
The light enters our eye through the transparent ___________, passes through the ___________ and is focused on the ________________. The ____________ is sensitive to light and sends images to our brain through __________
A) cornea, lens, retina, optic nerve
B) retina, cornea, lens, retina, optic nerve
C) retina, cornea, lens, optic nerve, retina
D) cornea, retina, lens, retina, optic nerve
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: We must understand the structure of the human eye and the function of different parts of the eye.
Complete step by step solution:
When light enters the human eye, different phenomena occur. Now we discuss the structure of the human eye in detail. First look into the diagrammatic representation of the eye. It will be helpful to understand the importance of each point of the human eye.
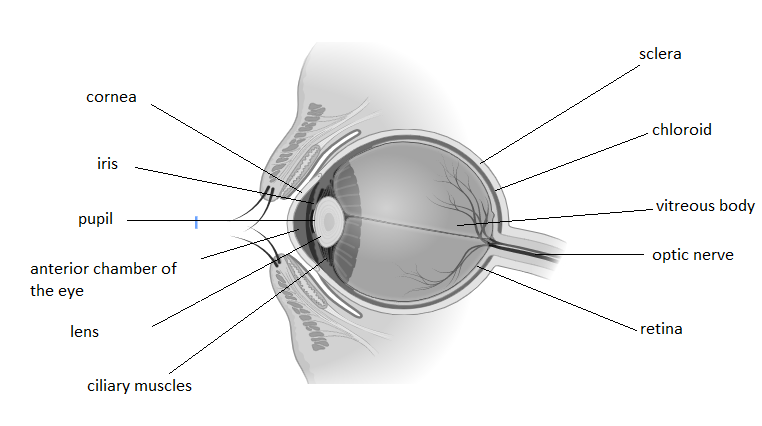
Light enters the eye through the cornea, cornea is a clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. From the cornea, the light passes through the pupil. The amount of light passing through is regulated by the iris, or the coloured part of your eye. From there, the light then hits the lens, the transparent structure inside the eye, which focuses light rays onto the retina. Finally, it reaches the retina, the light-sensitive nerve layer that lines the back of the eye, where the image appears inverted. The optic nerve carries signals of light, dark, and colours to the area of the brain (the visual cortex), which assembles the signals into images (our vision).
Light passes through the front of the eye (cornea) to the lens. The cornea and the lens help to focus the light rays onto the back of the eye (retina). The cells in the retina absorb and convert the light to electrochemical impulses which are transferred along the optic nerve and then to the brain.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note: The structure of the human eye can be compared with parts of a camera. So that it will be easier to understand the function of all parts.
Complete step by step solution:
When light enters the human eye, different phenomena occur. Now we discuss the structure of the human eye in detail. First look into the diagrammatic representation of the eye. It will be helpful to understand the importance of each point of the human eye.

Light enters the eye through the cornea, cornea is a clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. From the cornea, the light passes through the pupil. The amount of light passing through is regulated by the iris, or the coloured part of your eye. From there, the light then hits the lens, the transparent structure inside the eye, which focuses light rays onto the retina. Finally, it reaches the retina, the light-sensitive nerve layer that lines the back of the eye, where the image appears inverted. The optic nerve carries signals of light, dark, and colours to the area of the brain (the visual cortex), which assembles the signals into images (our vision).
Light passes through the front of the eye (cornea) to the lens. The cornea and the lens help to focus the light rays onto the back of the eye (retina). The cells in the retina absorb and convert the light to electrochemical impulses which are transferred along the optic nerve and then to the brain.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note: The structure of the human eye can be compared with parts of a camera. So that it will be easier to understand the function of all parts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




