
The radius of the base of a cone is 5 cm and its height is 12 cm. Its curved surface is:
\[\begin{align}
& (A)\text{ 60}\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& (B)\text{ 65}\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& (C)\text{ }30\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
& (D)\text{ 35}\pi \text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: The curved surface area of the cone is the area of the curved part of the cone. To calculate the curved surface area, we needed to find the slant height of the cone. We know that Slant height can be calculated by drawing a perpendicular from apex to base, which will form a right-angled triangle and Pythagoras theorem can be applied in it. As we know the slant height of cone and radius of cone, we can calculate the curved surface area of cone from the formula for curved surface area of cone. We know that the curved surface area of cone is equal to the product of \[\pi \], radius of base of cone and slant height of cone.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving the question, we should know the definition of cone.
“The locus of points where one end of a line is rotated keeping the other end of the line as fixed is said to be a cone.”
In the question, it is given that the radius of the base of a cone is 5 cm and the height of a cone is 12 cm.
Let us assume the centre of base of the cone as A, top of the cone as B and an arbitrary point on the circumference of the base of the cone as C.
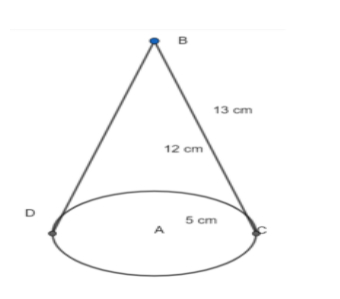
So, from the given assumption, we get
AC = radius of base of cone = 5 cm
AB = height of cone = 12 cm.
CB = slant height of cone
Let us have a front view of the cone.
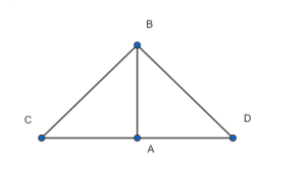
According to Pythagoras theorem, the square on the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal in area to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
In the front view, we get AB = 12 cm, AC =5 cm and CD =10 cm.
\[C{{B}^{2}}=C{{A}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow C{{B}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}+{{12}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow C{{B}^{2}}=25+144 \\
& \Rightarrow C{{B}^{2}}=169 \\
& \Rightarrow CB=13 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the slant height of the cone is equal to 13 cm.
We know that the curved surface area of cone is equal to the product of \[\pi \], radius of base of cone and slant height of cone.
Curved Surface area = \[\pi \text{ x radius of cone x slant height of cone}\]
\[\Rightarrow \]Curved Surface area = \[\pi \text{ x AC x BC}\]
\[\Rightarrow \]Curved Surface area = \[\pi \](5 cm) (13cm)
\[\Rightarrow \]Curved Surface area = \[65\pi c{{m}^{2}}\].
Hence option B is correct.
Note: The curved surface area of the cone is equal to \[\pi rl\] where “r” is radius of base of cone and “l” is slant height of cone. Alternatively, we can use the formulae of slant height of cone equal to \[l=\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}\]where “r” is radius of base of cone and “h” is height of cone. If we don’t remember this then we need to find it in the way we did in the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving the question, we should know the definition of cone.
“The locus of points where one end of a line is rotated keeping the other end of the line as fixed is said to be a cone.”
In the question, it is given that the radius of the base of a cone is 5 cm and the height of a cone is 12 cm.
Let us assume the centre of base of the cone as A, top of the cone as B and an arbitrary point on the circumference of the base of the cone as C.

So, from the given assumption, we get
AC = radius of base of cone = 5 cm
AB = height of cone = 12 cm.
CB = slant height of cone
Let us have a front view of the cone.

According to Pythagoras theorem, the square on the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal in area to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
In the front view, we get AB = 12 cm, AC =5 cm and CD =10 cm.
\[C{{B}^{2}}=C{{A}^{2}}+A{{B}^{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow C{{B}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}+{{12}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow C{{B}^{2}}=25+144 \\
& \Rightarrow C{{B}^{2}}=169 \\
& \Rightarrow CB=13 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the slant height of the cone is equal to 13 cm.
We know that the curved surface area of cone is equal to the product of \[\pi \], radius of base of cone and slant height of cone.
Curved Surface area = \[\pi \text{ x radius of cone x slant height of cone}\]
\[\Rightarrow \]Curved Surface area = \[\pi \text{ x AC x BC}\]
\[\Rightarrow \]Curved Surface area = \[\pi \](5 cm) (13cm)
\[\Rightarrow \]Curved Surface area = \[65\pi c{{m}^{2}}\].
Hence option B is correct.
Note: The curved surface area of the cone is equal to \[\pi rl\] where “r” is radius of base of cone and “l” is slant height of cone. Alternatively, we can use the formulae of slant height of cone equal to \[l=\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}\]where “r” is radius of base of cone and “h” is height of cone. If we don’t remember this then we need to find it in the way we did in the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What were the main changes brought about by the Bolsheviks class 9 social science CBSE

What is the theme or message of the poem The road not class 9 english CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




