
The nature of the bond in diamond is:
A. Ionic
B. Covalent
C. Metallic
D. Coordinates covalent
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: Diamond is composed entirely of the element carbon. Each carbon atom is connected to four other carbon atoms. The angles between the bonds are always 109.5 degrees. In diamond the bonds are formed through sharing of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
To answer this question, we have to understand the types of bonds given to us in the question.
Firstly we have ionic bonding.
It is the complete transfer of electrons between atoms. It generates two oppositely charged ions. In ionic bonds, if a metal loses electrons, it gains a positive charge and if non-metals accept that electron they gain a negative charge.
Common examples of compounds having ionic bonds in them are KCl, HCl etc.
Then we have covalent bonding.
A covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms. Atoms which do not have their valence shells fulfilled forms covalent bonding with a similar atom to complete its octet and hence gain stability. There are different types of covalent bonds like single bond, double bond and triple bond.
Common examples include carbon monoxide, CO, IBr etc.
Then we have metallic bonding.
It is a type of bonding which arises due to electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons and positively charged metal ions. It is formed between two metals atoms and has low ionization energy.
This type of bonding is found in metals like sodium, copper zinc etc.
Lastly, we have coordinate covalent bonding.
In a coordinate covalent bond the sharing is only by one atom i.e. one of the atoms will donate its electron density and the other will accept it. There will be no mutual sharing. We generally find this type of bonding in complex compounds where there is a metal-ligand interaction. We even call this as dipolar bond because the involved atoms are of opposite polarity.
Examples of coordinate covalent bonds are formation of ammonium ions or hydronium ions etc.
We know that diamond is an allotrope of carbon i.e. it contains only carbon atoms.
As it has a single type of atom and we have discussed above that among similar atoms covalent bonding is seen. Therefore, we can say that the nature of bond in diamonds is covalent. Each carbon atom is attached to 4 other carbon atoms through a single covalent bond.
Structure of diamond looks like –
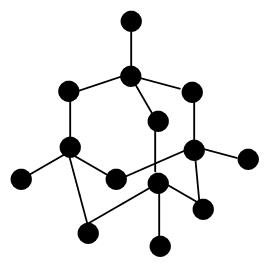
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Graphite and diamond both are allotropes of carbon however diamond does not conduct electricity as graphite. This is due to the fact that in diamond all the electrons in the valence shell of carbon are engaged to form a covalent bond with four other carbon atoms. Thus, there is no free electron in diamond like graphite.
Complete step by step answer:
To answer this question, we have to understand the types of bonds given to us in the question.
Firstly we have ionic bonding.
It is the complete transfer of electrons between atoms. It generates two oppositely charged ions. In ionic bonds, if a metal loses electrons, it gains a positive charge and if non-metals accept that electron they gain a negative charge.
Common examples of compounds having ionic bonds in them are KCl, HCl etc.
Then we have covalent bonding.
A covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms. Atoms which do not have their valence shells fulfilled forms covalent bonding with a similar atom to complete its octet and hence gain stability. There are different types of covalent bonds like single bond, double bond and triple bond.
Common examples include carbon monoxide, CO, IBr etc.
Then we have metallic bonding.
It is a type of bonding which arises due to electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons and positively charged metal ions. It is formed between two metals atoms and has low ionization energy.
This type of bonding is found in metals like sodium, copper zinc etc.
Lastly, we have coordinate covalent bonding.
In a coordinate covalent bond the sharing is only by one atom i.e. one of the atoms will donate its electron density and the other will accept it. There will be no mutual sharing. We generally find this type of bonding in complex compounds where there is a metal-ligand interaction. We even call this as dipolar bond because the involved atoms are of opposite polarity.
Examples of coordinate covalent bonds are formation of ammonium ions or hydronium ions etc.
We know that diamond is an allotrope of carbon i.e. it contains only carbon atoms.
As it has a single type of atom and we have discussed above that among similar atoms covalent bonding is seen. Therefore, we can say that the nature of bond in diamonds is covalent. Each carbon atom is attached to 4 other carbon atoms through a single covalent bond.
Structure of diamond looks like –

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Graphite and diamond both are allotropes of carbon however diamond does not conduct electricity as graphite. This is due to the fact that in diamond all the electrons in the valence shell of carbon are engaged to form a covalent bond with four other carbon atoms. Thus, there is no free electron in diamond like graphite.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




