
The process of Krebs’ cycle occurs in which organs? Write its four features.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The TCA Cycle may be a hub of metabolism, with central importance in both energy production and biosynthesis. Therefore, it's crucial for the cell to manage concentrations of TCA Cycle metabolites. The cycle chiefly occurs in the cell organelle that is called the powerhouse of the cells.
Complete answer:
The acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle) includes a series of oxidation- reduction reactions in mitochondria that end in the oxidation of acetyl to 2 molecules of CO$_2$ and reduce the coenzymes that are reoxidized through the electron transport chain, linked to the formation of ATP.
The four features of Krebs cycles are-
- The cycle operates only under aerobic conditions because NAD and FAD are often regenerated within the mitochondrion only by the transfer of electrons to molecular oxygen.
- Citric acid cycle and requirement of oxygen Oxygen is required for the acid cycle indirectly in the maximum amount because it is the electron acceptor at the top of the electron transport chain, necessary to regenerate NAD and FAD.
- The acid cycle, in conjunction with the organic process, provides the overwhelming majority of energy employed by aerobic cells in the citizenry, greater than 95%.
- The Krebs’ cycle is understood as amphibolic, therein it's both catabolic where breakdown molecules take place also as anabolic during which new molecules are built.
Additional Information:
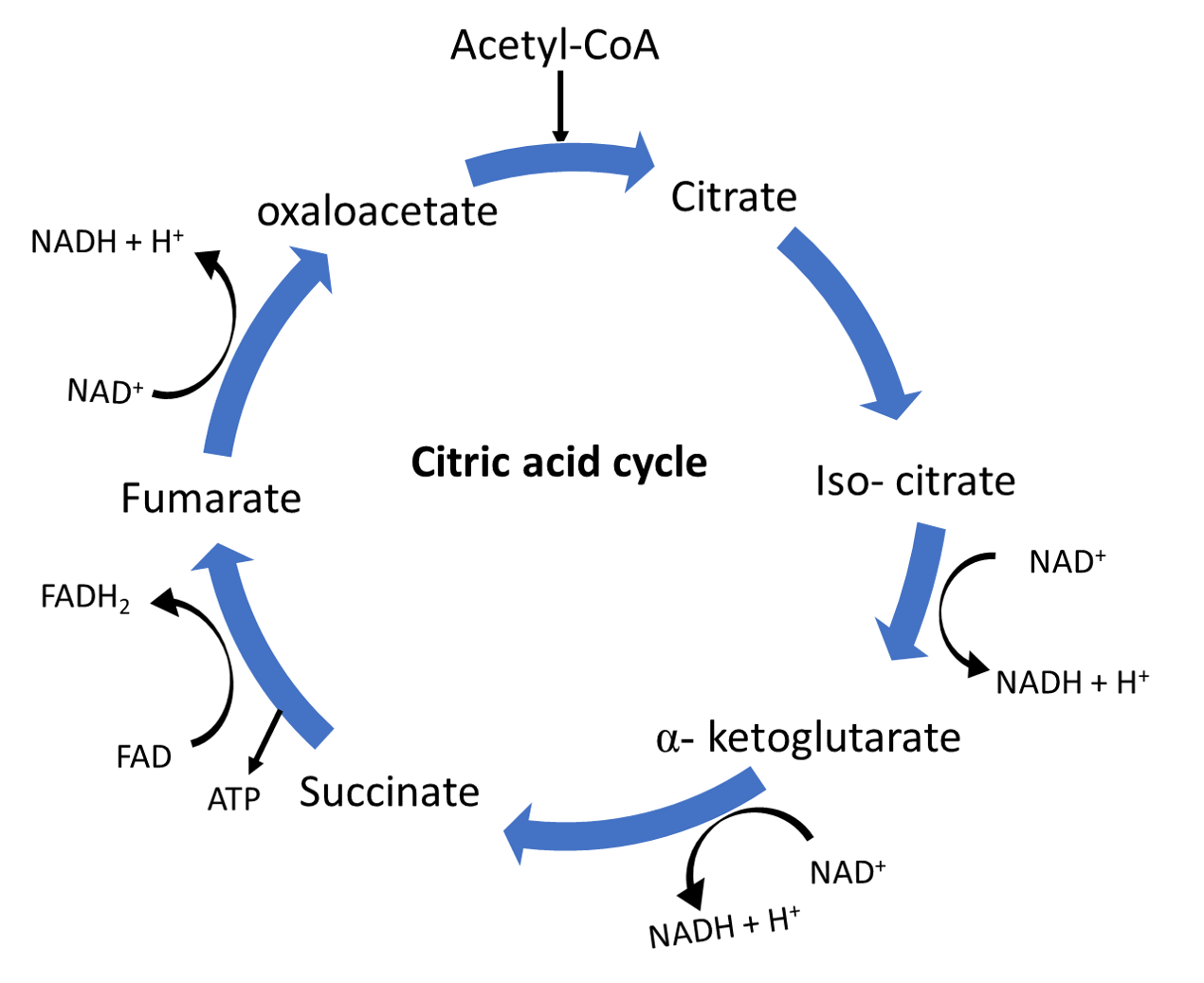
Steps of the acid cycle:
Step-I: Formation of citrate.
Step-II: Formation of isocitrate
Step-III: Oxidation of isocitrate and formation of carbon dioxide.
Step-IV: Oxidation of alpha- ketoglutarate and formation of carbon dioxide
Step-V: Thioester cleavage in succinyl CoA and phosphorylation of GDP
Step-VI: Oxidation of succinate
Step-VII: Hydration of fumarate
Step-VIII: Oxidation of L- malate to regenerate oxaloacetate
Note:
- Krebs cycle was named after Hans Adolf Kerbs who discovered it in 1937.
- Krebs cycle is additionally referred to as the acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA).
