
The power in series RLC –circuit with AC source is given by
A) Zero
B) $VI\operatorname{Sin} \phi $
C) VI
D) $VI\operatorname{Cos} \phi $
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: An RLC series circuit. It shows a resistor R connected in series with an inductor L, connected to a capacitor C in series to an A C source V. The voltage of the A C source is given by V. Here ohm’s law and power factor solve it. Ohm’s law is V=IR and power is equal to I${R^2}$
Step by step solution:
Step 1:
The question based on RLC-circuit and it is important to understand about the RLC-circuit and its functioning before getting about its power in series
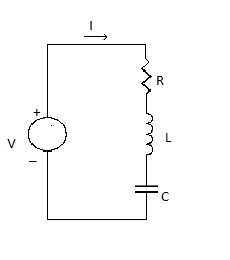
The figure describes an R LC series circuit. It shows a resistor R connected in series with an inductor L, connected to a capacitor C in series to an A C source V. The voltage of the A C source is given by V.
When a pure resistance of R ohms, a pure inductance of L Henry and a pure capacitance of C farads are connected together in series combination with each other then RLC Series Circuit is formed. As all the three elements are connected in series, the current flowing through each element of the circuit will be the same as the total current I flowing in the circuit.
R is denoted by ${V_r}$, L is denoted by${V_l}$ and C is denoted b${V_c}$ and in the RLC-circuit
$\therefore $ ${X_L}$ =2$\pi $ fL and ${X_c}$ =$\dfrac{1}{2}$ $\pi $ fC
${V_\pi }$= IR that is the voltage across the resistance R and is in phase with the current I.
${V_i}$ = I${X_L}$ that is the voltage across the inductance L and it leads the current I by an angle of 90 degrees.
${V_c}$ = I${X_c}$ that is the voltage across capacitor C and it lags the current I by an angle of 90 degrees.
Step 2:
The product of voltage and current is defined as P=VI$\cos \phi $ =I${R^2}$
Where, cos$\phi $ is the power factor of the circuit and expressed as: cos$\phi $=$\dfrac{{{V_r}}}{v}$ =$\dfrac{R}{Z}$ =$\dfrac{R}{{\sqrt {{{\left( {{X_c} - {X_l}} \right)}^2} + {R^2}} }}$
Hence this is the power in series by the RLC circuit in the AC source.
From the above equation option D is correct.
Note:For a series RLC circuit, an impedance triangle can be drawn by dividing each side of the voltage triangle by its current, I. The voltage drop across the resistive element is equal to IR, the voltage across the two reactive elements is IX = I${X_L}$ – I${X_c}$ while the source voltage is equal to IZ.
Step by step solution:
Step 1:
The question based on RLC-circuit and it is important to understand about the RLC-circuit and its functioning before getting about its power in series

The figure describes an R LC series circuit. It shows a resistor R connected in series with an inductor L, connected to a capacitor C in series to an A C source V. The voltage of the A C source is given by V.
When a pure resistance of R ohms, a pure inductance of L Henry and a pure capacitance of C farads are connected together in series combination with each other then RLC Series Circuit is formed. As all the three elements are connected in series, the current flowing through each element of the circuit will be the same as the total current I flowing in the circuit.
R is denoted by ${V_r}$, L is denoted by${V_l}$ and C is denoted b${V_c}$ and in the RLC-circuit
$\therefore $ ${X_L}$ =2$\pi $ fL and ${X_c}$ =$\dfrac{1}{2}$ $\pi $ fC
${V_\pi }$= IR that is the voltage across the resistance R and is in phase with the current I.
${V_i}$ = I${X_L}$ that is the voltage across the inductance L and it leads the current I by an angle of 90 degrees.
${V_c}$ = I${X_c}$ that is the voltage across capacitor C and it lags the current I by an angle of 90 degrees.
Step 2:
The product of voltage and current is defined as P=VI$\cos \phi $ =I${R^2}$
Where, cos$\phi $ is the power factor of the circuit and expressed as: cos$\phi $=$\dfrac{{{V_r}}}{v}$ =$\dfrac{R}{Z}$ =$\dfrac{R}{{\sqrt {{{\left( {{X_c} - {X_l}} \right)}^2} + {R^2}} }}$
Hence this is the power in series by the RLC circuit in the AC source.
From the above equation option D is correct.
Note:For a series RLC circuit, an impedance triangle can be drawn by dividing each side of the voltage triangle by its current, I. The voltage drop across the resistive element is equal to IR, the voltage across the two reactive elements is IX = I${X_L}$ – I${X_c}$ while the source voltage is equal to IZ.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




