
The pineal gland secretes melatonin which is connected to
(a) Colouration of skin
(b) Sleep
(c) Anger
(d) Body temperature
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: The pineal gland could also be a little, pea-shaped gland within the brain. Which is additionally called epiphysis and responsible for synthesizing and secreting melatonin, a structurally simple hormone.
Complete answer:
It is located on the midline, attached to the posterior end of the roof of the ventricle within the brain. The pineal varies in size among species; in humans, it's roughly 1 cm long. The foremost important function of the pineal gland is to receive information about the state of the light-dark cycle from the environment and convey this information to provide and secrete the hormone melatonin. This hormone is special due to its secretion being dictated by light. Many types of research have determined that melatonin features a primary function in humans—to help control your circadian (or biological) rhythm.
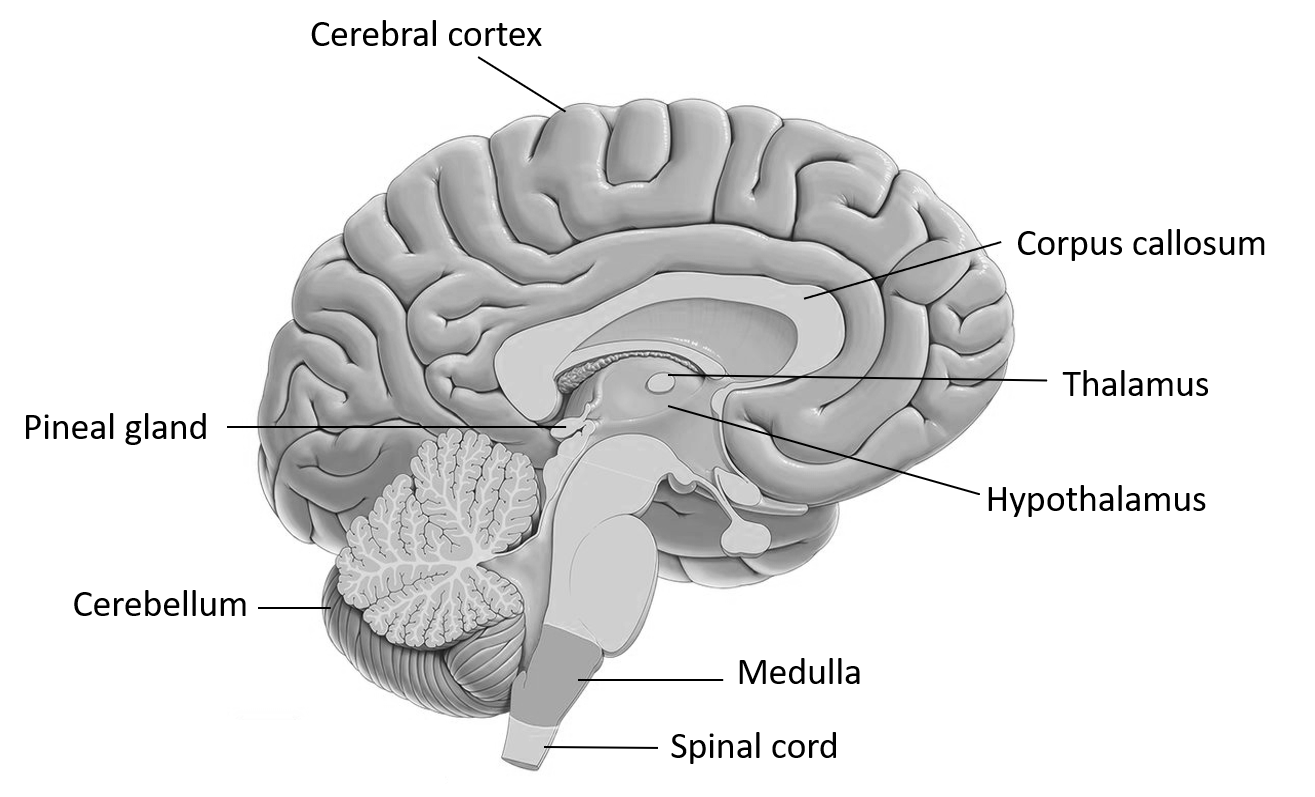
The time could also be a 24-hour biological cycle characterized by sleep-wake patterns. Daylight and darkness help dictate your time. Light exposure stops the discharge of melatonin, and successively, this helps control your circadian rhythms.
Naturally, photoperiod affects sleep patterns, but melatonin's degree of impact oversleep patterns is disputed.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) Sleep’.
Additional Information: The secretion of melatonin is low during the daylight and it is high during dark periods, which has some influence over the reaction to photoperiod (the length of day versus night). The pineal gland often appears calcified in x-rays, which is usually because of fluoride, calcium, and phosphorus deposits that build up with age. The other function of the pineal body is in reproduction where Melatonin blocks the secretion of gonadotropins (luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone) from the anterior pituitary gland. These hormones aid within the right development and functioning of the ovaries and testes.
Note:There are some research-based studies that state that melatonin levels are lower in elderly insomniacs relative to age-matched non-insomniacs, and melatonin therapy in such cases appears modestly beneficial in correcting the matter. Another disorder is seen in shift workers, who often find it difficult to manage to work at night and sleep during the day. The utility of melatonin therapy to alleviate this problem is equivocal and appears to not be as effective as phototherapy.
Complete answer:
It is located on the midline, attached to the posterior end of the roof of the ventricle within the brain. The pineal varies in size among species; in humans, it's roughly 1 cm long. The foremost important function of the pineal gland is to receive information about the state of the light-dark cycle from the environment and convey this information to provide and secrete the hormone melatonin. This hormone is special due to its secretion being dictated by light. Many types of research have determined that melatonin features a primary function in humans—to help control your circadian (or biological) rhythm.

The time could also be a 24-hour biological cycle characterized by sleep-wake patterns. Daylight and darkness help dictate your time. Light exposure stops the discharge of melatonin, and successively, this helps control your circadian rhythms.
Naturally, photoperiod affects sleep patterns, but melatonin's degree of impact oversleep patterns is disputed.
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) Sleep’.
Additional Information: The secretion of melatonin is low during the daylight and it is high during dark periods, which has some influence over the reaction to photoperiod (the length of day versus night). The pineal gland often appears calcified in x-rays, which is usually because of fluoride, calcium, and phosphorus deposits that build up with age. The other function of the pineal body is in reproduction where Melatonin blocks the secretion of gonadotropins (luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone) from the anterior pituitary gland. These hormones aid within the right development and functioning of the ovaries and testes.
Note:There are some research-based studies that state that melatonin levels are lower in elderly insomniacs relative to age-matched non-insomniacs, and melatonin therapy in such cases appears modestly beneficial in correcting the matter. Another disorder is seen in shift workers, who often find it difficult to manage to work at night and sleep during the day. The utility of melatonin therapy to alleviate this problem is equivocal and appears to not be as effective as phototherapy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




