
The ratio of recessive epistasis is –
A. 12:3:1
B. 9:3:4
C. 13:3
D. All of the above
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: In recessive epistasis the phenotypic expression of one allele is suppressed due to the allele of another gene, which is in homozygous recessive condition. So, the ratio of recessive epistasis comes out to be 9:3:4.
Complete answer:
As you know genes do not work in isolation. Every gene’s expression is interdependent on other genes for their expression. Epistasis is the phenomenon in which the gene expression of one allele is altered due to presence of another allele.
In the concept of recessive epistasis in the double hybrid cross, the phenotypic expression of a gene, for example A alters the expression of other gene B in the hair color of rats.
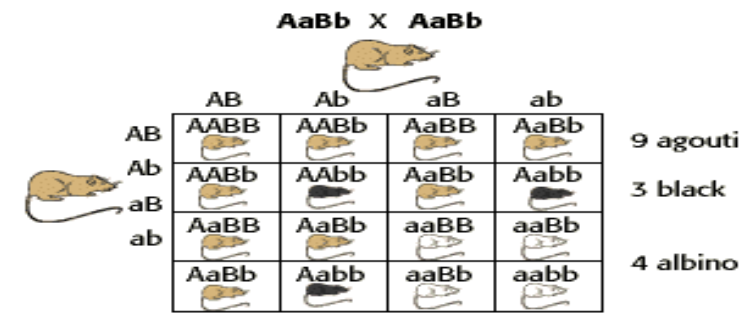
You see that a Punnett Square for the AaBb X AaBb cross is shown. Rather than the 9:3:3:1 segregation of phenotypes normally seen with an AaBb X AaBb dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio is 9:3:4. Since there are only three different phenotypes for hair color in rats that are agouti, black, and albino. But the individual with genotype recessive for both traits i.e. aabb, has the same albino phenotype as the aaBB and aaBb individuals as the phenomenon of epistasis comes into play. You may now get how the albino phenotype masks any phenotype that might be caused by the recessive homozygous, aa genotype.
Some live examples are flower color in peas, combs in chicken, coat color in horses etc.
Note: Epistasis is an interaction at the phenotypic level of organization. The genes that are involved in a specific epistatic interaction may still show independent assortment at the genotypic level. In such cases, the phenotypic ratios may appear to deviate from those expected with independent assortment.
Complete answer:
As you know genes do not work in isolation. Every gene’s expression is interdependent on other genes for their expression. Epistasis is the phenomenon in which the gene expression of one allele is altered due to presence of another allele.
In the concept of recessive epistasis in the double hybrid cross, the phenotypic expression of a gene, for example A alters the expression of other gene B in the hair color of rats.

You see that a Punnett Square for the AaBb X AaBb cross is shown. Rather than the 9:3:3:1 segregation of phenotypes normally seen with an AaBb X AaBb dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio is 9:3:4. Since there are only three different phenotypes for hair color in rats that are agouti, black, and albino. But the individual with genotype recessive for both traits i.e. aabb, has the same albino phenotype as the aaBB and aaBb individuals as the phenomenon of epistasis comes into play. You may now get how the albino phenotype masks any phenotype that might be caused by the recessive homozygous, aa genotype.
Some live examples are flower color in peas, combs in chicken, coat color in horses etc.
Note: Epistasis is an interaction at the phenotypic level of organization. The genes that are involved in a specific epistatic interaction may still show independent assortment at the genotypic level. In such cases, the phenotypic ratios may appear to deviate from those expected with independent assortment.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




