
The image formed by a concave mirror is:
A.always real.
B.always virtual.
C.certainly real if the object is virtual.
D.certainly virtual if the object is real.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: The mirror formula is basically an equation that relates the object distance and the mirror distance with the focal length. It is also known as the mirror equation. Using the mirror equation, we can answer the question.
Step by step answer:
Using the mirror equation we can write the following:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{v}}\text{ + }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{u}}\text{ = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{f}} \\
& \dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{v}}\text{ = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{f}}\text{ }-\text{ }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{u}} \\
\end{align}$
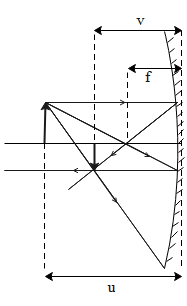
With the given diagram we can see that,
For concave mirrors the focal length is negative. Hence,
$\text{f }<\text{ 0}$
For a virtual object distance is positive. Hence,
${{\text{u}}_{\text{v}}}>\text{ 0}$
From the above equations, it can be observed that image distance v is negative when the object is virtual. Since image distance is negative, it is formed by the real intersection of rays and the image is also real.
For real objects distance is negative. Hence,
${{\text{u}}_{\text{r}}}<\text{ 0}$
In this case, as we can see image distance v can be positive or negative depending upon the location of the object.
Therefore, we can see that the image formed by a concave mirror is certainly real if the object is virtual. So the correct option among the mentioned for this following question is Option C.
Note: Therefore, we can see that concave mirrors can produce both real as well as virtual images. The image can be upright if the image is virtual or inverted if the image is real.
If the image is behind the mirror it is virtual, and if it is in front of the mirror, it is real. The image can also be enlarged, reduced, or the same size as the object.
Step by step answer:
Using the mirror equation we can write the following:

$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{v}}\text{ + }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{u}}\text{ = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{f}} \\
& \dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{v}}\text{ = }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{f}}\text{ }-\text{ }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{u}} \\
\end{align}$
With the given diagram we can see that,
For concave mirrors the focal length is negative. Hence,
$\text{f }<\text{ 0}$
For a virtual object distance is positive. Hence,
${{\text{u}}_{\text{v}}}>\text{ 0}$
From the above equations, it can be observed that image distance v is negative when the object is virtual. Since image distance is negative, it is formed by the real intersection of rays and the image is also real.
For real objects distance is negative. Hence,
${{\text{u}}_{\text{r}}}<\text{ 0}$
In this case, as we can see image distance v can be positive or negative depending upon the location of the object.
Therefore, we can see that the image formed by a concave mirror is certainly real if the object is virtual. So the correct option among the mentioned for this following question is Option C.
Note: Therefore, we can see that concave mirrors can produce both real as well as virtual images. The image can be upright if the image is virtual or inverted if the image is real.
If the image is behind the mirror it is virtual, and if it is in front of the mirror, it is real. The image can also be enlarged, reduced, or the same size as the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




