
The order of reactivity of phenyl magnesium bromide ($\text{ PhMgBr }$) with the following compounds:
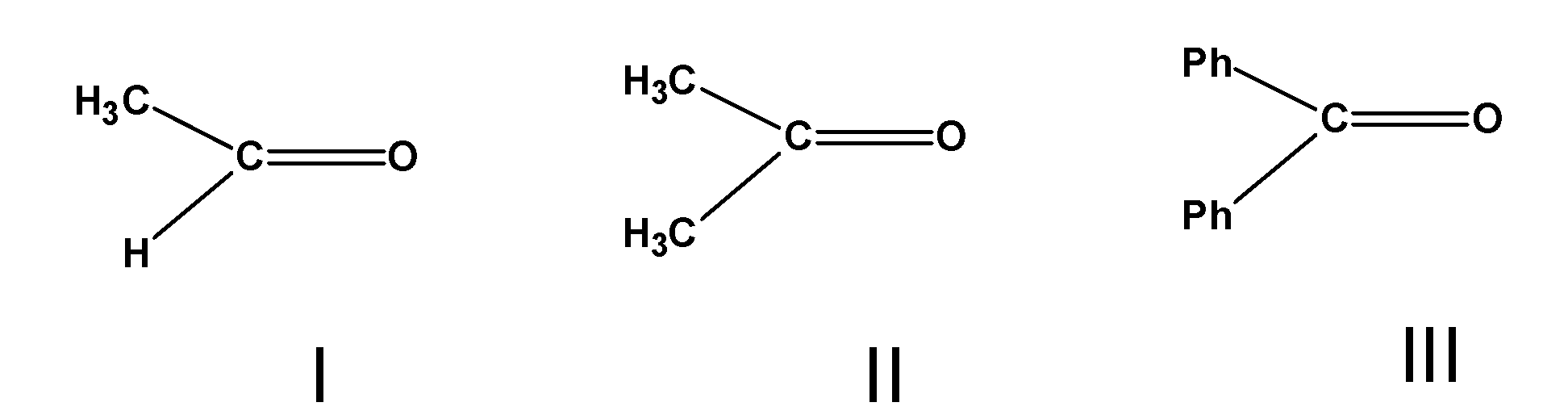
A) $\text{ III }>\text{ II }>\text{ I }$
B) $\text{ II }>\text{ I }>\text{ III }$
C) $\text{ I }>\text{ III }>\text{ II }$
D) $\text{ I }>\text{ II }>\text{ III }$

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The Grignard reagents are versatile in organic synthesis. Grignard reagent reacts with aldehyde, ketones, and esters to form an additional product that decomposes with dil.$\text{ HCl }$ or dil.$\text{ }{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{ }$ to give alcohols. The reactivity of the nucleophilic addition reaction depends on how easily a nucleophile can attack the substrate. The obstruction by the bulkier groups decreases the nucleophile attack.
Complete step by step answer:
A Grignard reagent is a chemical formula. The Grignard reagent has a general formula as$\text{ R}-\text{Mg}-\text{X }$, where X is the halogen, and R is an organic group may be alkyl or aryl group.
The reaction mechanism involves the simultaneous attack of the nucleophile alkyl carbanion $\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{-}}\text{ }$ of the Grignard reagent on the carboxyl atom and the remaining portions get attached to the oxygen of the carbonyl group forming an addition product. This decomposes by water to give alcohol.
The reactivity of the Grignard reagent $\text{ PhMgBr }$ towards the carbonyl compound depends on the type of carbonyl compound used. Grignard synthesis depends on substituents on the carbon of the carbonyl group.
The aldehyde has the general formula as $\text{ RCHO }$ and the ketones have the general formula as$\text{ RCOR }$. The alkyl or the aryl group on the carbon of the carbonyl compounds affect the reactivity of the Grignard reagent.
As the number of the alkyl substituents or the size of the alkyl groups increases on the carbon atom, the crowding increases on the organic compound. The larger alkyl groups repel each other and obstruct the attack of the nucleophile on the carbon atom. The crowding decreases the nucleophilic attack of the Grignard reagent.
Here, the Ethanal or acetaldehyde $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CHO }$ has one methyl group bonded to the carbonyl atom. However, the acetone has the two methyl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom. Thus, the acetone has a larger crowding effect compared to acetaldehyde. Thus, $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CHO }$which easily undergoes the Grignard synthesis.
The $\text{ PhCOPh }$have two phenyl groups bonded to the carbonyl atoms. Phenyl groups are larger and retards the nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl atom.
