
The number of optically active products obtained from the complete ozonolysis of the given compound are:
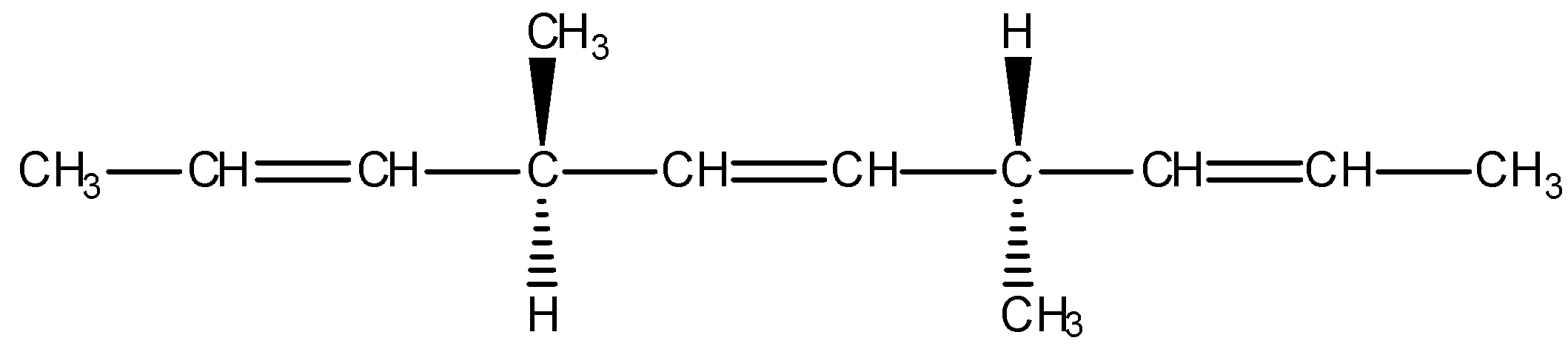
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4

Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Given compound is an alkene and when alkenes undergo ozonolysis, we get alcohols, aldehydes or ketones, or carboxylic acids as products. First do the ozonolysis reaction of the given compound and then identify the products as optically active or optically inactive. For compounds to be optically active, there should be a chiral centre in the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
Ozonolysis is an organic reaction in which the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, or azo compounds are cleaved by an ozone molecule (${O_3}$). In ozonolysis of alkenes, multiple carbon-carbon double bonds are cleaved by ozone molecules and are replaced by carbon-oxygen bonds i.e., carbonyl groups. Mechanism of ozonolysis includes two steps.
In the first step, ozone being electrophilic in nature, reacts with the alkene rapidly and cleaves the carbon-carbon double bond to produce a cyclic peroxide known as ozonide.
In the second step, the decomposition of ozonide (or work-up reaction) is carried out by reductive work-up or oxidative work-up. The reductive work-up yields aldehydes or ketones whereas oxidative work-up gives carboxylic acids as the products and this is the complete ozonolysis. The products of the reaction depends on the type of multiple bonds being oxidised and the work-up conditions.
