
The highly repetitive DNA is
A. ALU element
B. Histone gene cluster
C. DNA minisatellite
D. Dispersed repetitive DNA
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: There are several differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA, the presence of highly repetitive DNA units being one of them. The most highly variable DNA sequence element in the human genome usually comprises 10 to 100 base pairs.
Complete answer:One of the major differences found between the genomes of eukaryotes and that of prokaryotes is the fact that most of the eukaryotes have repetitive DNA sequences, with the repeats either being clustered or spread out between the unique genes. There are several categories of repetitive DNA:
(1) Single copy DNA, which contains the structural genes (protein-coding sequences).
(2) Families of DNA, in which one gene somehow copies itself, and the repeats are located in small clusters (tandem repeats) or spread throughout the genome (dispersed repeats).
(3) Satellite DNA, which contains short nucleotide sequences repeated as many as thousands of times. Such repeats are often found clustered in tandem near the centromeres (i.e., the attachment points for the nuclear spindle fibers that move chromosomes during cell division).
The microsatellite DNA is composed of tandem repeats of two nucleotide pairs that are dispersed throughout the genome. Minisatellite DNA, sometimes also known as variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), is composed of blocks of longer repeats also dispersed throughout the genome.
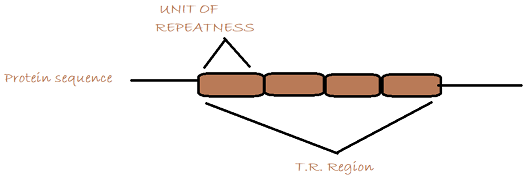
So, the correct answer is C, i.e., DNA minisatellite.
Note: It is important to note that DNA minisatellites are used for important fields such as DNA fingerprinting analysis in forensic science. There is no known function for satellite DNA, nor is it known how the repeats are created.
Complete answer:One of the major differences found between the genomes of eukaryotes and that of prokaryotes is the fact that most of the eukaryotes have repetitive DNA sequences, with the repeats either being clustered or spread out between the unique genes. There are several categories of repetitive DNA:
(1) Single copy DNA, which contains the structural genes (protein-coding sequences).
(2) Families of DNA, in which one gene somehow copies itself, and the repeats are located in small clusters (tandem repeats) or spread throughout the genome (dispersed repeats).
(3) Satellite DNA, which contains short nucleotide sequences repeated as many as thousands of times. Such repeats are often found clustered in tandem near the centromeres (i.e., the attachment points for the nuclear spindle fibers that move chromosomes during cell division).
The microsatellite DNA is composed of tandem repeats of two nucleotide pairs that are dispersed throughout the genome. Minisatellite DNA, sometimes also known as variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), is composed of blocks of longer repeats also dispersed throughout the genome.

So, the correct answer is C, i.e., DNA minisatellite.
Note: It is important to note that DNA minisatellites are used for important fields such as DNA fingerprinting analysis in forensic science. There is no known function for satellite DNA, nor is it known how the repeats are created.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




