
The planck’s constant h and frequency of a photon is $\nu $ then write the formula for Einstein photoelectric equation.
Answer
555.9k+ views
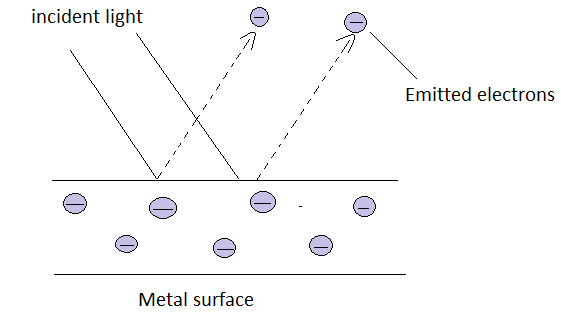
Hint: Light is emitted in the form of bundles or packets of energy known as photons and energy associated with each photons is given by product of Planck’s constant and frequency of photons, this quantum theory is responsible for explaining photoelectric effect or photoelectric emission from a metal surface, which will be discussed in below sections.
Formula used:
$\Rightarrow E=hv$
$\Rightarrow K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$
Complete answer:
When a photon of energy $E=hv$ falls on a metal surface the energy associated with them is transferred to electrons present on the metal surface. If this energy is greater than the minimum energy required by the electrons to leave the metal surface and the emission of electrons from the metal surface will take place. This minimum energy is known as the work function of a metal which is constant for a particular type of metal and varies with metal to metal.
So, the extra energy left for the electrons will convert into kinetic energy of those electrons as they have been excited from their ground state to some excited state.
Now, by above statements we can say that total energy of photons will be equal to sum of work function of metal and kinetic energy of electrons,
$\Rightarrow E=W.F+K.E$
Here, E (energy of photons), W.F(work function of metal) and K.E(kinetic energy of electrons)
$\Rightarrow W.F=\phi =h{{v}_{\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$ and
$\Rightarrow E=hv$
So, photoelectric equation will be given by,
$\Rightarrow hv=\phi +\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow hv=h{{v}_{\circ }}+\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$
Here, ${{v}_{\circ }}$ is known as threshold frequency which is defined as the minimum frequency required for photons to just overcome the potential barrier or work function of a metal.
$\therefore $ Einstein’s photoelectric equation is given by,
$\Rightarrow hv=\phi +\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$
Note:
Photoelectric effect is explained by the particle nature of light in which light is assumed to be bundled up into photons and the energy of these photons are transferred into electrons. In the photoelectric equation h is known as planck’s constant whose value is universal constant and is given by,
$\Rightarrow h=6.6261\times {{10}^{-34}}Js$
Formula used:
$\Rightarrow E=hv$
$\Rightarrow K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$
Complete answer:
When a photon of energy $E=hv$ falls on a metal surface the energy associated with them is transferred to electrons present on the metal surface. If this energy is greater than the minimum energy required by the electrons to leave the metal surface and the emission of electrons from the metal surface will take place. This minimum energy is known as the work function of a metal which is constant for a particular type of metal and varies with metal to metal.
So, the extra energy left for the electrons will convert into kinetic energy of those electrons as they have been excited from their ground state to some excited state.
Now, by above statements we can say that total energy of photons will be equal to sum of work function of metal and kinetic energy of electrons,
$\Rightarrow E=W.F+K.E$
Here, E (energy of photons), W.F(work function of metal) and K.E(kinetic energy of electrons)
$\Rightarrow W.F=\phi =h{{v}_{\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$ and
$\Rightarrow E=hv$
So, photoelectric equation will be given by,
$\Rightarrow hv=\phi +\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$

$\Rightarrow hv=h{{v}_{\circ }}+\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$
Here, ${{v}_{\circ }}$ is known as threshold frequency which is defined as the minimum frequency required for photons to just overcome the potential barrier or work function of a metal.
$\therefore $ Einstein’s photoelectric equation is given by,
$\Rightarrow hv=\phi +\dfrac{1}{2}M{{V}^{2}}$
Note:
Photoelectric effect is explained by the particle nature of light in which light is assumed to be bundled up into photons and the energy of these photons are transferred into electrons. In the photoelectric equation h is known as planck’s constant whose value is universal constant and is given by,
$\Rightarrow h=6.6261\times {{10}^{-34}}Js$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




