
The ratio of the number of kinds of double homozygous to double heterozygous to single homozygous genotypes of \[{F_2}\] generation of a mendelian dihybrid cross is
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: Calculation of this required the genotypic ratio of the \[{F_2}\] generation of a mendelian dihybrid cross. The double homozygous is not the same as the double homozygous recessive or dominant.
Complete answer:
The ratio of double homozygous to double heterozygous to the homozygous genotype of the \[{F_2}\] generation of a mendelian dihybrid cross is $4:4:8$.
Genotype: It is the set of the allele that an individual organism possesses
Homozygous: In homozygous conditions, a diploid organism has a genotype consisting of two identical alleles for a locus(position on the chromosome). E.g. \[TT\], \[bb\],\[BB\], \[tt\].
Heterozygous: it is the genotype possess two different alleles for a locus.e.g \[Tt\], \[Bb\],
Given below is the Mendelian dihybrid cross for two traits i.e. height and color for the \[{F_2}\] generation
1. Height (T = tall, t = small) and
2. Color (B = black b = white)
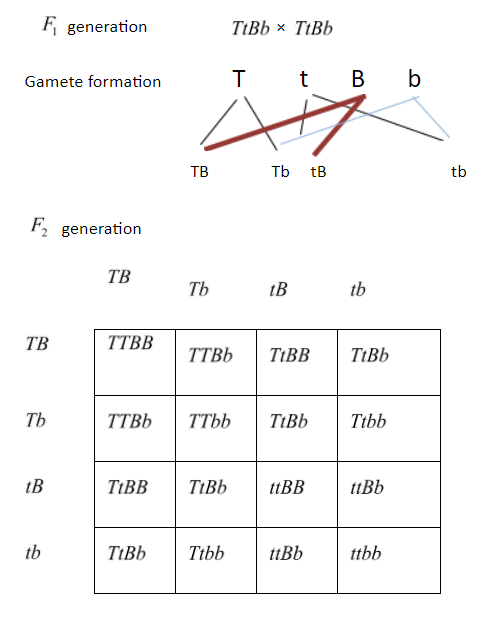
Genotypic ratio of \[{F_2}\] generation =\[TTBB\]:\[TTBb\]: \[TTbb\]: \[TtBB\]:\[TtBb\]: \[Ttbb\]:\[ttBB\]: \[ttBb\]: \[ttbb\] = 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 : 4 : 2 : 1 : 2 : 1
To find the ratio between double homozygous to double heterozygous to single homozygous genotypes we have to find the number of each of them from the mendelian dihybrid cross
Total Double homozygous = 4 i.e. \[TTBB\], \[TTbb\], \[ttBB\], \[ttbb\]
Total Double heterozygous = 4 i.e. \[TtBb\]
Single homozygous = 8 i.e.\[TTBb\],\[TtBB\], \[ttBb\], \[Ttbb\]
So, the ratio is $4:4:8$.
Additional information: This ratio can differ based on the type of parents that have been taken if it is a test cross i.e. \[TtBb\] × \[ttbb\] or \[TTBB\] ×\[ttbb\], the ratio will be different as different gametes are produced.
Note: In the above question we have to find the double homozygous which includes both double homozygous recessive (\[ttBb\]) and double homozygous dominant(\[TTBB\]) along with homozygous dominant one gene homozygous recessive another gene i.e. \[TTbb\], \[ttBB\].
Complete answer:
The ratio of double homozygous to double heterozygous to the homozygous genotype of the \[{F_2}\] generation of a mendelian dihybrid cross is $4:4:8$.
Genotype: It is the set of the allele that an individual organism possesses
Homozygous: In homozygous conditions, a diploid organism has a genotype consisting of two identical alleles for a locus(position on the chromosome). E.g. \[TT\], \[bb\],\[BB\], \[tt\].
Heterozygous: it is the genotype possess two different alleles for a locus.e.g \[Tt\], \[Bb\],
Given below is the Mendelian dihybrid cross for two traits i.e. height and color for the \[{F_2}\] generation
1. Height (T = tall, t = small) and
2. Color (B = black b = white)

Genotypic ratio of \[{F_2}\] generation =\[TTBB\]:\[TTBb\]: \[TTbb\]: \[TtBB\]:\[TtBb\]: \[Ttbb\]:\[ttBB\]: \[ttBb\]: \[ttbb\] = 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 : 4 : 2 : 1 : 2 : 1
To find the ratio between double homozygous to double heterozygous to single homozygous genotypes we have to find the number of each of them from the mendelian dihybrid cross
Total Double homozygous = 4 i.e. \[TTBB\], \[TTbb\], \[ttBB\], \[ttbb\]
Total Double heterozygous = 4 i.e. \[TtBb\]
Single homozygous = 8 i.e.\[TTBb\],\[TtBB\], \[ttBb\], \[Ttbb\]
So, the ratio is $4:4:8$.
Additional information: This ratio can differ based on the type of parents that have been taken if it is a test cross i.e. \[TtBb\] × \[ttbb\] or \[TTBB\] ×\[ttbb\], the ratio will be different as different gametes are produced.
Note: In the above question we have to find the double homozygous which includes both double homozygous recessive (\[ttBb\]) and double homozygous dominant(\[TTBB\]) along with homozygous dominant one gene homozygous recessive another gene i.e. \[TTbb\], \[ttBB\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




