
The pH value of gastric juice in the human stomach is about 1.8 and in the small intestine it is about 7.8. The \[p{K_a}\] value of aspirin is 3.5. Aspirin will be:
A ) completely ionised in the small intestine and in the stomach
B ) unionised in the small intestine and in the stomach
C ) ionised in the small intestine and almost unionised in the stomach
D ) ionised in the stomach and almost unionised in the small intestine
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Consider the functional groups present in aspirin. Determine if the functional group will ionise in the acidic medium or in the basic medium.
Complete answer:
Aspirin is 2-acetoxybenzoic acid. It contains a carboxylic functional group. Hence, it is acidic in nature. The structure of aspirin is as shown below:
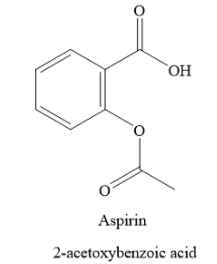
In the acidic medium, aspirin does not undergo ionisation. In basic medium, the carboxylic functional group of aspirin ionizes to form carboxylate anion.
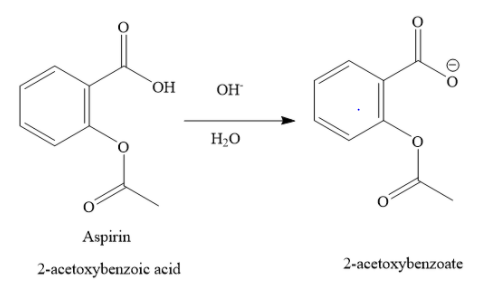
The hydroxide ion from basic medium, combines with protons of carboxylic functional group to form water molecule. The carboxylic functional group becomes carboxylate ion. Thus, in the basic medium aspirin undergoes ionisation.
Gastric juice in the human stomach is acidic with pH around 1.8 . This shows that aspirin will not ionise in the acidic gastric juice in the stomach. In the small intestine, the pH is 7.8, which suggests a slightly basic medium. Aspirin will ionise in this medium.
Hence, the option C ) is the correct option.
Note: The \[p{K_a}\] value of aspirin is 3.5. Which is close to the \[p{K_a}\] value of 3.74 for acetic acid. This suggests that like acetic acid ( a weak acid), aspirin is a weak acid.
Complete answer:
Aspirin is 2-acetoxybenzoic acid. It contains a carboxylic functional group. Hence, it is acidic in nature. The structure of aspirin is as shown below:

In the acidic medium, aspirin does not undergo ionisation. In basic medium, the carboxylic functional group of aspirin ionizes to form carboxylate anion.

The hydroxide ion from basic medium, combines with protons of carboxylic functional group to form water molecule. The carboxylic functional group becomes carboxylate ion. Thus, in the basic medium aspirin undergoes ionisation.
Gastric juice in the human stomach is acidic with pH around 1.8 . This shows that aspirin will not ionise in the acidic gastric juice in the stomach. In the small intestine, the pH is 7.8, which suggests a slightly basic medium. Aspirin will ionise in this medium.
Hence, the option C ) is the correct option.
Note: The \[p{K_a}\] value of aspirin is 3.5. Which is close to the \[p{K_a}\] value of 3.74 for acetic acid. This suggests that like acetic acid ( a weak acid), aspirin is a weak acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




