
The maximum efficiency of full wave rectifier is:
A.100%
B.25.20%
C.42.2%
D.81.2%
Answer
555.6k+ views
Hint: A rectifier circuit which converts an ac voltage into dc voltage with the help of both half cycles of applied ac voltage is known as full wave rectifier. To calculate the efficiency of a full wave rectifier we need to calculate the ratio of DC power to AC power which will be discussed in the below section.
Formula used:
Efficiency
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{{{P}_{DC}}}{{{P}_{AC}}}\times 100$
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{DC}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{AC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{RMS}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}$
Complete answer:
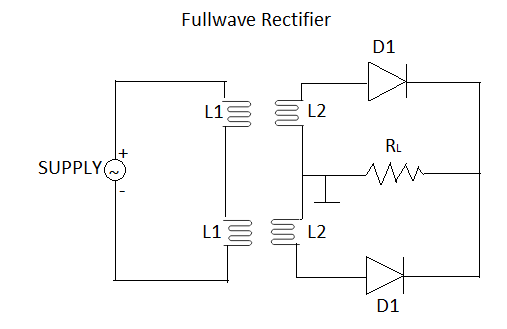
In a full wave rectifier circuit two diodes are used from which one conducts during one half cycle and another in the next half cycle of AC voltage. During positive half cycle diode one becomes forward biased and diode two will become reverse biased hence only diode one will conducts in the circuit and diode two will remain off in that time period and load current flows through diode one with some voltage drop across resistance, but in negative half cycle situation gets reversed and diode one will become reverse and diode two will become forward biased hence only diode two will conducts and load current will flow from diode two only.
Now to calculate efficiency of full wave rectifier we have,
DC Power can be defined as,
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{DC}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{M}}}{\pi }$
Here, ${{V}_{DC}}$(DC voltage across the load resistance), ${{V}_{M}}$(Voltage applied) and ${{R}_{L}}$(load resistance).
AC Power can be defined as,
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{AC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{RMS}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{RMS}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{M}}}{\sqrt{2}}$
Here,${{V}_{RMS}}$ (RMS voltage at the load resistance), ${{V}_{M}}$(Voltage applied) and ${{R}_{L}}$(load resistance).
Now, efficiency is the ratio of dc output to ac output so,
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{{{P}_{DC}}}{{{P}_{AC}}}$
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{\dfrac{{{V}_{DC}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}}{\dfrac{{{V}_{RMS}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{DC}}^{2}}{{{V}_{RMS}}^{2}}$
By putting value of ${{V}_{DC}}$and ${{V}_{RMS}}$ we have,
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{{{\left[ {}^{2{{V}_{M}}}/{}_{\pi } \right]}^{2}}}{{{\left[ {}^{{{V}_{M}}}/{}_{\sqrt{2}} \right]}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{8}{{{\pi }^{2}}}=0.812$
To calculate in percentage we just need to multiply by 100 so we have,
$\Rightarrow \eta =0.812\times 100=81.2%$
$\Rightarrow \eta =81.2%$
$\therefore $ The efficiency of a full wave rectifier is 81.2 % so option (D) is correct.
Note:
The output of a full wave rectifier can contain both ac and dc components which can cause damage to many appliances which can’t tolerate high value of ripple so to further rectify the output the ac components or ripple can be minimized by using filters. The common filters are inductor filter, LC filter, CLC filter and capacitor filter.
Formula used:
Efficiency
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{{{P}_{DC}}}{{{P}_{AC}}}\times 100$
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{DC}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{AC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{RMS}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}$
Complete answer:
In a full wave rectifier circuit two diodes are used from which one conducts during one half cycle and another in the next half cycle of AC voltage. During positive half cycle diode one becomes forward biased and diode two will become reverse biased hence only diode one will conducts in the circuit and diode two will remain off in that time period and load current flows through diode one with some voltage drop across resistance, but in negative half cycle situation gets reversed and diode one will become reverse and diode two will become forward biased hence only diode two will conducts and load current will flow from diode two only.
Now to calculate efficiency of full wave rectifier we have,
DC Power can be defined as,
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{DC}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{M}}}{\pi }$
Here, ${{V}_{DC}}$(DC voltage across the load resistance), ${{V}_{M}}$(Voltage applied) and ${{R}_{L}}$(load resistance).
AC Power can be defined as,

$\Rightarrow {{P}_{AC}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{RMS}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{RMS}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{M}}}{\sqrt{2}}$
Here,${{V}_{RMS}}$ (RMS voltage at the load resistance), ${{V}_{M}}$(Voltage applied) and ${{R}_{L}}$(load resistance).
Now, efficiency is the ratio of dc output to ac output so,
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{{{P}_{DC}}}{{{P}_{AC}}}$
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{\dfrac{{{V}_{DC}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}}{\dfrac{{{V}_{RMS}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{DC}}^{2}}{{{V}_{RMS}}^{2}}$
By putting value of ${{V}_{DC}}$and ${{V}_{RMS}}$ we have,
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{{{\left[ {}^{2{{V}_{M}}}/{}_{\pi } \right]}^{2}}}{{{\left[ {}^{{{V}_{M}}}/{}_{\sqrt{2}} \right]}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \eta =\dfrac{8}{{{\pi }^{2}}}=0.812$
To calculate in percentage we just need to multiply by 100 so we have,
$\Rightarrow \eta =0.812\times 100=81.2%$
$\Rightarrow \eta =81.2%$
$\therefore $ The efficiency of a full wave rectifier is 81.2 % so option (D) is correct.
Note:
The output of a full wave rectifier can contain both ac and dc components which can cause damage to many appliances which can’t tolerate high value of ripple so to further rectify the output the ac components or ripple can be minimized by using filters. The common filters are inductor filter, LC filter, CLC filter and capacitor filter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




