
The high melting point of \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] is due to:
(A) \[{\text{sp}}\] hybridised silicon atom.
(B) tetrahedral polymer structure.
(C) its solid state.
(D) \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] hybridised silicon atom.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Consider the bonding present in \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] . Relate the bonding in \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] to the bonding in diamond. We can call \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] as silica or quartz or Silicic oxide or silicic acid. It is an oxide of silicon.
Complete answer:
\[{\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] is transparent to grey in nature. It can be either in crystalline form or in amorphous powdered form. It lacks a test and odor.
We will find that silica has a structure that is very similar to the structure of diamond.
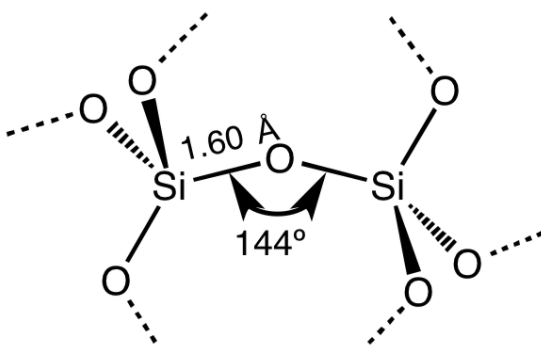
Diamond is a network solid with a very high melting point. Diamond contains tetrahedral units linked together by strong covalent bonds to form a giant network solid. Each tetrahedral unit has four carbon atoms at four corners of the tetrahedron and one carbon atom at the center. Similarly, in silica, each silicon atom is present at the center of regular tetrahedron and forms four covalent bonds with four oxygen atoms. These oxygen atoms are present at four corners of a regular tetrahedron. These oxygen atoms are also connected to other silicon atoms.
Thus, each carbon-carbon bond of diamond is replaced with silicon-oxygen-silicon linkage.
This forms a strong covalent network that results in high melting point.
Thus, the high melting point of \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] is due to tetrahedral polymer structure.
The option (C) its solid state is incorrect as all solids do not have high melting points. There are solids having low melting points.
Hence, the correct option is the option (B).
Note: The central silicon atom in silica undergoes \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\] hybridization as it has four single bonds with four oxygen atoms. Four single bonds and zero lone pairs of electrons for the central silicon atom results in a steric number of 4. The steric number of 4 is associated with \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\] hybridization.
Complete answer:
\[{\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] is transparent to grey in nature. It can be either in crystalline form or in amorphous powdered form. It lacks a test and odor.
We will find that silica has a structure that is very similar to the structure of diamond.
Diamond is a network solid with a very high melting point. Diamond contains tetrahedral units linked together by strong covalent bonds to form a giant network solid. Each tetrahedral unit has four carbon atoms at four corners of the tetrahedron and one carbon atom at the center. Similarly, in silica, each silicon atom is present at the center of regular tetrahedron and forms four covalent bonds with four oxygen atoms. These oxygen atoms are present at four corners of a regular tetrahedron. These oxygen atoms are also connected to other silicon atoms.
Thus, each carbon-carbon bond of diamond is replaced with silicon-oxygen-silicon linkage.
This forms a strong covalent network that results in high melting point.
Thus, the high melting point of \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] is due to tetrahedral polymer structure.

The option (C) its solid state is incorrect as all solids do not have high melting points. There are solids having low melting points.
Hence, the correct option is the option (B).
Note: The central silicon atom in silica undergoes \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\] hybridization as it has four single bonds with four oxygen atoms. Four single bonds and zero lone pairs of electrons for the central silicon atom results in a steric number of 4. The steric number of 4 is associated with \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\] hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




