
The morphological nature of the edible part of the coconut is
A. Pericarp
B. Perisprem
C. Cotyledon
D. Endosperm
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: After the act of double fertilization the flower begins to lose its shine.
The petals, stamens, and the style either fall or wither away.
The major events include:
(i) development of endosperm from triploid endosperm nucleus in the central cell of the embryo sac.
(ii) development of an embryo from a diploid zygote.
(iii) development of seed from the ovule.
(iv) Development of fruit from the ovary.
Complete answer: Endosperm is the food-laden tissue formed during the development of angiospermous seed which provides essential nutrients to the growing embryo and also the young seedling at the time of seed germination.
1. In angiosperm, the endosperm develops from triploid primary endosperm nucleus which is formed as a result of vegetative fertilization, triple fusion, or fusion of male gamete with a secondary nucleus of the central cell.
2. Based on the first and subsequent divisions of the primary endosperm nucleus, the endosperm is of three types – nuclear, cellular, and helobial.
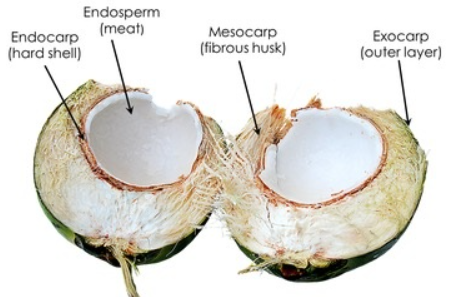
3. The coconut water from tender coconut free-nuclear endosperm (made up of thousands of nuclei) and the surrounding white kernel is the cellular endosperm.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: 1. Nuclear endosperms: In the nuclear type of endosperm development, the primary endosperm nucleus divides by repeated mitotic free nuclear divisions without the formation of walls.
2. Cellular endosperms: Cellular type of endosperm development, the first nuclear division of the primary endosperm nucleus is followed by the formation of either a longitudinal or transverse cell wall in the central cell.
3. Helobial endosperm: In the helobial endosperm development, the primary endosperm nucleus moves to the chalazal end of the embryo sac.
Note: Endosperm may either be completely consumed by developing (eg. Pea, groundnut, beans) before seed maturation or it may persist in the mature seeds (eg. Castor and coconut) and used up during seed germination.
The petals, stamens, and the style either fall or wither away.
The major events include:
(i) development of endosperm from triploid endosperm nucleus in the central cell of the embryo sac.
(ii) development of an embryo from a diploid zygote.
(iii) development of seed from the ovule.
(iv) Development of fruit from the ovary.
Complete answer: Endosperm is the food-laden tissue formed during the development of angiospermous seed which provides essential nutrients to the growing embryo and also the young seedling at the time of seed germination.
1. In angiosperm, the endosperm develops from triploid primary endosperm nucleus which is formed as a result of vegetative fertilization, triple fusion, or fusion of male gamete with a secondary nucleus of the central cell.
2. Based on the first and subsequent divisions of the primary endosperm nucleus, the endosperm is of three types – nuclear, cellular, and helobial.
3. The coconut water from tender coconut free-nuclear endosperm (made up of thousands of nuclei) and the surrounding white kernel is the cellular endosperm.

So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: 1. Nuclear endosperms: In the nuclear type of endosperm development, the primary endosperm nucleus divides by repeated mitotic free nuclear divisions without the formation of walls.
2. Cellular endosperms: Cellular type of endosperm development, the first nuclear division of the primary endosperm nucleus is followed by the formation of either a longitudinal or transverse cell wall in the central cell.
3. Helobial endosperm: In the helobial endosperm development, the primary endosperm nucleus moves to the chalazal end of the embryo sac.
Note: Endosperm may either be completely consumed by developing (eg. Pea, groundnut, beans) before seed maturation or it may persist in the mature seeds (eg. Castor and coconut) and used up during seed germination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




