
The helical structure of a protein is stabilized by
(a)Dipeptide bonds
(b)Hydrogen bonds
(c)Ether bonds
(d)Peptide bonds
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: The helical structure of the protein is stabilized by a type of bond that is usually formed between highly electronegative atoms like nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine and a low electronegative atom. These types of bonds are also seen in the water and liquid ammonia.
Complete answer:
The helical structure of proteins or the alpha-helix (α-helix) is the secondary structure of proteins. The alpha helix is also known as a classic Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix. It is a right-handed helix conformation in which all the backbone ${ N }-{ H }$ group are bonded to the backbone
${ C }={ O }$ group of the amino acid by hydrogen bonds located three or four residues earlier along the protein sequence. These hydrogen bonds keep the structure stable and are represented by dashed lines.
Additional Information:
-Helices seen in proteins can generally range from four to over forty residues long, but a typical helix contains about ten amino acids which form about three turns.
-Generally, shorter polypeptides do not exhibit much α-helical structure in solution, since the entropic cost required for the folding of the polypeptide chain is not compensated for by a sufficient amount of stabilizing interactions.
-The helix has a dipole moment because of the aggregate effect of the individual micro dipoles from the carbonyl groups of the peptide bonds.
-This complete structure is kept stable by the hydrogen bonds.
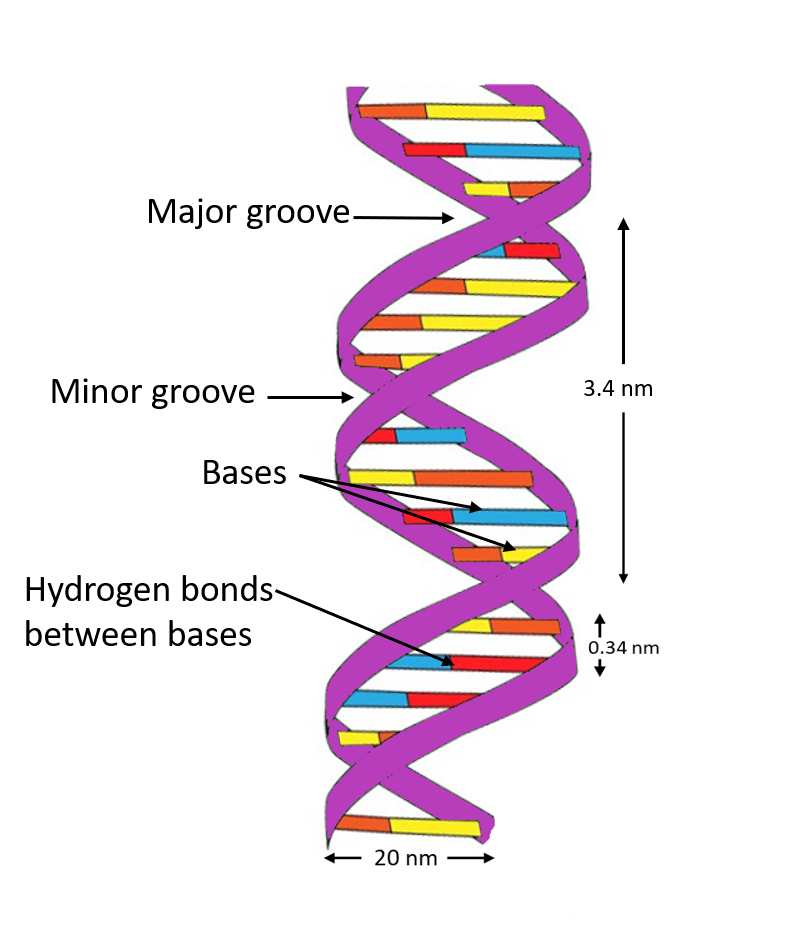
So, the correct answer is, ‘Hydrogen Bonds.’
Note: The helix structure is one of the secondary forms of proteins. They can also be present as β-pleated sheets. They can be also present as supercoiled coils, in which 2 or 3 helices coil around each other to form a more stable structure. It should be remembered that alpha helix is one of the most common and stable primary structures of protein. It is seen in hemoglobin and myoglobin.
Complete answer:
The helical structure of proteins or the alpha-helix (α-helix) is the secondary structure of proteins. The alpha helix is also known as a classic Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix. It is a right-handed helix conformation in which all the backbone ${ N }-{ H }$ group are bonded to the backbone
${ C }={ O }$ group of the amino acid by hydrogen bonds located three or four residues earlier along the protein sequence. These hydrogen bonds keep the structure stable and are represented by dashed lines.
Additional Information:
-Helices seen in proteins can generally range from four to over forty residues long, but a typical helix contains about ten amino acids which form about three turns.
-Generally, shorter polypeptides do not exhibit much α-helical structure in solution, since the entropic cost required for the folding of the polypeptide chain is not compensated for by a sufficient amount of stabilizing interactions.
-The helix has a dipole moment because of the aggregate effect of the individual micro dipoles from the carbonyl groups of the peptide bonds.
-This complete structure is kept stable by the hydrogen bonds.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Hydrogen Bonds.’
Note: The helix structure is one of the secondary forms of proteins. They can also be present as β-pleated sheets. They can be also present as supercoiled coils, in which 2 or 3 helices coil around each other to form a more stable structure. It should be remembered that alpha helix is one of the most common and stable primary structures of protein. It is seen in hemoglobin and myoglobin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




