
The period of a geostationary satellite is _______________________ hours.
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, we start with the geostationary satellite that is a satellite that is orbiting around the earth which is placed at a height of around 35,800 kilometers and as it revolves with the earth in the same direction it, therefore, it take the same period as earth takes to complete one revolution around its own axis that is a day.
Complete step-by-step solution -
First, we know that a geostationary satellite is a satellite that is orbiting around the earth which is placed at a height of around 35,800 kilometers or 22,300 miles over the earth's equator, therefore it rotates in the same direction as the earth revolves around its axis that is from west to east. So as it rotates with the earth, it will also take the same time to complete one rotation as the earth takes to complete one rotation on its own axis that is 24 hours 56 minutes. This is nearly 23.934461223 hours or one sidereal day. As shown in the below figure.
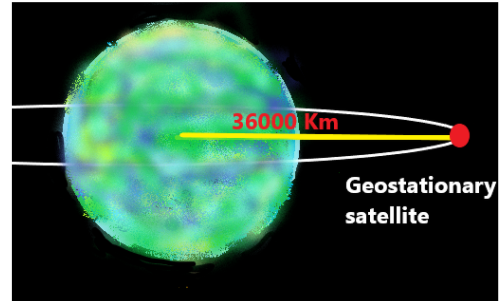
A single geostationary satellite when present in the line of sight provides coverage of around 40 % of the earth's surface. If three geostationary satellites are placed in orbit with each separated by 120 degrees can easily cover the complete earth's surface except for small circular regions at the northern and southern poles. Geostationary satellites are very famous because they can be easily accessed using an earthbound directional antenna which just needs adjustment ones and then it can be left without further modification. Another major advantage of these types of satellites is that as it uses highly directional antennas the interference from and other satellites and ground-based sources are reduced drastically.
Note: For these types of questions, we need to know about different types of orbit that are geostationary orbit, geosynchronous orbit, lower earth orbit (LEO), and the medium earth orbit (MEO). We also need to know their characteristics and application.
Complete step-by-step solution -
First, we know that a geostationary satellite is a satellite that is orbiting around the earth which is placed at a height of around 35,800 kilometers or 22,300 miles over the earth's equator, therefore it rotates in the same direction as the earth revolves around its axis that is from west to east. So as it rotates with the earth, it will also take the same time to complete one rotation as the earth takes to complete one rotation on its own axis that is 24 hours 56 minutes. This is nearly 23.934461223 hours or one sidereal day. As shown in the below figure.

A single geostationary satellite when present in the line of sight provides coverage of around 40 % of the earth's surface. If three geostationary satellites are placed in orbit with each separated by 120 degrees can easily cover the complete earth's surface except for small circular regions at the northern and southern poles. Geostationary satellites are very famous because they can be easily accessed using an earthbound directional antenna which just needs adjustment ones and then it can be left without further modification. Another major advantage of these types of satellites is that as it uses highly directional antennas the interference from and other satellites and ground-based sources are reduced drastically.
Note: For these types of questions, we need to know about different types of orbit that are geostationary orbit, geosynchronous orbit, lower earth orbit (LEO), and the medium earth orbit (MEO). We also need to know their characteristics and application.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




