
The inversion of cane sugar into glucose and fructose is:
A) I order
B) II order
C) III order
D) Zero order
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:Inversion of sugar is chemical conversion of sucrose in solution into glucose and fructose. This inversion can be catalyzed by acid and high temperature. Therefore the angle of rotation of polarized light sent through the solution changes during the inversion of cane sugar.
Complete answer:
Cane sugar has sucrose in it. Sucrose is a disaccharide in which glucose and fructose are joined by glycosidic linkage. Sucrose is an optically active compound, which means it rotates the polarized light when it falls on it. Sucrose rotates light to the right side (dextrorotatory).
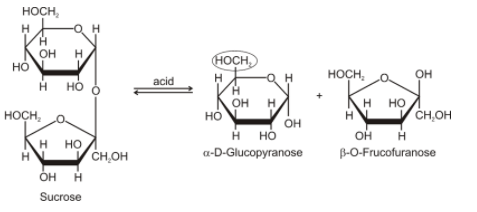
In the presence of acid, sucrose breaks down into one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose and both the molecules are also optically active. The glucose rotated the light slightly to the right, and fructose rotated that light to slightly more towards left, therefore overall the light rotated to left. So we call it invert sugar, as the solution of sucrose with acid inverts the light to the left (levorotatory) now, and earlier it was rotating the light to the right.
The kinetics of this reaction- the molecularity of this reaction is 2, but the reaction is of first order. Since both the water and sucrose is participating, therefore it is bimolecular.
$sucrose + water\underset {} \leftrightarrows glu\cos e + fructose$
But the water in present here in excess so the concentration of water will not appear in the rate law expression, as-
$rate = k[sucrose]$
Here the power of sucrose in the rate law expression is 1. Therefore the inversion of cane sugar is first order reaction
Therefore the correct answer is option ‘A’
Note:Molecularity is the number of molecules that come together to react in a single step reaction. Reaction can be unimolecular, bimolecular or termolecular. While the order of the reaction is empirical quantity determined from the rate law expression of that reaction. It is the sum of exponents in the rate law equation.
Complete answer:
Cane sugar has sucrose in it. Sucrose is a disaccharide in which glucose and fructose are joined by glycosidic linkage. Sucrose is an optically active compound, which means it rotates the polarized light when it falls on it. Sucrose rotates light to the right side (dextrorotatory).

In the presence of acid, sucrose breaks down into one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose and both the molecules are also optically active. The glucose rotated the light slightly to the right, and fructose rotated that light to slightly more towards left, therefore overall the light rotated to left. So we call it invert sugar, as the solution of sucrose with acid inverts the light to the left (levorotatory) now, and earlier it was rotating the light to the right.
The kinetics of this reaction- the molecularity of this reaction is 2, but the reaction is of first order. Since both the water and sucrose is participating, therefore it is bimolecular.
$sucrose + water\underset {} \leftrightarrows glu\cos e + fructose$
But the water in present here in excess so the concentration of water will not appear in the rate law expression, as-
$rate = k[sucrose]$
Here the power of sucrose in the rate law expression is 1. Therefore the inversion of cane sugar is first order reaction
Therefore the correct answer is option ‘A’
Note:Molecularity is the number of molecules that come together to react in a single step reaction. Reaction can be unimolecular, bimolecular or termolecular. While the order of the reaction is empirical quantity determined from the rate law expression of that reaction. It is the sum of exponents in the rate law equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




