
The potential difference across a 150mH inductor as a function of time is shown in figure. Assume that the initial value of the current in the inductor is zero. What is the current when\[t=2.0ms\]and\[t=4.0ms\]?
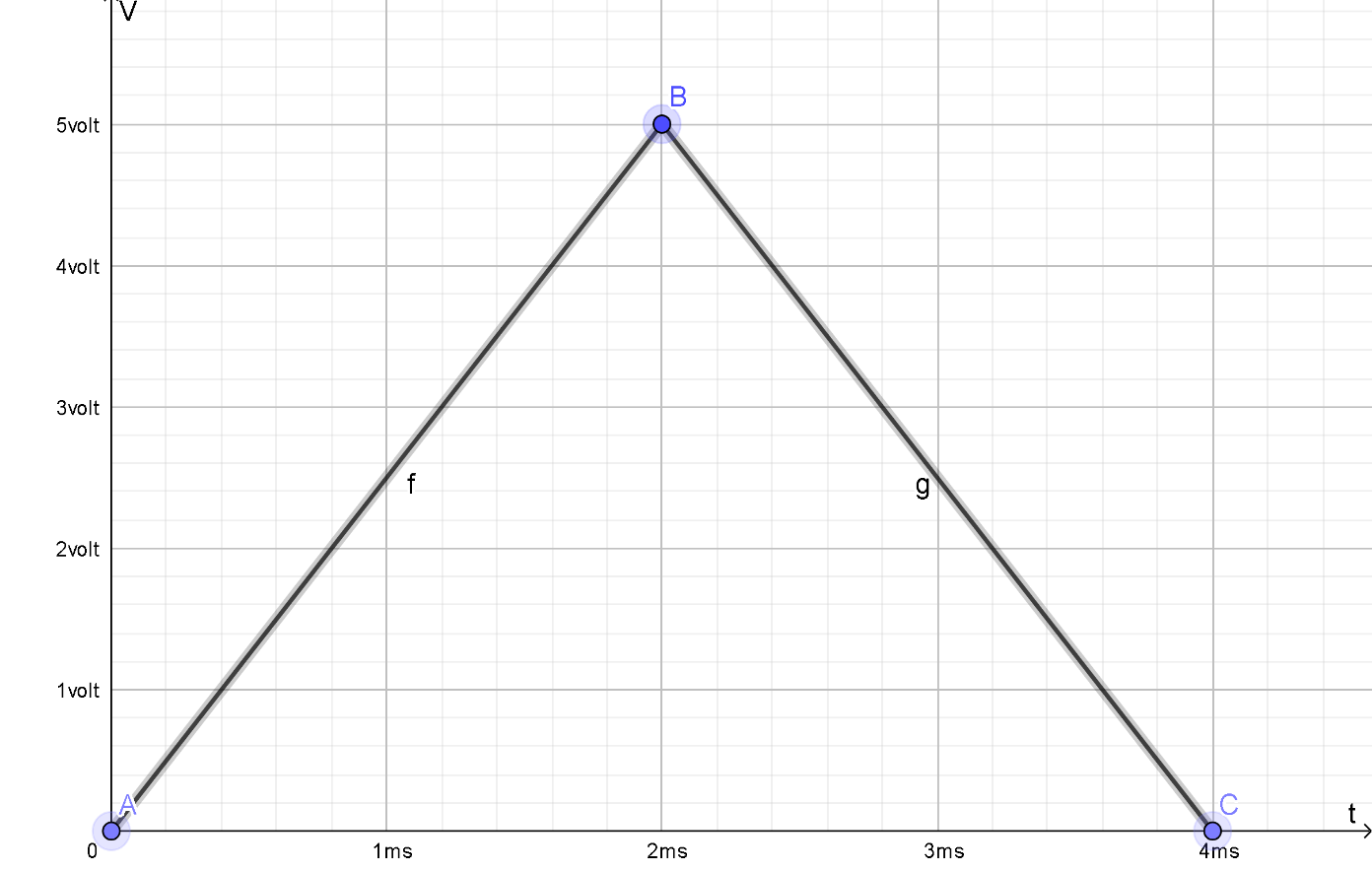

Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: The voltage across the inductor is directly proportional to the rate of change of current through the inductor. When applied voltage is variable then integration logic is applied for solving such types of questions and we get current is directly proportional to the area of the Voltage-time graph.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The V - I equation of the inductor is given as:
-\[{{V}_{L}}=L\frac{di}{dt}----equation\text{ 1}\]
Equation 1 can be written as,
\[di=\frac{1}{L}{{V}_{L}}dt\]- - - - - - - - - - -Equation 2
As it is given in the question at time t = 0, current i = 0 and so let us assume at after time t current becomes i.
