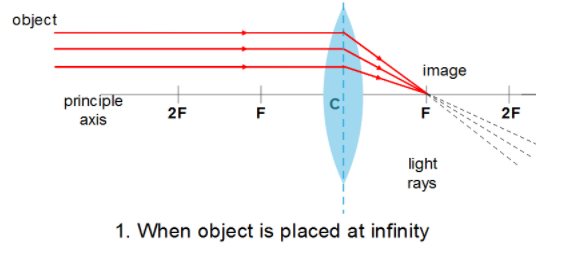
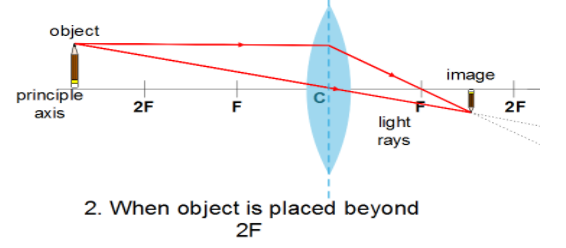
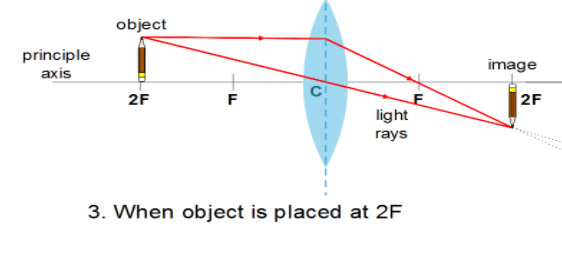
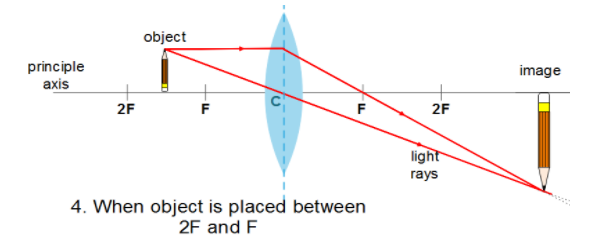
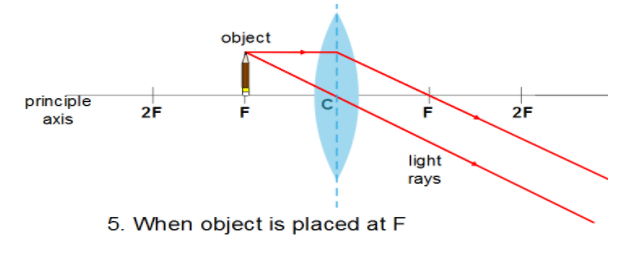
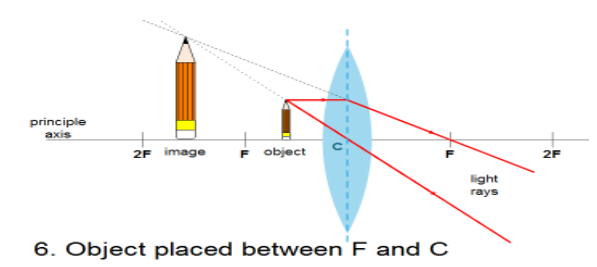
Also, a convex lens can form images of all sizes such as enlarged, diminished, same sized, point sized, even infinitely large. So now we will compare the images formed by a convex lens at different cases using the ray diagram and tabulate the result.
When we look the positions and nature of images formed, we can conclude that,
So now we can understand that if the object is kept \[(\infty )\]the image will be having a distance of \[f\]. As we keep the object closer to the convex lens, the image distance increases and reaches infinity. So the graph which resembles this trend is,

So the correct answer is option A.
Note:
When we look at the options given, we will be confused that option c also resembles the same type of graph. But always keep in mind that the object distance in any lenses will be taken as negative because of sign convention. Sign convention means we will take only those measurements taken in a particular direction as positive, and the opposite direction as negative.
Complete answer:
We will keep the objects at particular points on the principle axis and conclude the trend of how the image is formed.
A convex lens can produce both real and virtual images. Real images can be captured by a screen and we cannot capture a virtual image on a screen but only to imagine the position of it by extending the ray diagram. The images formed could be either inverted (opposite direction of object) or erect (same direction as object).






Also, a convex lens can form images of all sizes such as enlarged, diminished, same sized, point sized, even infinitely large. So now we will compare the images formed by a convex lens at different cases using the ray diagram and tabulate the result.
When we look the positions and nature of images formed, we can conclude that,
| Object Location | Image Location | Image Nature | Image Size |
| At Infinity $\left( \infty \right)$ | At F | Real and Inverted | Diminished |
| Beyond 2F | Between 2F and F | Real and Inverted | Diminished |
| At 2F | At 2F | Real and Inverted | Same Size |
| Between 2F and F | Beyond 2F | Real and Inverted | Enlarged |
| At F | At Infinity $\left( \infty \right)$ | Real and Inverted | Enlarged |
| Between F and C | On the same side as the object | Virtual and Erect | Enlarged |
So now we can understand that if the object is kept \[(\infty )\]the image will be having a distance of \[f\]. As we keep the object closer to the convex lens, the image distance increases and reaches infinity. So the graph which resembles this trend is,

So the correct answer is option A.
Note:
When we look at the options given, we will be confused that option c also resembles the same type of graph. But always keep in mind that the object distance in any lenses will be taken as negative because of sign convention. Sign convention means we will take only those measurements taken in a particular direction as positive, and the opposite direction as negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




