
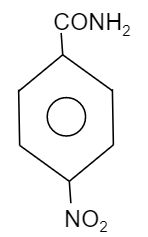
The most reactive compound towards Hoffmann bromamide degradation is:
A.
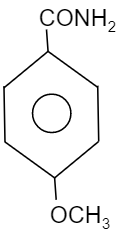
B.
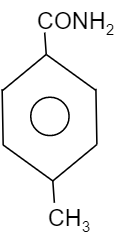
C.
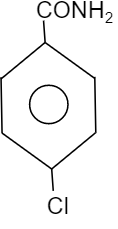
D.




Answer
576k+ views
Hint: You must know that; in Hoffmann bromamide reaction, amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide and there is degradation of the amide. To find out which compound is reactive, see the functional group attached to each compound and check which group is more electronegative.
Complete step by step answer:
Before proceeding to find the correct option, let us first have some knowledge regarding Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
In Hoffmann bromamide reaction, there is the degradation of amide. An amide group (i.e. $CON{{H}_{2}}$) is a group in which the carbonyl group is linked to the nitrogen atom. In this reaction, the amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous solution of the ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide. This further results in the formation of primary amine. Primary amines are those in which the amino group is directly attached to the carbon atom and the primary amine which is formed will have one carbon less than the actual compound.
Now, looking to the option we see all the compounds given are amide having a functional group. So, to find out which compound is most reactive we have to figure out which functional group is more electronegative in nature.
So, to find out the electron dense functional group, see which element is attached directly to the benzene group. We know that oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine, carbon and nitrogen. Whereas chlorine is more electronegative than nitrogen and carbon while nitrogen is more electronegative then carbon. Therefore the compound having $-OC{{H}_{3}}$ will be more electronegative in nature when compared to other groups i.e. $-N{{O}_{2}}$, $-C{{H}_{3}}$ and $-Cl$. Thus, the compound will provide a good migrating tendency. So, the most reactive compound towards Hoffmann bromamide reaction will be the option B.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: It should be noted that Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction is used for the preparation of primary aliphatic and primary amines. Secondary and tertiary amides cannot be used in the Hoffmann bromamide reaction to produce primary amines.
Complete step by step answer:
Before proceeding to find the correct option, let us first have some knowledge regarding Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
In Hoffmann bromamide reaction, there is the degradation of amide. An amide group (i.e. $CON{{H}_{2}}$) is a group in which the carbonyl group is linked to the nitrogen atom. In this reaction, the amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous solution of the ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide. This further results in the formation of primary amine. Primary amines are those in which the amino group is directly attached to the carbon atom and the primary amine which is formed will have one carbon less than the actual compound.
Now, looking to the option we see all the compounds given are amide having a functional group. So, to find out which compound is most reactive we have to figure out which functional group is more electronegative in nature.
So, to find out the electron dense functional group, see which element is attached directly to the benzene group. We know that oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine, carbon and nitrogen. Whereas chlorine is more electronegative than nitrogen and carbon while nitrogen is more electronegative then carbon. Therefore the compound having $-OC{{H}_{3}}$ will be more electronegative in nature when compared to other groups i.e. $-N{{O}_{2}}$, $-C{{H}_{3}}$ and $-Cl$. Thus, the compound will provide a good migrating tendency. So, the most reactive compound towards Hoffmann bromamide reaction will be the option B.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: It should be noted that Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction is used for the preparation of primary aliphatic and primary amines. Secondary and tertiary amides cannot be used in the Hoffmann bromamide reaction to produce primary amines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