So on integrating above equation 2 from time 0 to t and current 0 to i , we get ,
\[\int\limits_{0}^{i}{di}=\frac{1}{L}\int\limits_{0}^{t}{{{V}_{L}}dt}\]
\[\therefore i=\frac{1}{L}\int\limits_{0}^{t}{{{V}_{L}}dt}\]
According to the above equation current through the inductor is equal to the\[\frac{1}{L}\] times the area under \[{{V}_{L}}\]-time graph.
\[i=\frac{1}{L}(Area\_under\_{{V}_{L}}-t\_grpah)\] - - - - - - Equation 3
Now we calculate current for \[t=2.0ms\], then half the graph is drawn.
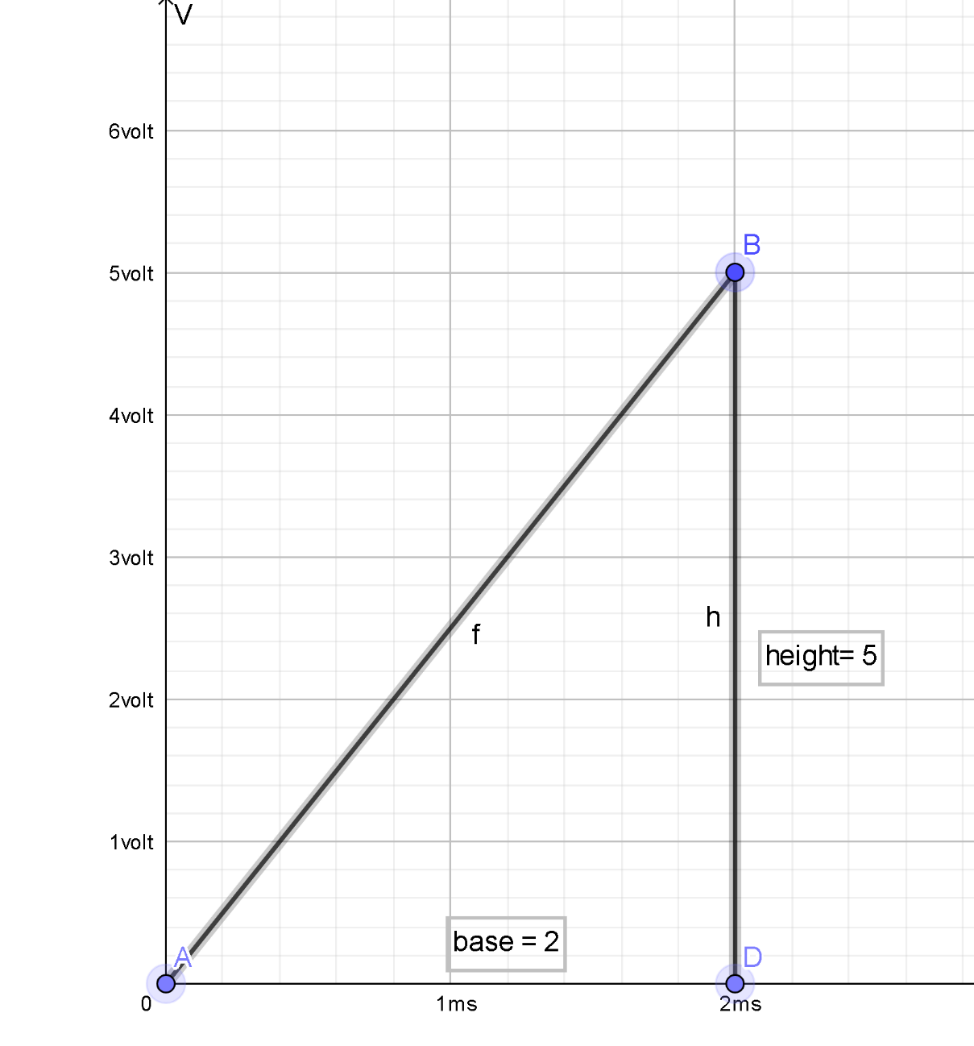
