
The movement of a chromosome segment from one linkage group to another is called
A. Translocation
B. Crossing over
C. Inversion
D. Duplication
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: The effect that usually results in unusual chromosome reordering is the translocation of chromosomes. This usually includes balanced and unbalanced translocation, with two primary categories of translocation: Reciprocal and Robertsonian.
Complete solution:
A group of genes on the very same chromosome at multiple locations appear to function in meiosis as a unified pair of genes instead of experiencing individual assortment. The translocation of chromosomes is induced by the rearrangement of components between chromosomes which are not homologous. Consequently, in translocation, a chromosome segment shifts from one linkage group to the next. A gene fusion can indeed be created when the translocation connects two otherwise-separated genes. It's also observed on cytogenetic or a karyotype of damaged cells. In even an exchange of material without any additional or missing genetic information and preferably full functionality, translocations can be balanced or unbalanced.
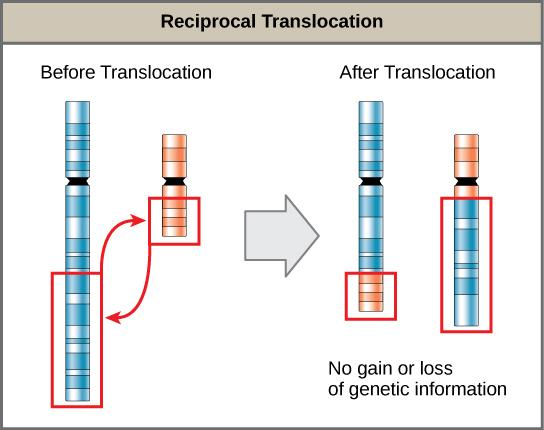
So, the correct answer is option A.
Additional Information: Down syndrome can be an example for translocation by the disintegration and attachment of one chromosome to the next chromosome. There are three 21 chromosomes in this case, and one of the 21 chromosomes is linked to another chromosome. More commonly, translocations are connected with harmful consequences such as aneuploidy, infertility or tumours. Variety of genetic abnormalities, such as XX male syndrome, can also result in chromosomal translocations among sex chromosome which is Induced by the SRY gene translocation from the Y chromosome to the X chromosome. The genetic trademark of malignancies originating from the hematopoietic system seems to be chromosomal translocations. Chromosomal translocations, both in respect to tumour onset and tumour progression, are underlying pathogenetic incidents in cancer.
Note: For leukaemia, lymphoma, and a few forms of solid tumour, chromosomal translocations serve as valuable therapeutic markers and treatment targets. For centuries, insights into the mechanisms of developing chromosomal translocation have remained a key biological issue.
Complete solution:
A group of genes on the very same chromosome at multiple locations appear to function in meiosis as a unified pair of genes instead of experiencing individual assortment. The translocation of chromosomes is induced by the rearrangement of components between chromosomes which are not homologous. Consequently, in translocation, a chromosome segment shifts from one linkage group to the next. A gene fusion can indeed be created when the translocation connects two otherwise-separated genes. It's also observed on cytogenetic or a karyotype of damaged cells. In even an exchange of material without any additional or missing genetic information and preferably full functionality, translocations can be balanced or unbalanced.

So, the correct answer is option A.
Additional Information: Down syndrome can be an example for translocation by the disintegration and attachment of one chromosome to the next chromosome. There are three 21 chromosomes in this case, and one of the 21 chromosomes is linked to another chromosome. More commonly, translocations are connected with harmful consequences such as aneuploidy, infertility or tumours. Variety of genetic abnormalities, such as XX male syndrome, can also result in chromosomal translocations among sex chromosome which is Induced by the SRY gene translocation from the Y chromosome to the X chromosome. The genetic trademark of malignancies originating from the hematopoietic system seems to be chromosomal translocations. Chromosomal translocations, both in respect to tumour onset and tumour progression, are underlying pathogenetic incidents in cancer.
Note: For leukaemia, lymphoma, and a few forms of solid tumour, chromosomal translocations serve as valuable therapeutic markers and treatment targets. For centuries, insights into the mechanisms of developing chromosomal translocation have remained a key biological issue.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




