
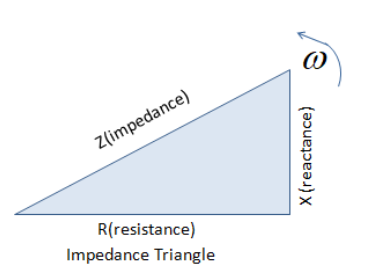
The impedance vector, in a vector-impedance diagram, is parallel to X-axis. The circuit is:
Answer
476.7k+ views
Hint:First we need to draw a RLC circuit either parallel or series and to find the nature of its circuit. The analysis of parallel RLC circuits can be a little more mathematically difficult than for series RLC circuits. Hence we can find out the impedance vector in a vector impedance triangle. Draw the phasor diagram for this parallel RLC circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
The impedance vector from a vector-impedance diagram is always parallel to X-axis. The circuit is entirely resistive. In a parallel RLC circuit that contains a resistor, an inductor and a capacitor the circuit current IS is the phasor addition consisting of three components, \[{I_R},\;{I_L}\;\] and \[{I_C}\;\] with the supply voltage common to all three. As the supply voltage is common to all three components it is used as the horizontal reference while constructing a current triangle.
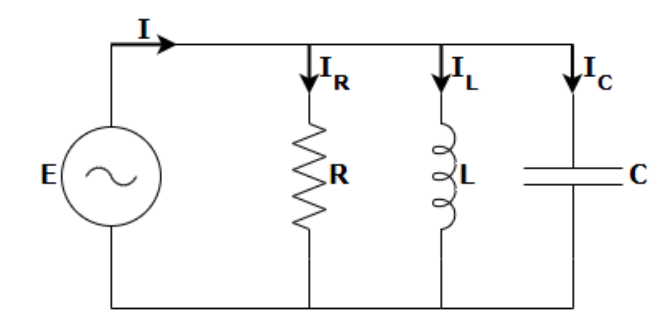
Parallel RLC networks can be observed by vector diagrams just like series RLC circuits. But, the analysis of parallel RLC circuits is mathematically hard for series RLC circuits when it contains two or more current divisions. So an AC parallel circuit can be simply evaluated by using the reciprocal of impedance.
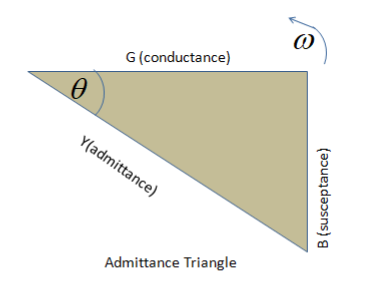
Note:Admittance is the reciprocal of impedance given the symbol, Y. Similarly impedance is a complex quantity containing a real part and an imaginary part. The real part is the reciprocal of resistance and is known as Conductance, with the symbol Y while the imaginary part is the reciprocal of reactance and is known as Susceptance.
Complete step by step answer:
The impedance vector from a vector-impedance diagram is always parallel to X-axis. The circuit is entirely resistive. In a parallel RLC circuit that contains a resistor, an inductor and a capacitor the circuit current IS is the phasor addition consisting of three components, \[{I_R},\;{I_L}\;\] and \[{I_C}\;\] with the supply voltage common to all three. As the supply voltage is common to all three components it is used as the horizontal reference while constructing a current triangle.

Parallel RLC networks can be observed by vector diagrams just like series RLC circuits. But, the analysis of parallel RLC circuits is mathematically hard for series RLC circuits when it contains two or more current divisions. So an AC parallel circuit can be simply evaluated by using the reciprocal of impedance.


Note:Admittance is the reciprocal of impedance given the symbol, Y. Similarly impedance is a complex quantity containing a real part and an imaginary part. The real part is the reciprocal of resistance and is known as Conductance, with the symbol Y while the imaginary part is the reciprocal of reactance and is known as Susceptance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




