
The major product of nitration of benzoic acid is:
A. 3-nitrobenzoic acid
B. 4-nitrobenzoic acid
C. 2-nitrobenzoic acid
D. 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: The answer to this question lies in the fact that nitration is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and the presence of a deactivating group that is carboxylic acid groups facilitates the aromatic attack at meta position.
Complete step by step answer:
The concepts of several named reactions and also some of the basic reactions like substitution reactions, addition reactions and also types in it such as electrophilic substitution, nucleophilic substitution etc., are familiar to us.
Now, let us write the reaction that takes place when benzoic acid is subjected to a nitration reaction.
- Benzoic acid is an aromatic compound where it is susceptible to common electrophilic substitution reactions like nitration.
- The carboxylic acid functional group is an electron withdrawing group and thus when we see the resonance structure of this compound, the electrophilic attack is favoured at meta position.
- Thus, nitronium ion attaches to the meta position of benzoic acid and therefore, the product formed will be m - nitrobenzoic acid also written as 3 – nitrobenzoic acid.
The schematic reaction is as shown below,
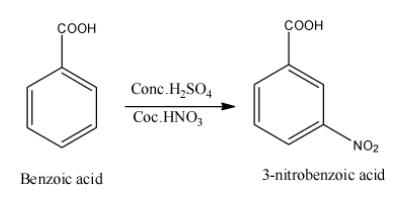
Here, when nitric acid and sulphuric acid reacts together, they generate nitronium ion and this electrophile attacks the meta position to give m – nitrobenzoic acid or 3 – nitrobenzoic acid.
Thus, the correct answer is option A. 3-nitrobenzoic acid.
Note: Nitration always doesn’t mean that it involves sulphuric acid and nitric acid as reagent. This is the name given for the generation of nitronium ion that is an electrophile that introduces nitro group into the aromatic ring and thus any reagent that generates nitronium ion is used for nitration reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The concepts of several named reactions and also some of the basic reactions like substitution reactions, addition reactions and also types in it such as electrophilic substitution, nucleophilic substitution etc., are familiar to us.
Now, let us write the reaction that takes place when benzoic acid is subjected to a nitration reaction.
- Benzoic acid is an aromatic compound where it is susceptible to common electrophilic substitution reactions like nitration.
- The carboxylic acid functional group is an electron withdrawing group and thus when we see the resonance structure of this compound, the electrophilic attack is favoured at meta position.
- Thus, nitronium ion attaches to the meta position of benzoic acid and therefore, the product formed will be m - nitrobenzoic acid also written as 3 – nitrobenzoic acid.
The schematic reaction is as shown below,

Here, when nitric acid and sulphuric acid reacts together, they generate nitronium ion and this electrophile attacks the meta position to give m – nitrobenzoic acid or 3 – nitrobenzoic acid.
Thus, the correct answer is option A. 3-nitrobenzoic acid.
Note: Nitration always doesn’t mean that it involves sulphuric acid and nitric acid as reagent. This is the name given for the generation of nitronium ion that is an electrophile that introduces nitro group into the aromatic ring and thus any reagent that generates nitronium ion is used for nitration reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




