
The growth hormone responsible for apical dominance is
A. Auxin
B. Cytokinin
C. Gibberellin
D. Ethylene
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: Apical growth means a longitudinal increase in the tip of the central stem. The central stem dominates the lateral stems. The lateral stems, on the other hand, stay suppressed. This occurs due to plant hormone found in the tip of the apex of the central shoot.
Complete answer:
Several plant hormones are present in a plant that performs separate functions involved in the growth and development of plants. The auxin hormones were the first to be discovered. Auxin is a Greek origin word that means “to grow” in literal terms. Thus, auxins are involved in the regulation of the growth and behavioral processes of the plant. They are the most essential hormones for plant body development.
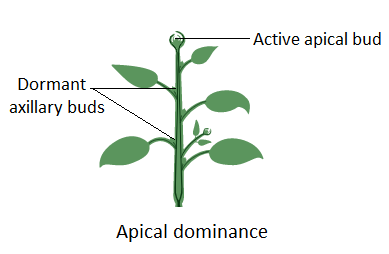
Auxins are responsible for shoot apical dominance seen in the central shoot. The growth of axillary buds into shoots is inhibited by auxin. Auxin stimulates high levels of ethylene production in axillary buds and this causes inhibition of their growth. Auxins are primarily present in the tip of the apex of the central shoot. This causes them to grow longitudinally. Also, auxins lie in the part of the shoot which is away from the sun. This causes cell elongation only in the shady part of the shoot and results in bending of the shoot towards the sun.
Auxins also play an important role in fruit development, flowering, wound response, root growth and development, and ethylene biosynthesis. Auxins also respond towards geotropism, phototropism, and hydrotropism.
Cytokinin is an inhibitory hormone in apical dominance. It is responsible for breaking down apical dominance.
Thus, from the above discussion, we can conclude that option A is the correct one.
Note: It is observed that gardeners usually cut the tip of the central stem to promote lateral stem growth. This is because auxins lie in the tip of the central shoot which prevents growth in lateral shoots due to apical dominance. When the central shoot is cut from the tip, the inhibitory effect on lateral or axillary buds is removed and they grow equally.
Complete answer:
Several plant hormones are present in a plant that performs separate functions involved in the growth and development of plants. The auxin hormones were the first to be discovered. Auxin is a Greek origin word that means “to grow” in literal terms. Thus, auxins are involved in the regulation of the growth and behavioral processes of the plant. They are the most essential hormones for plant body development.

Auxins are responsible for shoot apical dominance seen in the central shoot. The growth of axillary buds into shoots is inhibited by auxin. Auxin stimulates high levels of ethylene production in axillary buds and this causes inhibition of their growth. Auxins are primarily present in the tip of the apex of the central shoot. This causes them to grow longitudinally. Also, auxins lie in the part of the shoot which is away from the sun. This causes cell elongation only in the shady part of the shoot and results in bending of the shoot towards the sun.
Auxins also play an important role in fruit development, flowering, wound response, root growth and development, and ethylene biosynthesis. Auxins also respond towards geotropism, phototropism, and hydrotropism.
Cytokinin is an inhibitory hormone in apical dominance. It is responsible for breaking down apical dominance.
Thus, from the above discussion, we can conclude that option A is the correct one.
Note: It is observed that gardeners usually cut the tip of the central stem to promote lateral stem growth. This is because auxins lie in the tip of the central shoot which prevents growth in lateral shoots due to apical dominance. When the central shoot is cut from the tip, the inhibitory effect on lateral or axillary buds is removed and they grow equally.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




