
The rainbow and rainbow-like colours seen on a thin film of oil on a water surface are two phenomena. They are:
A. Similar in nature and both are due to interference of light
B. Different in nature and rainbow is due to interference of light, while colour of this film is due to diffraction
C. Similar in nature and both are due to refraction of light
D. Difference in nature and rainbow is due to refraction, while colour of thin film is due to interference of light.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Before we get to answer the question, the definitions of refraction and interference should be considered.
Refraction is the phenomenon of bending of light when the light enters from one medium to another medium of different optical density.
Interference is the phenomenon of variation of the intensity in light when two or more sources of light waves superimpose on one another.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, there are two different phenomena observed – rainbow and rainbow-like colours on drop of water. Let us examine the formation of each of them to understand their nature.
Step 1: Formation of a Rainbow
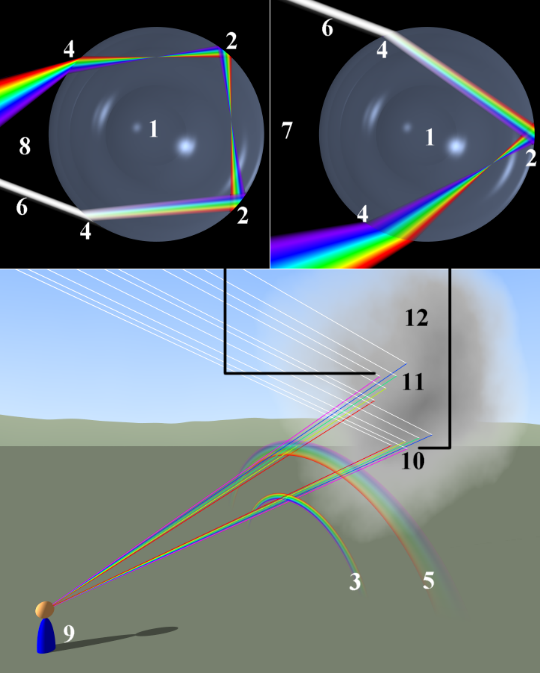
Rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon caused by refraction, total internal reflection, and dispersion, all of which are related to the fact that light ray bends when moving from air, the rarer medium to water droplet, the denser medium. During the cloudy atmosphere, the white light coming from the sun undergoes dispersion in the water droplet, thereby splitting the white light into the seven colours of VIBGYOR. This later undergoes a series of total internal reflections where the 7 colours emerge out of the cloud in the sky. Thus, rainbow occurs due to refraction since all these processes viz. dispersion and total internal reflection happen because of refraction.
Step 2: Rainbow-like colours on thin film of oil
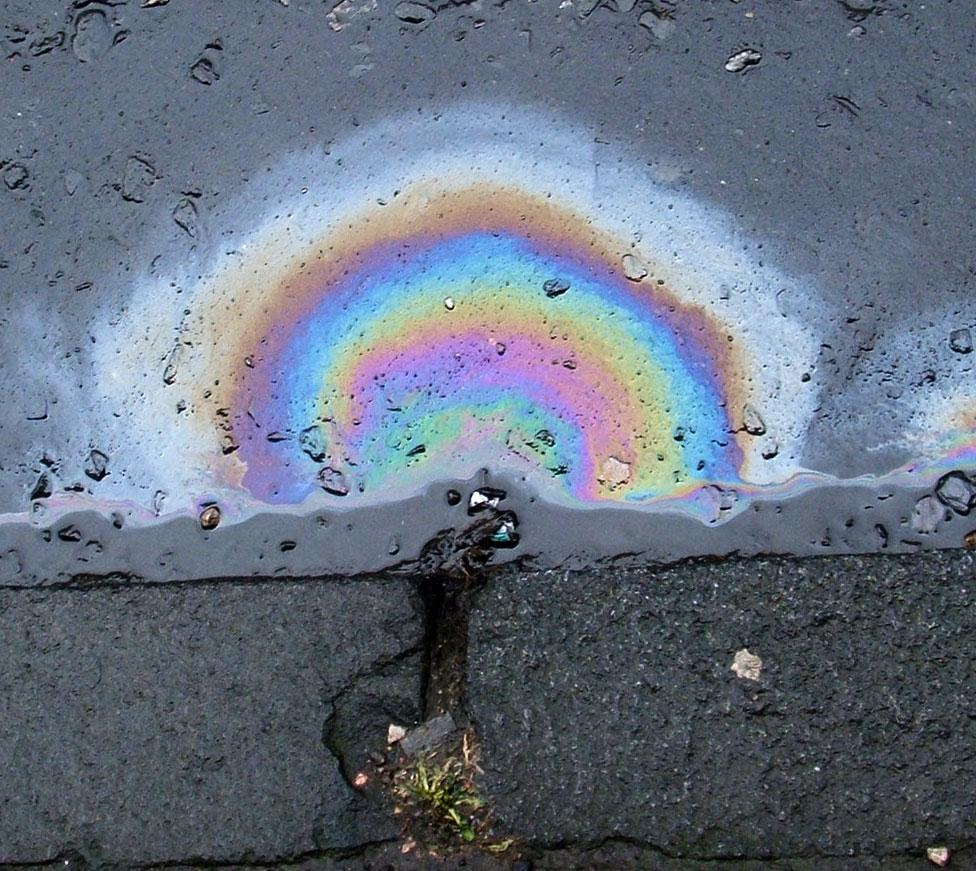
The rainbow-like colours appearing on the thin film of oil floating on water, is due to the phenomenon of thin film interference.
Due to the oil film floating on top of the water forming a thin film, the light emerging from the bottom layer of the oil film and the light emerging from the top layer of the oil film undergo interference. Depending on the thickness of the film, the light entering our eye across the film, can be reflected completely, or transmitted separately, depending on the individual wavelengths of these colours. In this process, some colours undergo constructive interference and shine while others undergo destructive interference and hence, subside their intensity.
Therefore, the reason for seeing rainbow-like colours on the thin film of oil is due to interference.

