
The graph between wave number $(\overline{v})$ and angular frequency $(\omega )$ is:
$A)$
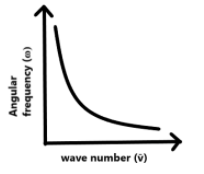
$B)$
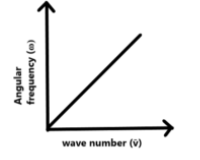
$C)$
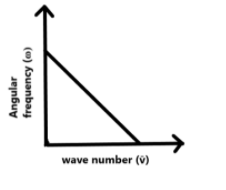
$D)$
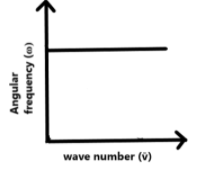




Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Wave number refers to the number of waves per unit distance. Angular frequency of a wave refers to the angular displacement of the wave per unit time. Both wave number and angular frequency of a wave are directly proportional to the frequency of that wave.
Formula used:
$\overline{v}=\dfrac{\omega }{v}$
Complete answer:
Wave number of a wave is defined as the number of waves per unit distance whereas frequency of a wave is defined as the number of waves per unit time. Wave number of a wave is dependent on the wavelength of that wave as follows:
$\overline{v}=\dfrac{2\pi }{\lambda }$
where
$\overline{v}$ is the wavenumber of a wave
$\lambda $ is the wavelength of the wave
Let this be equation 1.
Wavelength of a wave is defined as the distance between two successive crests or two successive troughs in the wave. It is related to the frequency of wave as given below:
$\lambda =\dfrac{v}{f}$
where
$\lambda $ is the wavelength of a wave
$v$ is the speed of the wave
$f$ is the frequency of the wave
Let this be equation 2.
Combining equation 1 and equation 2, we have
$\overline{v}=\dfrac{2\pi }{\lambda }=\dfrac{2\pi f}{v}$
where
$\overline{v}$ is the wavenumber of a wave
$v$ is the speed of the wave
$f$ is the frequency of the wave
Let this be equation 3.
Now, angular frequency of a wave is defined as the angular displacement of the wave per unit time. It is related to the time period of a wave as follows:
$\omega =\dfrac{2\pi }{T}$
where
$\omega $ is the angular frequency of a wave
$T$ is the time period of the wave
Let this be equation 4.
Time period of a wave is defined as the time required by the wave to complete one cycle. It is related to the frequency of wave as follows:
$T=\dfrac{1}{f}$
where
$T$ is the time period of a wave
$f$ is the frequency of the wave
Let this be equation 5.
Combining equation 4 and equation 5, we have
$\omega =\dfrac{2\pi }{T}=2\pi f$
where
$\omega $ is the angular frequency of a wave
$f$ is the frequency of the wave
Let this be equation 6.
Now, from equation 3 and equation 6, we can conclude that both wave number and angular frequency of a wave is directly proportional to the frequency of that wave. If we combine equation 3 and equation 6 together, we get
$\overline{v}=\dfrac{2\pi f}{v}=\dfrac{\omega }{v}$
where
$\overline{v}$ is the wavenumber of a wave
$v$ is the speed of that wave
$\omega $ is the angular frequency of that wave
Let this be equation 7.
Clearly, from equation 7, we can conclude that wave number of a wave and angular frequency of that wave are directly proportional to each other.
If we plot a graph between wave number ($\overline{v}$) and angular frequency ($\omega $) of a wave, it looks similar to a graph of the form $y=mx$, as given below.
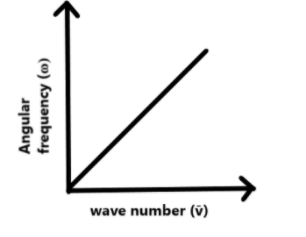
Therefore, the correct answer is option $B$.
Note:
Students need to thoroughly learn definitions as well as formulas of different characteristics of a wave. The shapes of graphs between any two characteristics of a wave can be asked. These characteristics need not be directly related to, as in the above case. Therefore, if students are thorough with formulas of these characteristics, they can easily derive the respective relation and try plotting graphs of the same.
Formula used:
$\overline{v}=\dfrac{\omega }{v}$
Complete answer:
Wave number of a wave is defined as the number of waves per unit distance whereas frequency of a wave is defined as the number of waves per unit time. Wave number of a wave is dependent on the wavelength of that wave as follows:
$\overline{v}=\dfrac{2\pi }{\lambda }$
where
$\overline{v}$ is the wavenumber of a wave
$\lambda $ is the wavelength of the wave
Let this be equation 1.
Wavelength of a wave is defined as the distance between two successive crests or two successive troughs in the wave. It is related to the frequency of wave as given below:
$\lambda =\dfrac{v}{f}$
where
$\lambda $ is the wavelength of a wave
$v$ is the speed of the wave
$f$ is the frequency of the wave
Let this be equation 2.
Combining equation 1 and equation 2, we have
$\overline{v}=\dfrac{2\pi }{\lambda }=\dfrac{2\pi f}{v}$
where
$\overline{v}$ is the wavenumber of a wave
$v$ is the speed of the wave
$f$ is the frequency of the wave
Let this be equation 3.
Now, angular frequency of a wave is defined as the angular displacement of the wave per unit time. It is related to the time period of a wave as follows:
$\omega =\dfrac{2\pi }{T}$
where
$\omega $ is the angular frequency of a wave
$T$ is the time period of the wave
Let this be equation 4.
Time period of a wave is defined as the time required by the wave to complete one cycle. It is related to the frequency of wave as follows:
$T=\dfrac{1}{f}$
where
$T$ is the time period of a wave
$f$ is the frequency of the wave
Let this be equation 5.
Combining equation 4 and equation 5, we have
$\omega =\dfrac{2\pi }{T}=2\pi f$
where
$\omega $ is the angular frequency of a wave
$f$ is the frequency of the wave
Let this be equation 6.
Now, from equation 3 and equation 6, we can conclude that both wave number and angular frequency of a wave is directly proportional to the frequency of that wave. If we combine equation 3 and equation 6 together, we get
$\overline{v}=\dfrac{2\pi f}{v}=\dfrac{\omega }{v}$
where
$\overline{v}$ is the wavenumber of a wave
$v$ is the speed of that wave
$\omega $ is the angular frequency of that wave
Let this be equation 7.
Clearly, from equation 7, we can conclude that wave number of a wave and angular frequency of that wave are directly proportional to each other.
If we plot a graph between wave number ($\overline{v}$) and angular frequency ($\omega $) of a wave, it looks similar to a graph of the form $y=mx$, as given below.

Therefore, the correct answer is option $B$.
Note:
Students need to thoroughly learn definitions as well as formulas of different characteristics of a wave. The shapes of graphs between any two characteristics of a wave can be asked. These characteristics need not be directly related to, as in the above case. Therefore, if students are thorough with formulas of these characteristics, they can easily derive the respective relation and try plotting graphs of the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




