
The height of mercury barometer is h when the atmospheric pressure is $10^{5}Pa$, the pressure at x in the shown figure is
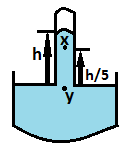
A. $10^{5}Pa$
B. $0.8\times{10^{5}Pa}$
C. $0.2\times{10^{5}Pa}$
D. $120\times{10^{5}Pa}$

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The above figure shows a setup of a static fluid. The horizontal surface of mercury will experience an exertion by the atmosphere. Pressure at point y can be calculated by formula of pressure. So by equating two equations for pressure at the horizontal surface we can easily encounter our answer.
As per the given data;
Height at which point x is situated $=h-\dfrac{h}{5}$
Atmospheric pressure $P_\circ ={{10}^{5}}$ Pa
Formula used:
Pressure, $P=P_\circ +\rho gh$
Complete answer:
Hydrostatic pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a fluid (gas or liquid) at any point in space within that fluid, assuming that the fluid is incompressible and at rest.
Pressure within a liquid depends only on the density of the liquid, the acceleration due to gravity, and the depth within the liquid. The pressure exerted by such a static liquid increases linearly with increasing depth.
Mathematically;
Pressure, $P=P_\circ +\rho gh$
Where, $P_\circ $ the pressure due to empty space or atmospheric formula
So pressure at the bottom surface of the glass tube of the barometer $(P_{y})$ .will be;
(Assume that pressure due to the empty space in the glass tube is zero)
\[P_{y}= 0+\rho gh\]
\[P_{y}=\rho gh\]
Let us see the pressure at y due to point x under the glass tube:
\[P_x=\rho gh-\rho g\dfrac{h}{5}\]
$P_x=\rho gh-\rho g\dfrac{h}{5}$
\[=\rho gh\left ( 1-\dfrac{1}{5} \right )\]
We know that, In case of static fluid, pressure on the horizontal level is constant at every point.
Thus;
\[P_{y}=\rho gh= 10^{5}Pa\]
By putting the value of$\rho gh$:
$P_x={{10}^{5}}\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{5} \right)$
\[= 10^{5}\times \dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[P_x=0.2\times {{10}^{5}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Read the question carefully. Remember that we don’t have to consider the whole height of the glass tube. Most importantly this is a static fluid setup so apply properties according to that only.
As per the given data;
Height at which point x is situated $=h-\dfrac{h}{5}$
Atmospheric pressure $P_\circ ={{10}^{5}}$ Pa
Formula used:
Pressure, $P=P_\circ +\rho gh$
Complete answer:
Hydrostatic pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a fluid (gas or liquid) at any point in space within that fluid, assuming that the fluid is incompressible and at rest.
Pressure within a liquid depends only on the density of the liquid, the acceleration due to gravity, and the depth within the liquid. The pressure exerted by such a static liquid increases linearly with increasing depth.
Mathematically;
Pressure, $P=P_\circ +\rho gh$
Where, $P_\circ $ the pressure due to empty space or atmospheric formula
So pressure at the bottom surface of the glass tube of the barometer $(P_{y})$ .will be;
(Assume that pressure due to the empty space in the glass tube is zero)
\[P_{y}= 0+\rho gh\]
\[P_{y}=\rho gh\]
Let us see the pressure at y due to point x under the glass tube:
\[P_x=\rho gh-\rho g\dfrac{h}{5}\]
$P_x=\rho gh-\rho g\dfrac{h}{5}$
\[=\rho gh\left ( 1-\dfrac{1}{5} \right )\]
We know that, In case of static fluid, pressure on the horizontal level is constant at every point.
Thus;
\[P_{y}=\rho gh= 10^{5}Pa\]
By putting the value of$\rho gh$:
$P_x={{10}^{5}}\left( 1-\dfrac{1}{5} \right)$
\[= 10^{5}\times \dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[P_x=0.2\times {{10}^{5}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Read the question carefully. Remember that we don’t have to consider the whole height of the glass tube. Most importantly this is a static fluid setup so apply properties according to that only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




