
The number of atoms in each hcp unit cell is-
[A] 4
[B] 6
[C] 12
[D] 17
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: The basic structure of the hcp lattice is a hexagon. It is divided into 3 layers. Each layer consists of a different number of atoms. The atoms are divided into corners, faces and the middle of the hexagon.
Complete step by step solution: A unit cell is the basic repetitive structure which makes the whole solid structure. The network formed by the unit cell is known as lattice.
These unit cells are arranged in different formations to make different closely packed structures like cubic close packing, orthorhombic close packing, hexagonal close packing etc.
Each unit cell contains a different number of atoms and this is what makes them different from each other.
Hcp is the abbreviation for hexagonal close packing system.
In hexagonal close packing, atoms are arranged in layers of spheres where the spheres of alternating layers lie over each other. Hexagonal close packing is shown in the figure below-
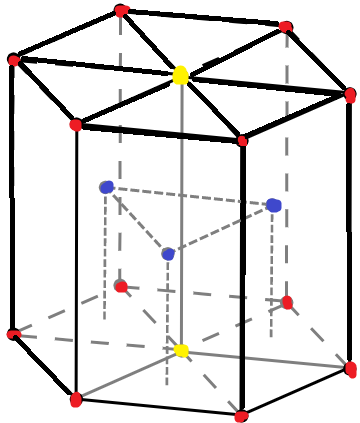 The above diagram indicates a unit cell of a hcp lattice.The red dots indicate corner atoms, the yellow dots indicate atoms at the two face centres and the blue dots are for the atoms present at the middle of the unit cell.
The above diagram indicates a unit cell of a hcp lattice.The red dots indicate corner atoms, the yellow dots indicate atoms at the two face centres and the blue dots are for the atoms present at the middle of the unit cell.
Contribution of each middle atom is 1 as it is not shared with any other cell. There are 3 atoms in the middle.
Contribution of each corner atom is $1\div 6$ as every corner atom is shared among 6 unit cells. There are 12 corner atoms.
Contribution of each face centre atom is $1\div 2$ as each atom lies between two faces hence, shared among 2 unit cell faces. There are 2 face centred atoms.
Therefore, the total number of atoms in one unit cell is $\{12\times (1\div 6)\}+(3\times 1)+\{(2\times (1\div 2)\}$=6
Therefore, there are 6 unit cells in one hcp unit cell.
Therefore the correct answer is option [B] 6.
Note: It is important to remember here that the contribution of each atom is different. Contribution is calculated by checking the position of the atom and dividing the total number of the atoms which are in a similar position by the number of faces it is shared among.
Complete step by step solution: A unit cell is the basic repetitive structure which makes the whole solid structure. The network formed by the unit cell is known as lattice.
These unit cells are arranged in different formations to make different closely packed structures like cubic close packing, orthorhombic close packing, hexagonal close packing etc.
Each unit cell contains a different number of atoms and this is what makes them different from each other.
Hcp is the abbreviation for hexagonal close packing system.
In hexagonal close packing, atoms are arranged in layers of spheres where the spheres of alternating layers lie over each other. Hexagonal close packing is shown in the figure below-

Contribution of each middle atom is 1 as it is not shared with any other cell. There are 3 atoms in the middle.
Contribution of each corner atom is $1\div 6$ as every corner atom is shared among 6 unit cells. There are 12 corner atoms.
Contribution of each face centre atom is $1\div 2$ as each atom lies between two faces hence, shared among 2 unit cell faces. There are 2 face centred atoms.
Therefore, the total number of atoms in one unit cell is $\{12\times (1\div 6)\}+(3\times 1)+\{(2\times (1\div 2)\}$=6
Therefore, there are 6 unit cells in one hcp unit cell.
Therefore the correct answer is option [B] 6.
Note: It is important to remember here that the contribution of each atom is different. Contribution is calculated by checking the position of the atom and dividing the total number of the atoms which are in a similar position by the number of faces it is shared among.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




