
The number of resonating structures of aniline are:
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: The lone pair of the nitrogen occupies the single bond, making a double bond, and a negative charge is generated. This process repeats in cycle until the same structure is contained again.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about resonance. In many organic compounds, a single structural formula for a particular compound is not in a position to explain all the characteristics of that compound. In such cases, mesomerism or resonance is used. If a compound having certain molecular formulas can be represented by different structural formulae which differ only in the arrangement of electron pairs and not the atoms, such structures are called resonating or contributing or canonical structures. The compound as a whole cannot be represented by any of these structures but as a hybrid called resonance hybrid with characteristics of all contributing structures. Some facts about resonance are:
A. The resonating structures should differ only in the position of electron pairs and not atomic nuclei. All resonating structures must nearly have same energies
B. In aniline, resonance takes place as there is a benzene ring and also, there is a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
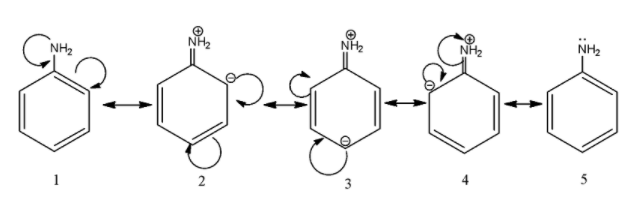
As we can see the double bond of the benzene breaks and a negative charge is produced on the carbon, moreover, the lone pair of the electrons takes place of the single bond and a double bond is formed. The negative charge and the double bond displaces again and this process is repeated in a cyclic fashion. As we can see, there are 5 resonating structures for aniline.
So our correct answer is option D.
Note: The difference in the internal energies of the most stable contributing structure for a particular compound and its resonance hybrid structure is called the resonance energy. Resonance energy for benzene is nearly $150kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about resonance. In many organic compounds, a single structural formula for a particular compound is not in a position to explain all the characteristics of that compound. In such cases, mesomerism or resonance is used. If a compound having certain molecular formulas can be represented by different structural formulae which differ only in the arrangement of electron pairs and not the atoms, such structures are called resonating or contributing or canonical structures. The compound as a whole cannot be represented by any of these structures but as a hybrid called resonance hybrid with characteristics of all contributing structures. Some facts about resonance are:
A. The resonating structures should differ only in the position of electron pairs and not atomic nuclei. All resonating structures must nearly have same energies
B. In aniline, resonance takes place as there is a benzene ring and also, there is a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.

As we can see the double bond of the benzene breaks and a negative charge is produced on the carbon, moreover, the lone pair of the electrons takes place of the single bond and a double bond is formed. The negative charge and the double bond displaces again and this process is repeated in a cyclic fashion. As we can see, there are 5 resonating structures for aniline.
So our correct answer is option D.
Note: The difference in the internal energies of the most stable contributing structure for a particular compound and its resonance hybrid structure is called the resonance energy. Resonance energy for benzene is nearly $150kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




