
The monohybrid genotypic ratio is
(a) 1:1
(b) 3:1
(c) 1:2:1
(d) 9:3:3:1
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The monohybrid genotypic ratio depicts the occurrence of the heterozygous and homozygous conditions in the F2 generation when one homozygous dominant parent is crossed with a homozygous recessive one.
Complete answer:
When two plants or animals with a pair of contrasting characters are crossed with each other, it is called a monohybrid cross. Purebred tall and dwarf plants are crossed producing all heterozygous tall plants. They are self-pollinated and both tall and dwarf plants appear in a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1.
Additional Information:
A gene is defined as a unit of heredity that influences the outcome of an organism’s trait. Each gene is expressed as a pair of alleles.
Dominant allele and recessive allele are the two types of allele. Dominant allele masks or hides the expression of a recessive allele. Recessive allele exerts its effect only in homozygous condition.
The genotype is defined as the genetic combination of an individual for any particular trait. It is expressed by a symbol e.g. TT or Tt. When both the alleles are similar in a genotype, the plant is said to be homozygous. If contrasting alleles are present, then the plant is heterozygous. Phenotype is defined as the physical appearance of an individual for any particular trait and is the result of its genotype.
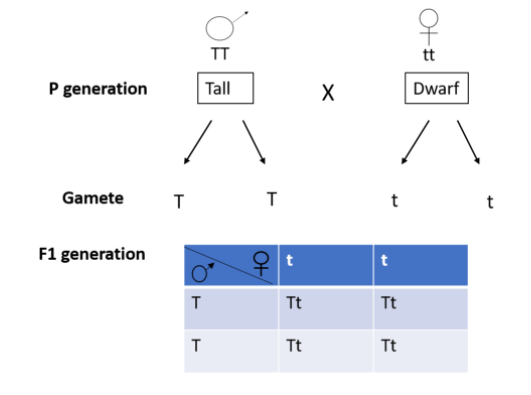
All the plants in the F1 generation are genetically same i.e. Tt and phenotypically same i.e. tall similar to the purebred tall plants of genotype TT. Upon self-pollinating the F1 generation, the following results are observed.
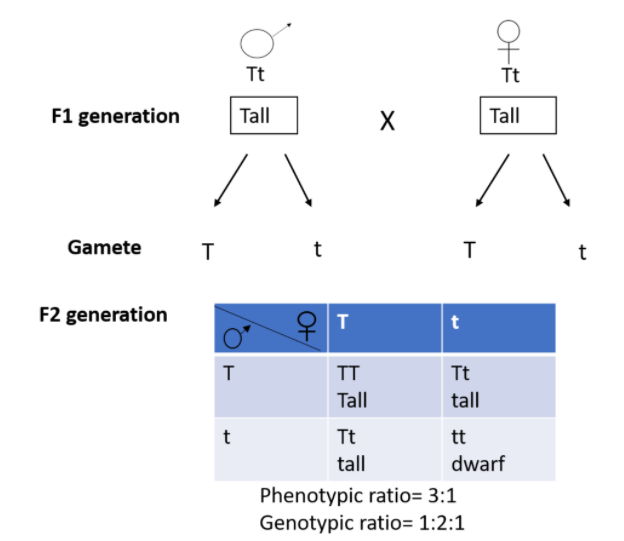
Both tall and dwarf plants appeared in the second generation.
So, the correct answer is, ‘1:2:1’.
Note: Alleles occupy corresponding positions on homologous chromosomes. These alleles control the same characteristics (e.g. height of plant) but their combination may produce different effects (e.g. tall or dwarf). The term ‘homologous’ refers to the chromosomes that carry the same set of genes in the same sequence, although they may not necessarily carry identical alleles of each gene.
Complete answer:
When two plants or animals with a pair of contrasting characters are crossed with each other, it is called a monohybrid cross. Purebred tall and dwarf plants are crossed producing all heterozygous tall plants. They are self-pollinated and both tall and dwarf plants appear in a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1.
Additional Information:
A gene is defined as a unit of heredity that influences the outcome of an organism’s trait. Each gene is expressed as a pair of alleles.
Dominant allele and recessive allele are the two types of allele. Dominant allele masks or hides the expression of a recessive allele. Recessive allele exerts its effect only in homozygous condition.
The genotype is defined as the genetic combination of an individual for any particular trait. It is expressed by a symbol e.g. TT or Tt. When both the alleles are similar in a genotype, the plant is said to be homozygous. If contrasting alleles are present, then the plant is heterozygous. Phenotype is defined as the physical appearance of an individual for any particular trait and is the result of its genotype.

All the plants in the F1 generation are genetically same i.e. Tt and phenotypically same i.e. tall similar to the purebred tall plants of genotype TT. Upon self-pollinating the F1 generation, the following results are observed.

Both tall and dwarf plants appeared in the second generation.
So, the correct answer is, ‘1:2:1’.
Note: Alleles occupy corresponding positions on homologous chromosomes. These alleles control the same characteristics (e.g. height of plant) but their combination may produce different effects (e.g. tall or dwarf). The term ‘homologous’ refers to the chromosomes that carry the same set of genes in the same sequence, although they may not necessarily carry identical alleles of each gene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