Step 3: Concluding the statements.
From the above, it is clear that the actual rainbow in the sky is different from the rainbow-like colours on the thin oil film and in no way, are similar. The actual rainbow is because of refraction while the colours on the thin film of oil is due to interference.
Hence, the correct option is Option D.
Note: The criteria for determining whether there is constructive or destructive interference is as follows:
If the path difference is equal to even multiples of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ such as $\lambda, 2\lambda, 3\lambda ...2n\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$, there is a constructive interference at this point and we obtain a bright fringe.
If the path difference is equal to odd multiples of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ such as $\dfrac{\lambda }{2},\dfrac{{3\lambda }}{2},\dfrac{{5\lambda }}{2}...\left( {2n + 1} \right)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$, there is a destructive interference at this point and we obtain a dark fringe.
Refraction is the phenomenon of bending of light when the light enters from one medium to another medium of different optical density.
Interference is the phenomenon of variation of the intensity in light when two or more sources of light waves superimpose on one another.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, there are two different phenomena observed – rainbow and rainbow-like colours on drop of water. Let us examine the formation of each of them to understand their nature.
Step 1: Formation of a Rainbow
Rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon caused by refraction, total internal reflection, and dispersion, all of which are related to the fact that light ray bends when moving from air, the rarer medium to water droplet, the denser medium. During the cloudy atmosphere, the white light coming from the sun undergoes dispersion in the water droplet, thereby splitting the white light into the seven colours of VIBGYOR. This later undergoes a series of total internal reflections where the 7 colours emerge out of the cloud in the sky. Thus, rainbow occurs due to refraction since all these processes viz. dispersion and total internal reflection happen because of refraction.

Step 2: Rainbow-like colours on thin film of oil
The rainbow-like colours appearing on the thin film of oil floating on water, is due to the phenomenon of thin film interference.
Due to the oil film floating on top of the water forming a thin film, the light emerging from the bottom layer of the oil film and the light emerging from the top layer of the oil film undergo interference. Depending on the thickness of the film, the light entering our eye across the film, can be reflected completely, or transmitted separately, depending on the individual wavelengths of these colours. In this process, some colours undergo constructive interference and shine while others undergo destructive interference and hence, subside their intensity.
Therefore, the reason for seeing rainbow-like colours on the thin film of oil is due to interference.

Step 3: Concluding the statements.
From the above, it is clear that the actual rainbow in the sky is different from the rainbow-like colours on the thin oil film and in no way, are similar. The actual rainbow is because of refraction while the colours on the thin film of oil is due to interference.
Hence, the correct option is Option D.
Note: The criteria for determining whether there is constructive or destructive interference is as follows:
If the path difference is equal to even multiples of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ such as $\lambda, 2\lambda, 3\lambda ...2n\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$, there is a constructive interference at this point and we obtain a bright fringe.
If the path difference is equal to odd multiples of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ such as $\dfrac{\lambda }{2},\dfrac{{3\lambda }}{2},\dfrac{{5\lambda }}{2}...\left( {2n + 1} \right)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$, there is a destructive interference at this point and we obtain a dark fringe.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




