
The oxidation of benzene by ${{V}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$ in the presence of air produces:
A. benzoic acid
B. benzaldehyde
C. benzoic anhydride
D. maleic anhydride
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Think about the D.A.Dowden mechanism that shows the oxidation of benzene by vanadium oxide in the presence of air. Consider where the cleavage will take place and what kind of anhydride will be formed.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that during this process, the cleavage of the benzene ring will occur and the formation of a dioic acid will take place. This dioic acid will then undergo dehydration to form an anhydride by the same vanadium oxide molecules. Vanadium oxide will cleave any double bonds that are present in the ring (but not all of them) and oxidize the terminal ends to form carboxylic acid groups with the help of the oxygen present in the air.
When one molecule of benzene reacts with two molecules of vanadium pentoxide and one and a half mole of oxygen, we get one mole of maleic anhydride, one mole of glyoxylic or aldehydic acid, two moles of vanadium trioxide, and one mole of water. The general reaction of this process is:
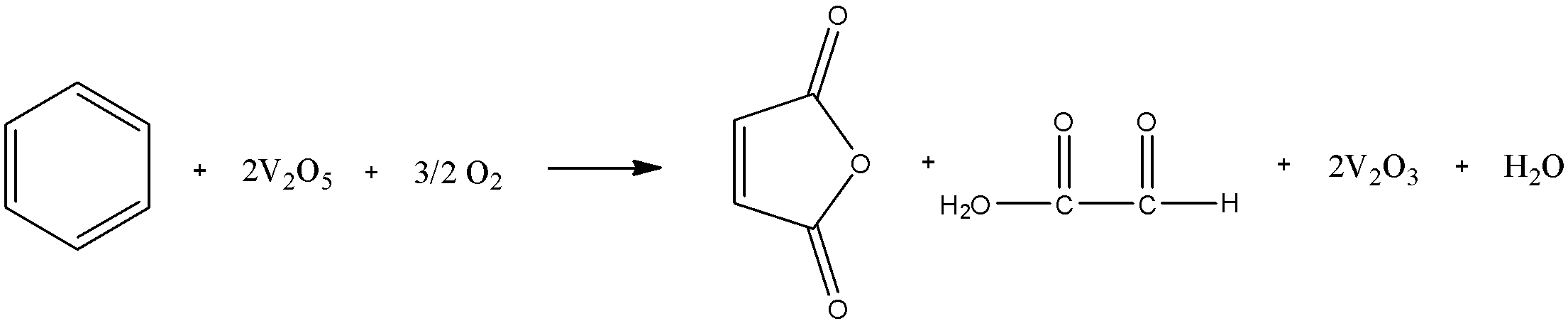
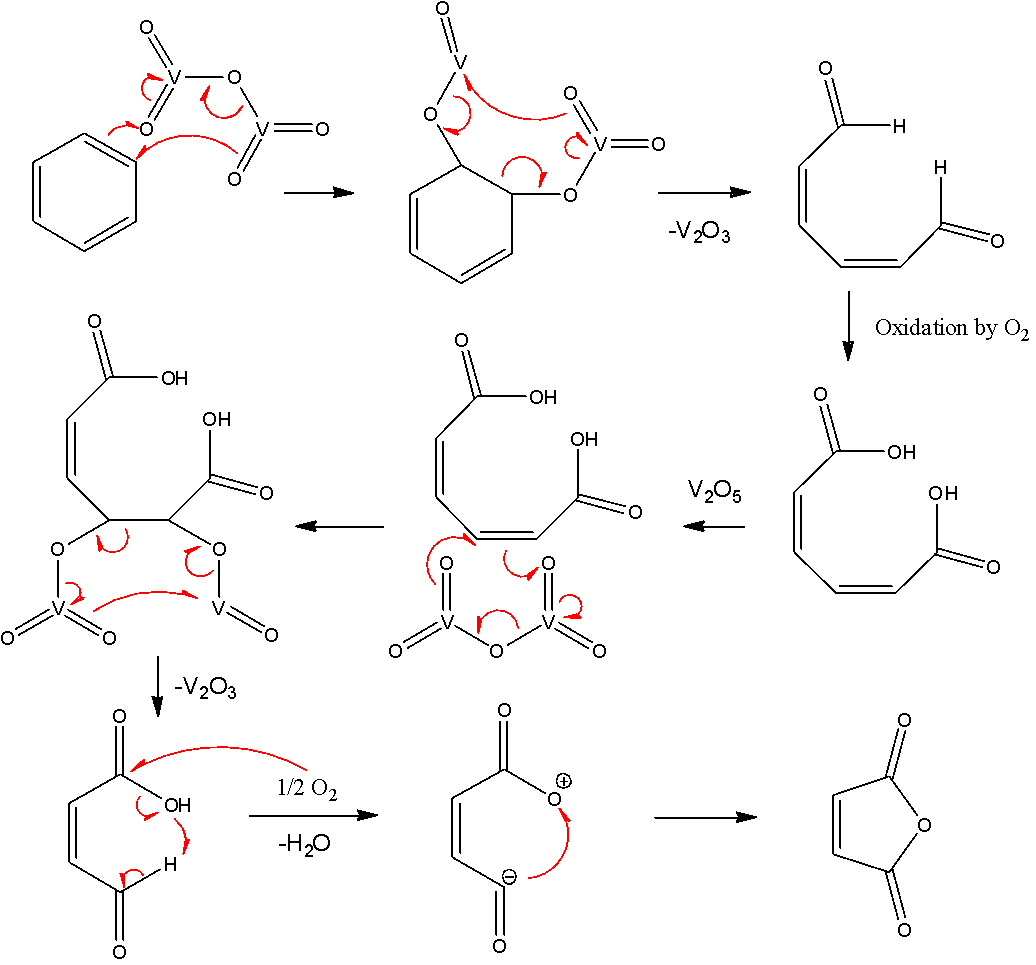
Now, let us look at the mechanism to get a deeper understanding of how this reaction works. The vanadium pentoxide attaches itself to one of the double bonds and breaks the ring. Then the aldehydic groups at the terminal ends are oxidized to form carboxylic acid groups. Then vanadium pentoxide attacks the second double bond, this causes another breakage and aldehydic acid to be liberated. Dehydration takes place after this and the anhydride of maleic acid is formed. The mechanism is as follows:

