
The plots of log V vs. log T at constant P for 1 mole of an ideal gas gives intercept equal to:
A.\[\log \dfrac{P}{R}\]
B.\[ - \dfrac{P}{R}\]
C.\[ - \dfrac{R}{P}\]
D.\[\log \dfrac{R}{P}\]
Answer
501k+ views
Hint: We can use the ideal gas equation to solve this problem. The ideal gas equation can be rearranged to obtain the graph. We know that the log V vs log T graph will yield us a straight line. By using the straight-line equation, we can say that y=mx+c and thus the value of c will give us the value of the intercept.
Complete answer:
According to the ideal gas equation we can say that
\[ \Rightarrow PV = nRT\]
This means that the pressure, volume, Temperature and the universal gas constant R can be related by this formula.
According to the question, we are given 1 mole of the gas. This means that the value of n=1.
Thus the equation becomes:
\[ \Rightarrow PV = RT\]
Applying logarithm on both the sides we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \log P + \log V = \log R + \log T\]
\[ \Rightarrow \log V = \log R + \log T - \log P\]
By simplifying the logarithm we will obtain:
\[ \Rightarrow \log V = \log \dfrac{R}{P} + \log T\]
This is of the form y=mx+c
Here log V is in the y-axis and log T is in the x-axis. Thus we can say that the value of c will be \[\log \dfrac{R}{P}\] .
The graph of the equation will be given by:
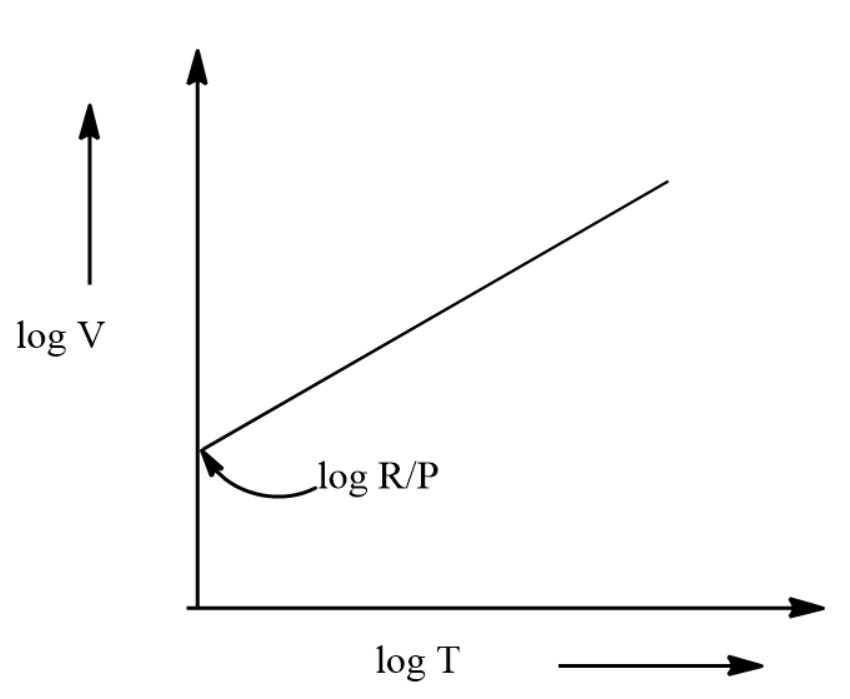
Hence the correct answer is option D.
Note:
While doing the simplification of the log terms we are taking the log P term to the right-hand side instead of log V because the value of P is a constant and thus the value of intercept obtained can be a constant. It is mentioned in the question that the experiment is done under constant pressure. Thus we need the intercept term to be a constant value and hence use P in it.
Complete answer:
According to the ideal gas equation we can say that
\[ \Rightarrow PV = nRT\]
This means that the pressure, volume, Temperature and the universal gas constant R can be related by this formula.
According to the question, we are given 1 mole of the gas. This means that the value of n=1.
Thus the equation becomes:
\[ \Rightarrow PV = RT\]
Applying logarithm on both the sides we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \log P + \log V = \log R + \log T\]
\[ \Rightarrow \log V = \log R + \log T - \log P\]
By simplifying the logarithm we will obtain:
\[ \Rightarrow \log V = \log \dfrac{R}{P} + \log T\]
This is of the form y=mx+c
Here log V is in the y-axis and log T is in the x-axis. Thus we can say that the value of c will be \[\log \dfrac{R}{P}\] .
The graph of the equation will be given by:

Hence the correct answer is option D.
Note:
While doing the simplification of the log terms we are taking the log P term to the right-hand side instead of log V because the value of P is a constant and thus the value of intercept obtained can be a constant. It is mentioned in the question that the experiment is done under constant pressure. Thus we need the intercept term to be a constant value and hence use P in it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