Given compound:
Complete ozonolysis reaction of given compound is as follows:
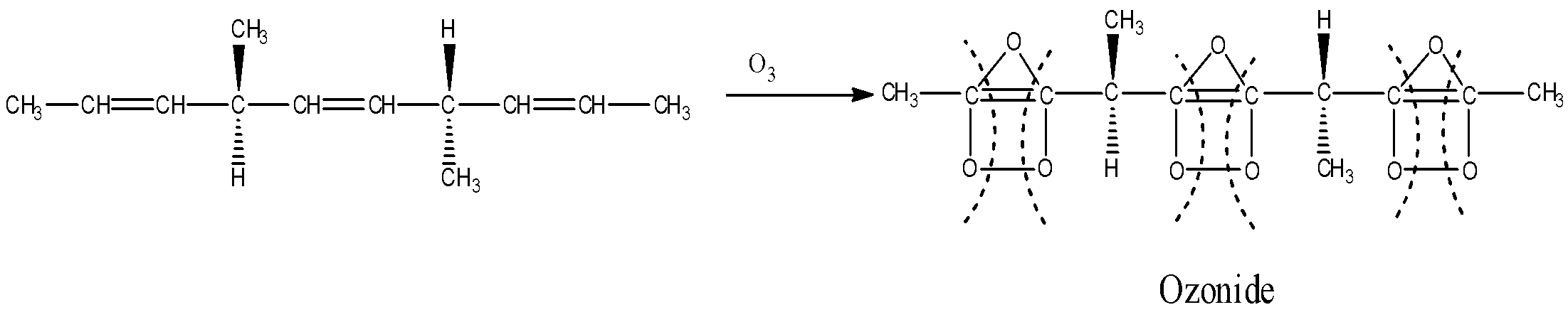
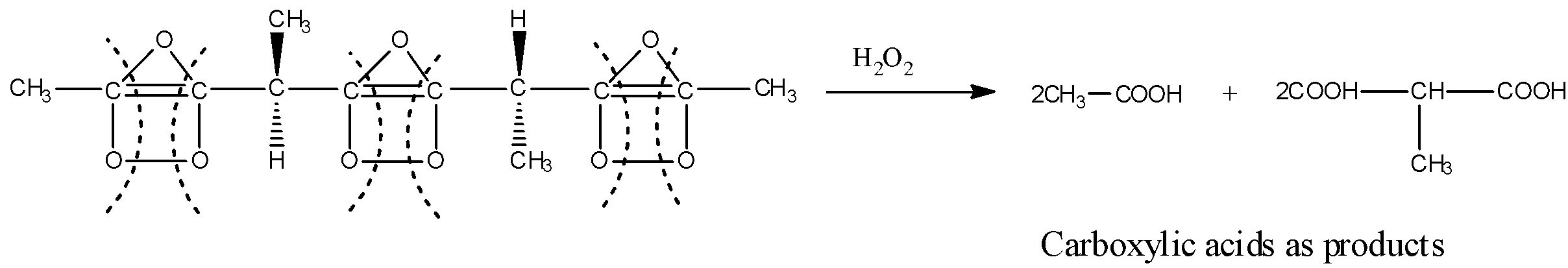
Thus, on complete ozonolysis of the given compound, we get products: $2C{H_3}COOH$ and $2COOH - CH(C{H_3}) - COOH$. Now, for a molecule to be optically active, there must be a chiral carbon centre in the molecule which means the carbon atom must be attached to the four different groups. But the products obtained do not contain any chiral carbon centre, hence the products obtained are optically inactive. Thus, the number of optically active products obtained from the complete ozonolysis of the given compound are zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The reductive ozonolysis or work-up with $Zn,{H_2}O$ results in the formation of aldehydes and/or ketones. The oxidative ozonolysis is done with ${H_2}{O_2}$ and we get carboxylic acids and/or ketones.
Complete step by step answer:
Ozonolysis is an organic reaction in which the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, or azo compounds are cleaved by an ozone molecule (${O_3}$). In ozonolysis of alkenes, multiple carbon-carbon double bonds are cleaved by ozone molecules and are replaced by carbon-oxygen bonds i.e., carbonyl groups. Mechanism of ozonolysis includes two steps.
In the first step, ozone being electrophilic in nature, reacts with the alkene rapidly and cleaves the carbon-carbon double bond to produce a cyclic peroxide known as ozonide.
In the second step, the decomposition of ozonide (or work-up reaction) is carried out by reductive work-up or oxidative work-up. The reductive work-up yields aldehydes or ketones whereas oxidative work-up gives carboxylic acids as the products and this is the complete ozonolysis. The products of the reaction depends on the type of multiple bonds being oxidised and the work-up conditions.
Given compound:
Complete ozonolysis reaction of given compound is as follows:


Thus, on complete ozonolysis of the given compound, we get products: $2C{H_3}COOH$ and $2COOH - CH(C{H_3}) - COOH$. Now, for a molecule to be optically active, there must be a chiral carbon centre in the molecule which means the carbon atom must be attached to the four different groups. But the products obtained do not contain any chiral carbon centre, hence the products obtained are optically inactive. Thus, the number of optically active products obtained from the complete ozonolysis of the given compound are zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The reductive ozonolysis or work-up with $Zn,{H_2}O$ results in the formation of aldehydes and/or ketones. The oxidative ozonolysis is done with ${H_2}{O_2}$ and we get carboxylic acids and/or ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




