
The ornithine cycle removes two waste products from the blood in the liver. These products are
(a) $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ and urea
(b) Ammonia and urea
(c) $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ and ammonia
(d) Ammonia and uric acid
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Urea is excreted in the ornithine cycle starting with the two most toxic substances in the human blood. One is the one we exhale and the other is the major product of nitrogen metabolism that is highly toxic.
Complete step by step answer:
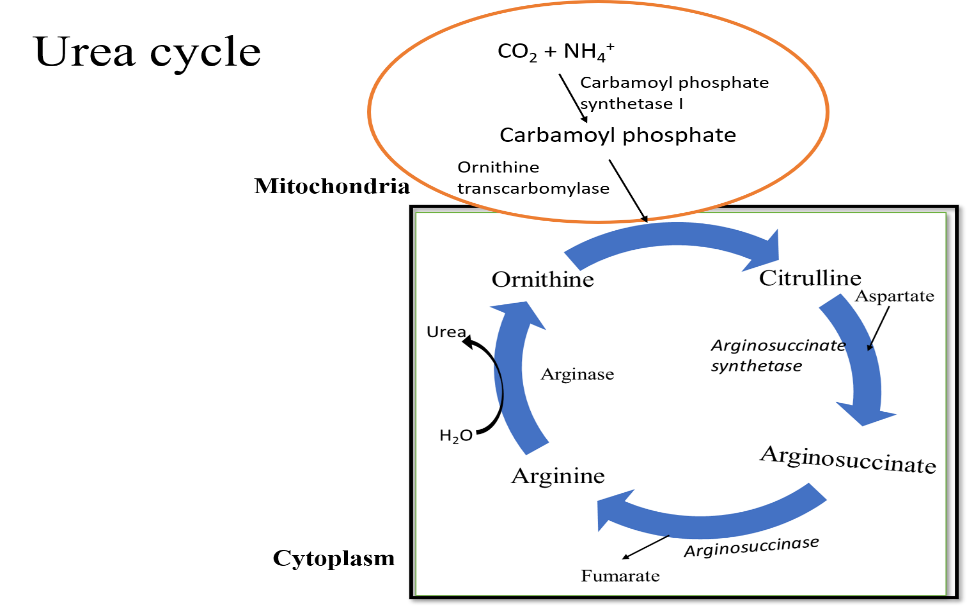
- Almost 80% of the nitrogen in mammals including humans is excreted is in the form of urea. Urea is produced through a series of reactions occurring in the cytosol and mitochondrial matrix of liver cells.
- Ammonia is a toxic product of nitrogen metabolism which must be removed from our blood. This is achieved via the ornithine cycle.
- The ornithine cycle starts with the metabolism of ammonia and $C{ O }_{ 2 }$. The main purpose of the ornithine cycle is to eliminate toxic ammonia from the body. Eventually, ammonia and carbon dioxide are the two waste products removed from the body.
So the correct answer is, ‘$C{ O }_{ 2 }$ and ammonia.’
Additional information:
1. The ammonia combines with $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }_{ 2 }O$ to form carbamoyl phosphate.
2. Now, carbamoyl phosphate reacts with ornithine to form citrulline. This occurs in the matrix of mitochondria in the liver cells.
3. This citrulline produced now reacts with aspartate to form argininosuccinate.
4. Argininosuccinate breaks down to form fumarate & arginine. Later, fumarate produced is diverted towards Krebs Cycle.
5. Arginine is hydrolyzed by water to form urea & ornithine.
6. Ornithine is released and recycled. While urea is carried to the kidneys to be excreted through urine.
Note:
- The initial two steps of the ornithine cycle occur in the mitochondrial matrix.
- From the matrix, citrulline is released to the cytosol, where it condenses with aspartate to form argininosuccinate.
- Urea cycle defects cause hyperammonemia. Defects in the area could cause vomiting, coma, and convulsions in newborn babies.
- Krebs- Henseleit cycle is the other name of the ornithine cycle.
- Even a minute amount of excess ammonia can cause severe and irreversible damages.
- A dysfunctional urea (ornithine) cycle means an excessive amount of ammonia in the body, which can lead to cell toxicity and various disorders.
Complete step by step answer:
- Almost 80% of the nitrogen in mammals including humans is excreted is in the form of urea. Urea is produced through a series of reactions occurring in the cytosol and mitochondrial matrix of liver cells.
- Ammonia is a toxic product of nitrogen metabolism which must be removed from our blood. This is achieved via the ornithine cycle.
- The ornithine cycle starts with the metabolism of ammonia and $C{ O }_{ 2 }$. The main purpose of the ornithine cycle is to eliminate toxic ammonia from the body. Eventually, ammonia and carbon dioxide are the two waste products removed from the body.

So the correct answer is, ‘$C{ O }_{ 2 }$ and ammonia.’
Additional information:
1. The ammonia combines with $C{ O }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }_{ 2 }O$ to form carbamoyl phosphate.
2. Now, carbamoyl phosphate reacts with ornithine to form citrulline. This occurs in the matrix of mitochondria in the liver cells.
3. This citrulline produced now reacts with aspartate to form argininosuccinate.
4. Argininosuccinate breaks down to form fumarate & arginine. Later, fumarate produced is diverted towards Krebs Cycle.
5. Arginine is hydrolyzed by water to form urea & ornithine.
6. Ornithine is released and recycled. While urea is carried to the kidneys to be excreted through urine.
Note:
- The initial two steps of the ornithine cycle occur in the mitochondrial matrix.
- From the matrix, citrulline is released to the cytosol, where it condenses with aspartate to form argininosuccinate.
- Urea cycle defects cause hyperammonemia. Defects in the area could cause vomiting, coma, and convulsions in newborn babies.
- Krebs- Henseleit cycle is the other name of the ornithine cycle.
- Even a minute amount of excess ammonia can cause severe and irreversible damages.
- A dysfunctional urea (ornithine) cycle means an excessive amount of ammonia in the body, which can lead to cell toxicity and various disorders.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




