
The image distance of an object placed \[10cm\] in front of a thin lens of focal length \[+5cm\]
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: The relation between object distance, image distance and focal length is given by the lens formula. Substituting corresponding values in the lens formula and putting the correct sign for each by following the sign convention will give us the required value of image distance.
Formulas Used:
\[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\]
Complete answer:
Refraction is the bending of rays of light when it passes from one medium to the other. When light passes through a lens, it undergoes refraction.
Given- focal length is \[+5cm\]. This means that it is a convex lens as convex lenses have positive focal lengths.
By convention all distances in front of the lens are taken as positive and distances behind the lens are taken as negative. Therefore, image distance in a convex lens is positive but object distance is negative.
The Lens formula is given by-
\[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\] - (1)
Here, \[v\] is the image distance from the centre of lens
\[u\] is the object distance from center of lens
\[f\] is focal length of the lens
Substituting the given values in eq (1), we have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-10}=\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{1}{10} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{10} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore v=10cm\] - (2)
The image distance is \[10cm\] in front of the lens, this is equal to object distance behind the lens. The image is formed at \[2f\], it is real, inverted and the same size as the object
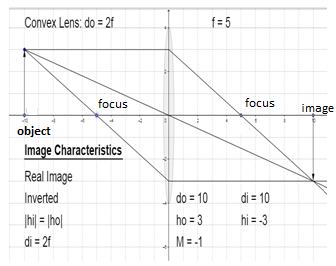
Here,
\[{{d}_{o}}\] is the object distance
\[{{d}_{i}}\] is the image distance
\[{{h}_{o}}\] is the object height
\[{{h}_{i}}\] is the image height
\[M\] is the magnification, that is, ratio of image height to object height
Note:
There are different image formations in a convex lens. It forms a virtual image if the object distance is \[u2f\] the image formed is diminished, real and inverted and formed beyond \[2f\].
Formulas Used:
\[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\]
Complete answer:
Refraction is the bending of rays of light when it passes from one medium to the other. When light passes through a lens, it undergoes refraction.

Given- focal length is \[+5cm\]. This means that it is a convex lens as convex lenses have positive focal lengths.
By convention all distances in front of the lens are taken as positive and distances behind the lens are taken as negative. Therefore, image distance in a convex lens is positive but object distance is negative.
The Lens formula is given by-
\[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\] - (1)
Here, \[v\] is the image distance from the centre of lens
\[u\] is the object distance from center of lens
\[f\] is focal length of the lens
Substituting the given values in eq (1), we have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-10}=\dfrac{1}{5} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{1}{10} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{10} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore v=10cm\] - (2)
The image distance is \[10cm\] in front of the lens, this is equal to object distance behind the lens. The image is formed at \[2f\], it is real, inverted and the same size as the object

Here,
\[{{d}_{o}}\] is the object distance
\[{{d}_{i}}\] is the image distance
\[{{h}_{o}}\] is the object height
\[{{h}_{i}}\] is the image height
\[M\] is the magnification, that is, ratio of image height to object height
Note:
There are different image formations in a convex lens. It forms a virtual image if the object distance is \[u
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