So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Note that in the second to last step of the mechanism, oxygen has a positive charge despite forming just a single bond. Remember that although oxygen has formed only one bond, it has been formed due to oxygen donating one of its lone pairs and not due to receiving a lone pair. Hence, that atom has a positive charge.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that during this process, the cleavage of the benzene ring will occur and the formation of a dioic acid will take place. This dioic acid will then undergo dehydration to form an anhydride by the same vanadium oxide molecules. Vanadium oxide will cleave any double bonds that are present in the ring (but not all of them) and oxidize the terminal ends to form carboxylic acid groups with the help of the oxygen present in the air.
When one molecule of benzene reacts with two molecules of vanadium pentoxide and one and a half mole of oxygen, we get one mole of maleic anhydride, one mole of glyoxylic or aldehydic acid, two moles of vanadium trioxide, and one mole of water. The general reaction of this process is:

Now, let us look at the mechanism to get a deeper understanding of how this reaction works. The vanadium pentoxide attaches itself to one of the double bonds and breaks the ring. Then the aldehydic groups at the terminal ends are oxidized to form carboxylic acid groups. Then vanadium pentoxide attacks the second double bond, this causes another breakage and aldehydic acid to be liberated. Dehydration takes place after this and the anhydride of maleic acid is formed. The mechanism is as follows:

So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Note that in the second to last step of the mechanism, oxygen has a positive charge despite forming just a single bond. Remember that although oxygen has formed only one bond, it has been formed due to oxygen donating one of its lone pairs and not due to receiving a lone pair. Hence, that atom has a positive charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