- The cycle occurs within the mitochondrial matrix
-It is the series of a biochemical reaction during which the acetyl portion of acetyl CoA is oxidized to CO$_2$ and therefore the reduced coenzyme FADH and NADH are produced.
Complete answer:
The acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle) includes a series of oxidation- reduction reactions in mitochondria that end in the oxidation of acetyl to 2 molecules of CO$_2$ and reduce the coenzymes that are reoxidized through the electron transport chain, linked to the formation of ATP.
The four features of Krebs cycles are-
- The cycle operates only under aerobic conditions because NAD and FAD are often regenerated within the mitochondrion only by the transfer of electrons to molecular oxygen.
- Citric acid cycle and requirement of oxygen Oxygen is required for the acid cycle indirectly in the maximum amount because it is the electron acceptor at the top of the electron transport chain, necessary to regenerate NAD and FAD.
- The acid cycle, in conjunction with the organic process, provides the overwhelming majority of energy employed by aerobic cells in the citizenry, greater than 95%.
- The Krebs’ cycle is understood as amphibolic, therein it's both catabolic where breakdown molecules take place also as anabolic during which new molecules are built.

Additional Information:
Steps of the acid cycle:
Step-I: Formation of citrate.
Step-II: Formation of isocitrate
Step-III: Oxidation of isocitrate and formation of carbon dioxide.
Step-IV: Oxidation of alpha- ketoglutarate and formation of carbon dioxide
Step-V: Thioester cleavage in succinyl CoA and phosphorylation of GDP
Step-VI: Oxidation of succinate
Step-VII: Hydration of fumarate
Step-VIII: Oxidation of L- malate to regenerate oxaloacetate
Note:
- Krebs cycle was named after Hans Adolf Kerbs who discovered it in 1937.
- Krebs cycle is additionally referred to as the acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA).
- The cycle occurs within the mitochondrial matrix
-It is the series of a biochemical reaction during which the acetyl portion of acetyl CoA is oxidized to CO$_2$ and therefore the reduced coenzyme FADH and NADH are produced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




