
The number of hydrogen bonds formed by a molecule each of ${{H}_{2}}O, HF$ and $N{{H}_{3}}$ respectively are
a.) $2,2,3$
b.) $4,2,3$
c.) $2,1,3$
d.) $4,4,3$
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalent bonded to a very Electronegative atom .
- A molecule having slightly negative charge or lone pair as in case of nitrogen or ammonia can also form hydrogen bonding with hydrogen of another ammonia molecule.
Complete Solution :
- For the formation of a hydrogen bond of a molecule with another molecule we need a H bond donor which are lone pair donors present in a molecule and H bond acceptors which is the number of hydrogen atoms present in a molecule.
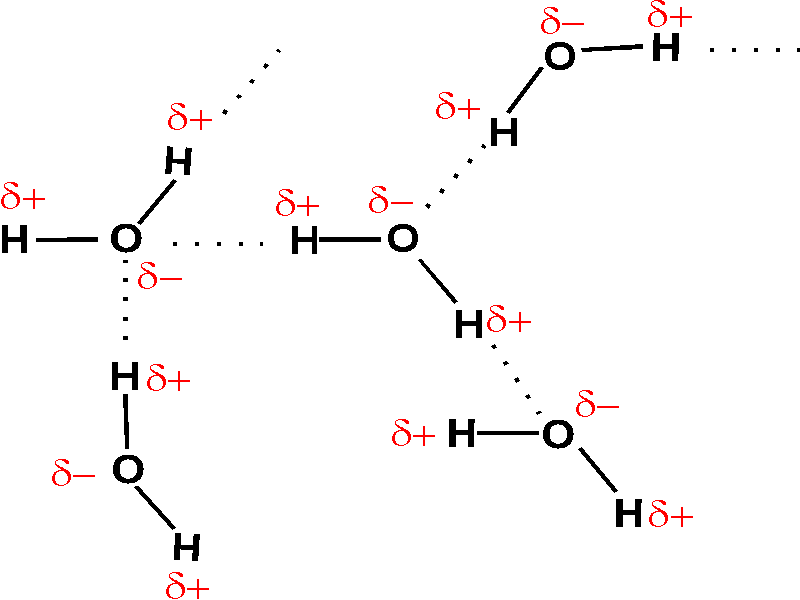
- For intermolecular hydrogen bonding considering case of water ${{H}_{2}}O$ molecule as shown in the diagram oxygen atom has two lone pairs and two hydrogen atoms, meaning that the total number of hydrogen bonds of a water molecule is up to four.
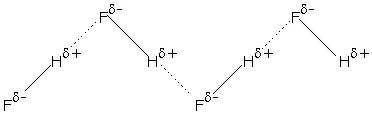
In the case of $HF$ molecule due to Electronegativity of fluorine ,hydrogen develops a partial positive charge and is attracted to nearby lone pairs on fluorine of similar atoms to form hydrogen bonding and one involving one of its lone pairs. The other lone pairs are not used.
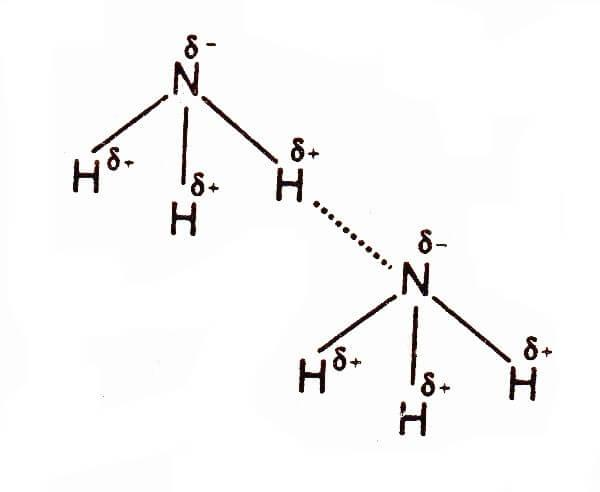
For the ammonia molecule case is different,where fluorine has three lone pairs ,nitrogen has only one lone pair to form hydrogen bonding with other molecules.for hydrogen in ammonia molecules, it is more a function of geometry. $N{{H}_{3}}$ is a Trigonal pyramidal. This means that in effect only one of the hydrogen atoms can effectively interact with the lone pairs because of the size and shape of the other side.
So the correct answer is ${{H}_{2}}O, HF$ molecule , and $N{{H}_{3}}$ molecule forms $4,2,3$ hydrogen bonds respectively..
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Hydrogen bonding formed between hydrogen atom and an Electronegative atom of the same compound ,it is known as intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Hydrogen bonding makes ice less dense than liquid water, so ice floats on water.
- It also affects the shear viscosity of water.
- A molecule having slightly negative charge or lone pair as in case of nitrogen or ammonia can also form hydrogen bonding with hydrogen of another ammonia molecule.
Complete Solution :
- For the formation of a hydrogen bond of a molecule with another molecule we need a H bond donor which are lone pair donors present in a molecule and H bond acceptors which is the number of hydrogen atoms present in a molecule.
- For intermolecular hydrogen bonding considering case of water ${{H}_{2}}O$ molecule as shown in the diagram oxygen atom has two lone pairs and two hydrogen atoms, meaning that the total number of hydrogen bonds of a water molecule is up to four.

In the case of $HF$ molecule due to Electronegativity of fluorine ,hydrogen develops a partial positive charge and is attracted to nearby lone pairs on fluorine of similar atoms to form hydrogen bonding and one involving one of its lone pairs. The other lone pairs are not used.

For the ammonia molecule case is different,where fluorine has three lone pairs ,nitrogen has only one lone pair to form hydrogen bonding with other molecules.for hydrogen in ammonia molecules, it is more a function of geometry. $N{{H}_{3}}$ is a Trigonal pyramidal. This means that in effect only one of the hydrogen atoms can effectively interact with the lone pairs because of the size and shape of the other side.

So the correct answer is ${{H}_{2}}O, HF$ molecule , and $N{{H}_{3}}$ molecule forms $4,2,3$ hydrogen bonds respectively..
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Hydrogen bonding formed between hydrogen atom and an Electronegative atom of the same compound ,it is known as intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Hydrogen bonding makes ice less dense than liquid water, so ice floats on water.
- It also affects the shear viscosity of water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




