
The plot of log k vs. 1/T helps to calculate:
A. The energy of activation.
B. The rate constant of the reaction.
C. The order of the reaction.
D. The energy of activations as well as the frequency factor.
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Use the Arrhenius equation related to log k and 1/T. Interpret the slope and intercept of the plot of log k vs \[1/T\].
Formula used:
Arrhenius equation
\[\log k = \log A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}} \times \dfrac{1}{T}\]
Complete step by step answer:
According to Arrhenius theory non-active or non-reactive molecules can become activated by absorption of heat energy.
The Arrhenius equation gives the relationship between the rate constant \[k\] and temperature.
\[\log k = \log A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}} \times \dfrac{1}{T}\]
Where,
\[k\] = rate constant
\[A\] = frequency factor
\[{E_a}\]= energy of activations
\[R\]= gas constant
\[T\] = temperature
The plot of \[\log k\] vs \[1/T\] is as follows:
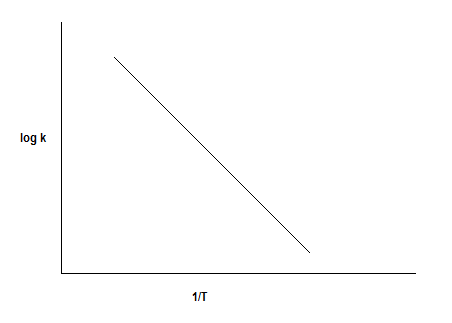
The linear equation for a straight line is \[y = mx + c\]
Where,
\[y = \log k\]
\[x = \dfrac{1}{T}\]
\[{\text{Slope = }}m = - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\]
\[{\text{Intercept = }}\log A\]
So, from the slope and intercept of the plot of \[\log k\] vs \[1/T\] we can calculate the energy of activation and frequency factor respectively.
The order of the reaction is experimental property. It can be determined from the concentration of the reactant and the rate of reaction. It cannot be determined from the plot of \[\log k\] vs \[1/T\].
Thus, the correct option is (D) The energy of activations as well as the frequency factor.
Note: Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to convert the reactant to product. Frequency factor (\[A\]) is constant for the given reaction and it describes the frequency of collision of reacting molecules. Using data of rate constant at various temperatures we can calculate the energy of activation and frequency factor of the reaction from the plot of \[\log k\] vs \[1/T\].
Formula used:
Arrhenius equation
\[\log k = \log A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}} \times \dfrac{1}{T}\]
Complete step by step answer:
According to Arrhenius theory non-active or non-reactive molecules can become activated by absorption of heat energy.
The Arrhenius equation gives the relationship between the rate constant \[k\] and temperature.
\[\log k = \log A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}} \times \dfrac{1}{T}\]
Where,
\[k\] = rate constant
\[A\] = frequency factor
\[{E_a}\]= energy of activations
\[R\]= gas constant
\[T\] = temperature
The plot of \[\log k\] vs \[1/T\] is as follows:

The linear equation for a straight line is \[y = mx + c\]
Where,
\[y = \log k\]
\[x = \dfrac{1}{T}\]
\[{\text{Slope = }}m = - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\]
\[{\text{Intercept = }}\log A\]
So, from the slope and intercept of the plot of \[\log k\] vs \[1/T\] we can calculate the energy of activation and frequency factor respectively.
The order of the reaction is experimental property. It can be determined from the concentration of the reactant and the rate of reaction. It cannot be determined from the plot of \[\log k\] vs \[1/T\].
Thus, the correct option is (D) The energy of activations as well as the frequency factor.
Note: Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to convert the reactant to product. Frequency factor (\[A\]) is constant for the given reaction and it describes the frequency of collision of reacting molecules. Using data of rate constant at various temperatures we can calculate the energy of activation and frequency factor of the reaction from the plot of \[\log k\] vs \[1/T\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