Now we have to find the current through the inductor at \[t=2.0ms\] then we have to substitute the values in equation 3, we get
\[i=\frac{1}{150\times {{10}^{-3}}}(\frac{1}{2}\times 2\times {{10}^{-3}}\times 5)\]
On Solving we get ,
\[\therefore i=3.33\times {{10}^{-3}}A\]
So, the value of current at \[t=2.0ms\] is \[\text{3}\text{.33}\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}A\]
Now for\[t=4.0ms\], full graph is drawn
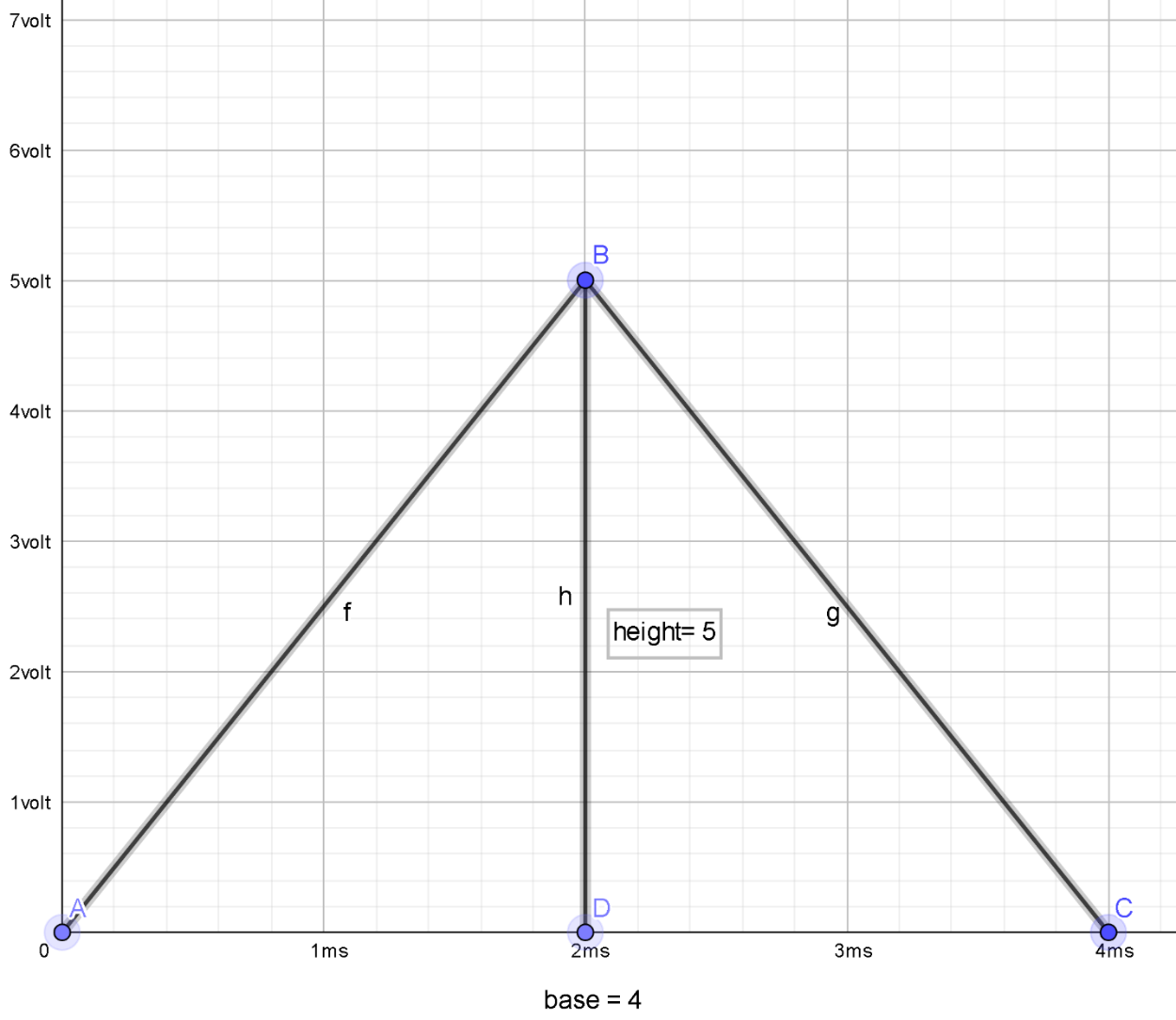
Similarly, to find the current through the inductor at t = 4.0ms we have to substitute the values below in equation 3.
