
The number of structural for \[{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_{14}}\]
A.3
B.4
C.5
D.6
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint:There are various types of structural isomerism. In the above molecule chain isomerism, position isomerism is contained in but functional group isomerism is not present in the above molecule. The given molecule is a saturated hydrocarbon.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomers are those molecules which have the same molecular formula but have different physical and chemical properties.Structural isomers are those having the same molecular formula but different properties due to different structures. They are classified as chain isomerism, position isomerism, functional group isomerism and linking isomerism.
Functional group isomerism is that structural isomerism which has the same molecular formula but different functional group chain isomerism by that structural isomerism which has the same molecular formula but different length of principal carbon. Chain position isomerism is that structural isomerism which has the same molecular formula but different position of functional groups or multiple bond or side substituents. Ring chain isomerism is that structural isomerism which has the same molecular formula but has either the multiple bonds or ring with respect to its isomer.
The given formula represents an alkane named as hexane representing the general formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{n}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2n}} + 2}}\] . It does not have any functional group and hence cannot possess functional isomerism. The conditions are also not suitable for ring formation because it contains only single bonds and the number of hydrogen required in a ring will be 12 and not 14. The structural isomerism of are as follow:
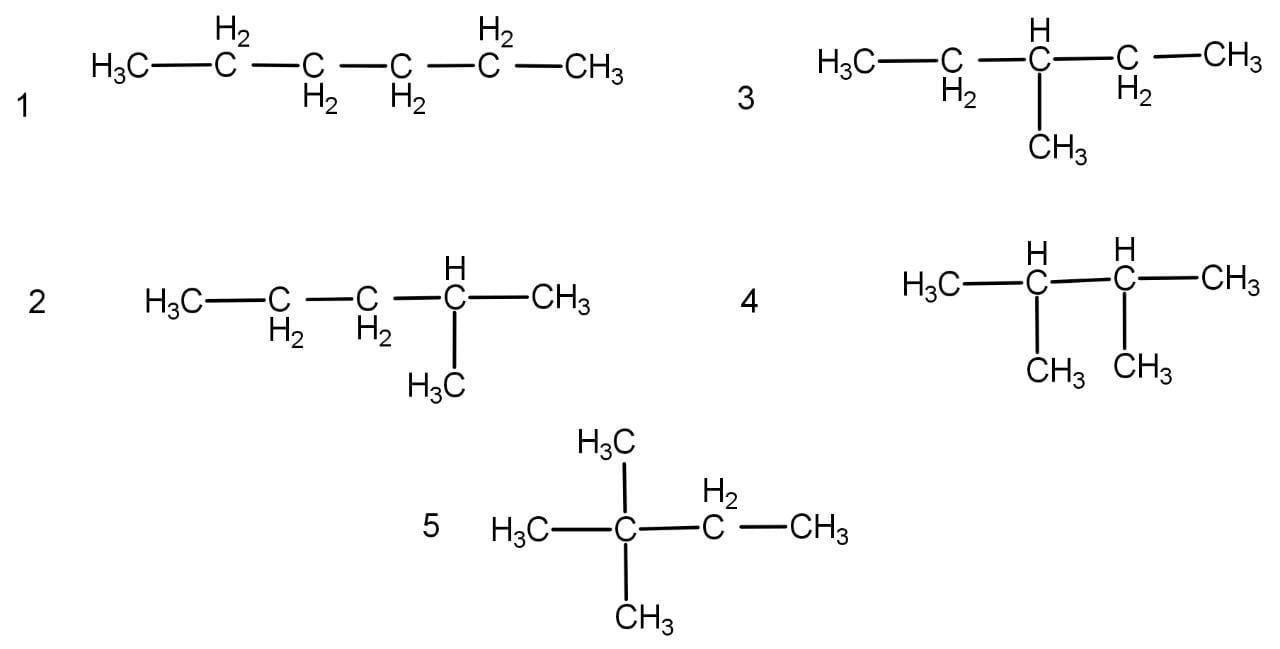
Hence, the correct option is option C.
Note:
There are two types of isomerism: structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Stereoisomerism is those isomers in which the molecules differ in the arrangement of atoms in space, i.e. 3D arrangement. They include R-S configuration, cis and trans isomers etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomers are those molecules which have the same molecular formula but have different physical and chemical properties.Structural isomers are those having the same molecular formula but different properties due to different structures. They are classified as chain isomerism, position isomerism, functional group isomerism and linking isomerism.
Functional group isomerism is that structural isomerism which has the same molecular formula but different functional group chain isomerism by that structural isomerism which has the same molecular formula but different length of principal carbon. Chain position isomerism is that structural isomerism which has the same molecular formula but different position of functional groups or multiple bond or side substituents. Ring chain isomerism is that structural isomerism which has the same molecular formula but has either the multiple bonds or ring with respect to its isomer.
The given formula represents an alkane named as hexane representing the general formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{n}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2n}} + 2}}\] . It does not have any functional group and hence cannot possess functional isomerism. The conditions are also not suitable for ring formation because it contains only single bonds and the number of hydrogen required in a ring will be 12 and not 14. The structural isomerism of are as follow:

Hence, the correct option is option C.
Note:
There are two types of isomerism: structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Stereoisomerism is those isomers in which the molecules differ in the arrangement of atoms in space, i.e. 3D arrangement. They include R-S configuration, cis and trans isomers etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