The order of decreasing of reactivity of $\text{ PhMgBr }$ with the given compounds is given as follows,
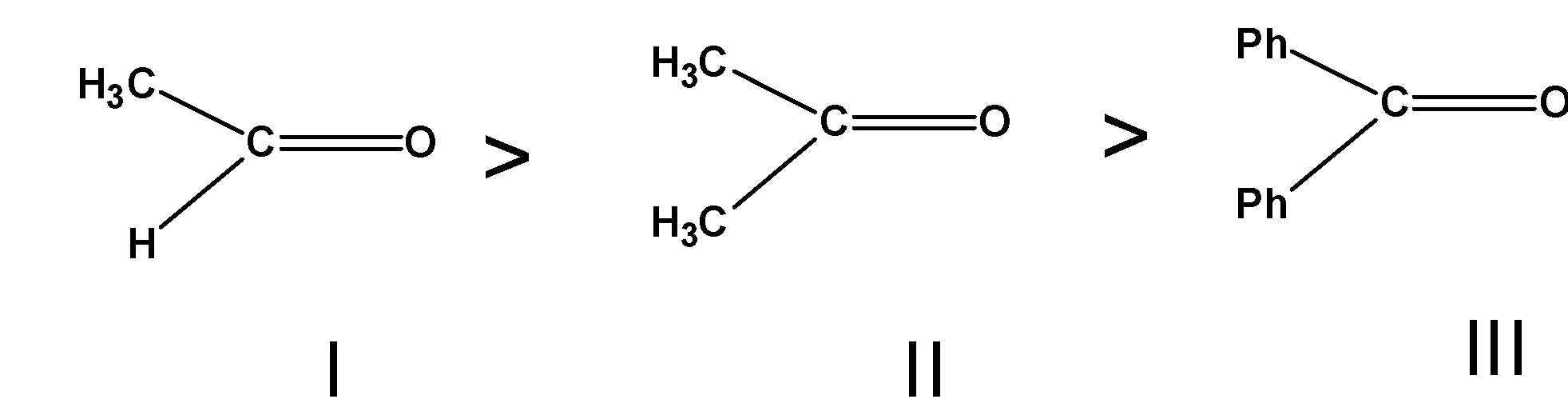
Thus, the order of reactivity is $\text{ I }>\text{ II }>\text{ III }$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Note that, the substituents also have a major role in deciding the nature of the product alcohol.
-The additional of a Grignard reagent to the methanal (formaldehyde) results in primary alcohol.
-The addition of Grignard reagent to another aldehyde (other than formaldehyde) like ethanal, propanal, etc. results in the secondary alcohol.
-The addition of the Grignard reagent to the ketone given out the tertiary alcohol.
Complete step by step answer:
A Grignard reagent is a chemical formula. The Grignard reagent has a general formula as$\text{ R}-\text{Mg}-\text{X }$, where X is the halogen, and R is an organic group may be alkyl or aryl group.
The reaction mechanism involves the simultaneous attack of the nucleophile alkyl carbanion $\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{-}}\text{ }$ of the Grignard reagent on the carboxyl atom and the remaining portions get attached to the oxygen of the carbonyl group forming an addition product. This decomposes by water to give alcohol.
The reactivity of the Grignard reagent $\text{ PhMgBr }$ towards the carbonyl compound depends on the type of carbonyl compound used. Grignard synthesis depends on substituents on the carbon of the carbonyl group.
The aldehyde has the general formula as $\text{ RCHO }$ and the ketones have the general formula as$\text{ RCOR }$. The alkyl or the aryl group on the carbon of the carbonyl compounds affect the reactivity of the Grignard reagent.
As the number of the alkyl substituents or the size of the alkyl groups increases on the carbon atom, the crowding increases on the organic compound. The larger alkyl groups repel each other and obstruct the attack of the nucleophile on the carbon atom. The crowding decreases the nucleophilic attack of the Grignard reagent.
Here, the Ethanal or acetaldehyde $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CHO }$ has one methyl group bonded to the carbonyl atom. However, the acetone has the two methyl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom. Thus, the acetone has a larger crowding effect compared to acetaldehyde. Thus, $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CHO }$which easily undergoes the Grignard synthesis.
The $\text{ PhCOPh }$have two phenyl groups bonded to the carbonyl atoms. Phenyl groups are larger and retards the nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl atom.
The order of decreasing of reactivity of $\text{ PhMgBr }$ with the given compounds is given as follows,

Thus, the order of reactivity is $\text{ I }>\text{ II }>\text{ III }$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Note that, the substituents also have a major role in deciding the nature of the product alcohol.
-The additional of a Grignard reagent to the methanal (formaldehyde) results in primary alcohol.
-The addition of Grignard reagent to another aldehyde (other than formaldehyde) like ethanal, propanal, etc. results in the secondary alcohol.
-The addition of the Grignard reagent to the ketone given out the tertiary alcohol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




