
The number of benzylic hydrogen atoms in ethyl benzene is:
(A) 3
(B) 5
(C) 2
(D) 7
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Draw the expanded structure of ethyl benzene. This structure should display hydrogen atoms as well. Now determine the number of hydrogen atoms present in the aromatic ring. Count the hydrogen atoms that are directly attached to the aromatic ring i.e. benzene.
Complete step by step answer:
As suggested in the hint we will draw the expanded structure of the organic compound ethyl benzene.
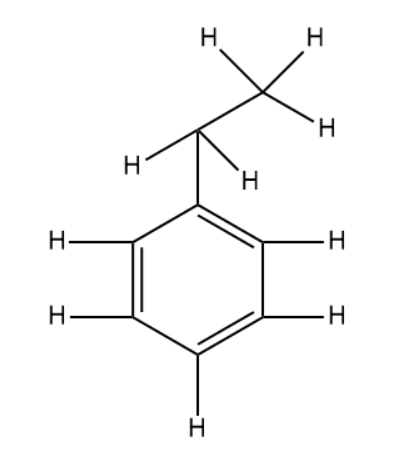
Benzylic hydrogen refers to the hydrogen atoms that are directly attached to the aromatic system i.e benzene in this case.
The total number of benzylic hydrogen atoms are 5.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
Benzene is an aromatic compound as it has resonance and obeys the Debye Huckel rule. Benzene does not undergo addition reactions. This is because, upon addition the aromaticity of the system ceases to exist which is highly unstable and infeasible. This is the reaction benzene and most aromatic systems undergo substitution reactions. In this type of reaction, the incoming atom or group is replaced by the benzylic hydrogen atom.
Note: It is important to know that although there are more than 5 hydrogen atoms seen in the diagram they are not counted as benzylic hydrogen atoms. This is because they are attached to the carbon atom which is not part of the benzene ring. Instead it is considered as a substituted group and is thus not counted in calculation performed above.
Complete step by step answer:
As suggested in the hint we will draw the expanded structure of the organic compound ethyl benzene.

Benzylic hydrogen refers to the hydrogen atoms that are directly attached to the aromatic system i.e benzene in this case.
The total number of benzylic hydrogen atoms are 5.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
Benzene is an aromatic compound as it has resonance and obeys the Debye Huckel rule. Benzene does not undergo addition reactions. This is because, upon addition the aromaticity of the system ceases to exist which is highly unstable and infeasible. This is the reaction benzene and most aromatic systems undergo substitution reactions. In this type of reaction, the incoming atom or group is replaced by the benzylic hydrogen atom.
Note: It is important to know that although there are more than 5 hydrogen atoms seen in the diagram they are not counted as benzylic hydrogen atoms. This is because they are attached to the carbon atom which is not part of the benzene ring. Instead it is considered as a substituted group and is thus not counted in calculation performed above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