\[\begin{align}
& i=\frac{1}{150\times {{10}^{-3}}}(\frac{1}{2}\times 4\times {{10}^{-3}}\times 5) \\
& \therefore i=6.67\times {{10}^{-3}}A \\
\end{align}\]
So, the value of current at \[t=4.0ms\] is\[6.67\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}A\].
So, we can conclude that current at \[t=2.0ms\] and at \[t=4.0ms\] is \[3.33\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}A\]and \[6.67\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}A\] respectively.
Note: Voltage in an inductor can only be calculated in the presence of changing current because changing current is having frequency. In the case of constant current passing through the inductor, the voltage is equal to zero and the inductor looks like a short circuit element.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The V - I equation of the inductor is given as:
-\[{{V}_{L}}=L\frac{di}{dt}----equation\text{ 1}\]
Equation 1 can be written as,
\[di=\frac{1}{L}{{V}_{L}}dt\]- - - - - - - - - - -Equation 2
As it is given in the question at time t = 0, current i = 0 and so let us assume at after time t current becomes i.
So on integrating above equation 2 from time 0 to t and current 0 to i , we get ,
\[\int\limits_{0}^{i}{di}=\frac{1}{L}\int\limits_{0}^{t}{{{V}_{L}}dt}\]
\[\therefore i=\frac{1}{L}\int\limits_{0}^{t}{{{V}_{L}}dt}\]
According to the above equation current through the inductor is equal to the\[\frac{1}{L}\] times the area under \[{{V}_{L}}\]-time graph.
\[i=\frac{1}{L}(Area\_under\_{{V}_{L}}-t\_grpah)\] - - - - - - Equation 3
Now we calculate current for \[t=2.0ms\], then half the graph is drawn.

Now we have to find the current through the inductor at \[t=2.0ms\] then we have to substitute the values in equation 3, we get
\[i=\frac{1}{150\times {{10}^{-3}}}(\frac{1}{2}\times 2\times {{10}^{-3}}\times 5)\]
On Solving we get ,
\[\therefore i=3.33\times {{10}^{-3}}A\]
So, the value of current at \[t=2.0ms\] is \[\text{3}\text{.33}\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}A\]
Now for\[t=4.0ms\], full graph is drawn

Similarly, to find the current through the inductor at t = 4.0ms we have to substitute the values below in equation 3.
\[\begin{align}
& i=\frac{1}{150\times {{10}^{-3}}}(\frac{1}{2}\times 4\times {{10}^{-3}}\times 5) \\
& \therefore i=6.67\times {{10}^{-3}}A \\
\end{align}\]
So, the value of current at \[t=4.0ms\] is\[6.67\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}A\].
So, we can conclude that current at \[t=2.0ms\] and at \[t=4.0ms\] is \[3.33\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}A\]and \[6.67\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-3}}A\] respectively.
Note: Voltage in an inductor can only be calculated in the presence of changing current because changing current is having frequency. In the case of constant current passing through the inductor, the voltage is equal to zero and the inductor looks like a short circuit element.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




